Learn more about product with this collection
The differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
The future of the internet
Understanding the potential of Web 3.0
Foundational Principles
The discipline of Product Management is built around two core principles:
- Define a clear, value-based product strategy
- Create and manage a healthy roadmap
These two ideas are inseparable. Product strategies should be value-based and roadmaps goal-based. The product values should translate to the user, therefore it should be the core of your roadmap.
2
5 reads
Differentiating between a roadmap and a backlog
A roadmap is a melting pot of ideas where teams experiment to find worthwhile ideas.
Your roadmap should achieve these key ideas:
- Communicate your progress towards achieving the product strategy
- Document the ideas which intend to bring the product strategy to life
- Align stakeholders on what you are currently working on
Roadmaps often become the enemy of the product, the user and the business because it is confused with backlogs.
Backlogs are purely output-focussed. They are concrete plans of what needs doing. It includes actionable tasks assigned to specific people.
2
1 read
The product discovery process
Product discovery is the process of moving from the problem to the solution. The team responsible for product discovery deals with the problem and the solution spaces in their pursuit of defining solutions. Once they define a solution, the delivery team takes the solutions to the backlog, adding the details to execute them.
The roadmap describes how the ideas are progressing through the discovery process. The roadmap is a snapshot of the process. At any given time, it should describe:
- Ideas currently investigated
- High-level solutions which are validated
2
0 reads
Key steps to producing solution ideas
The complete discovery process happens in the context of a value-based product strategy. There are four steps to producing solution ideas:
- Problem framing - understanding the problems you're trying to solve and the requirements of the solutions.
- Roadmap planning - prioritising the problems and planning iterations for each.
- Ideation and prototyping - generating ideas and bringing them to life with prototypes
- Solution testing - validating solution ideas against the original problem.
Once you have possible solutions, they must pass a validation criteria.
2
0 reads
How to set up a roadmap
- Before you start with ideas, structure your roadmap correctly.
- Ask if the ideas are worthwhile. A problem describes the gap between where we are now and where we want to be. The items on the roadmap should get us to where we want to be (the product vision).
- Plan your roadmap. Figure out which ideas should be tackled first.
- Ideate, prototype and test solutions.
2
0 reads
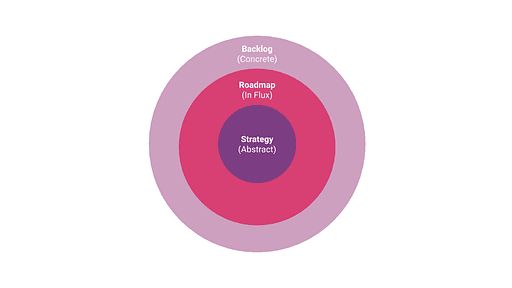
The roadmap structure
The primary task of the roadmap is communicating the discovery process, as it can be difficult to bridge the gap between the abstract product strategy and the tangible backlog.
The roadmap needs to represent:
- abstract product values (organised into themes)
- tangible and specific ideas, which will become the product goals.
Good values lead to good goals, which leads to a good product.
2
0 reads
Consider if the ideas are worthwhile
Ideas on the roadmap should be phrased in terms of problems and opportunities. But how the problems are framed is important. Problems should be framed in their purest form to empower the discovery team to find the best solution possible.
Problems should be phrased from the point of view of at least one of three product development disciplines: The user, the business, or technology.
2
0 reads
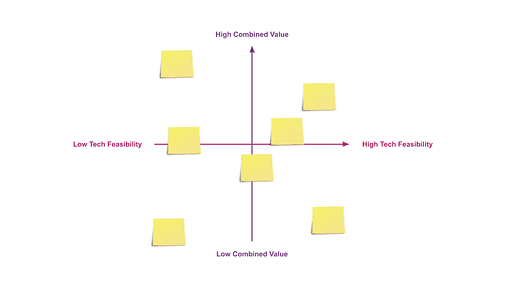
Plan your roadmap
You now have clearly articulated goals but may not know which ideas to tackle first.
Two main factors can help prioritise goals:
Expected value - the combined measure of expected user value and expected business value, and Complexity.
- Goals should be mapped on an expected user value scale.
- Then add another axis for the expected business value. This should give you a picture of how valuable the goals are.
- Rank the goals by overall value.
- Lastly, contrast the value with feasibility. High value, high feasibility will give quick, short-term wins.
2
0 reads
Ideate, prototype and test solution
These steps are BYOT (bring your own tools.) General principles to help with the right tools:
- Ideations: Ensure all of the relevant disciplines are present and that the problems are well framed.
- Prototype: show the idea without the frills to get to the root of the proposed solution.
- Test: use realistic tests.
During the documentation of the proposed solution, capture these three things as a minimum:
- Requirements at the epic level.
- UX: visuals of how this solution will manifest.
- Technical specification: The endpoints, integrations and components.
2
0 reads
CURATED BY
More like this
9 ideas
Product Roadmap Guide: Why It’s Important And Types
rocketblocks.me
7 ideas
Decision Time: How Decision Rules Help You Make Better Product Decisions
romanpichler.medium.com
5 ideas
The Product Strategy Stack
ravi-mehta.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving & library
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Personalized recommendations
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates