Inflation
In economics, inflation is a general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money.
10
291 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
By curating the content I consume, I document my journey through time and space.
Being aware of social situations gives me a sense of personal responsibility towards the betterment of our communal crisis.
“
Similar ideas to Inflation
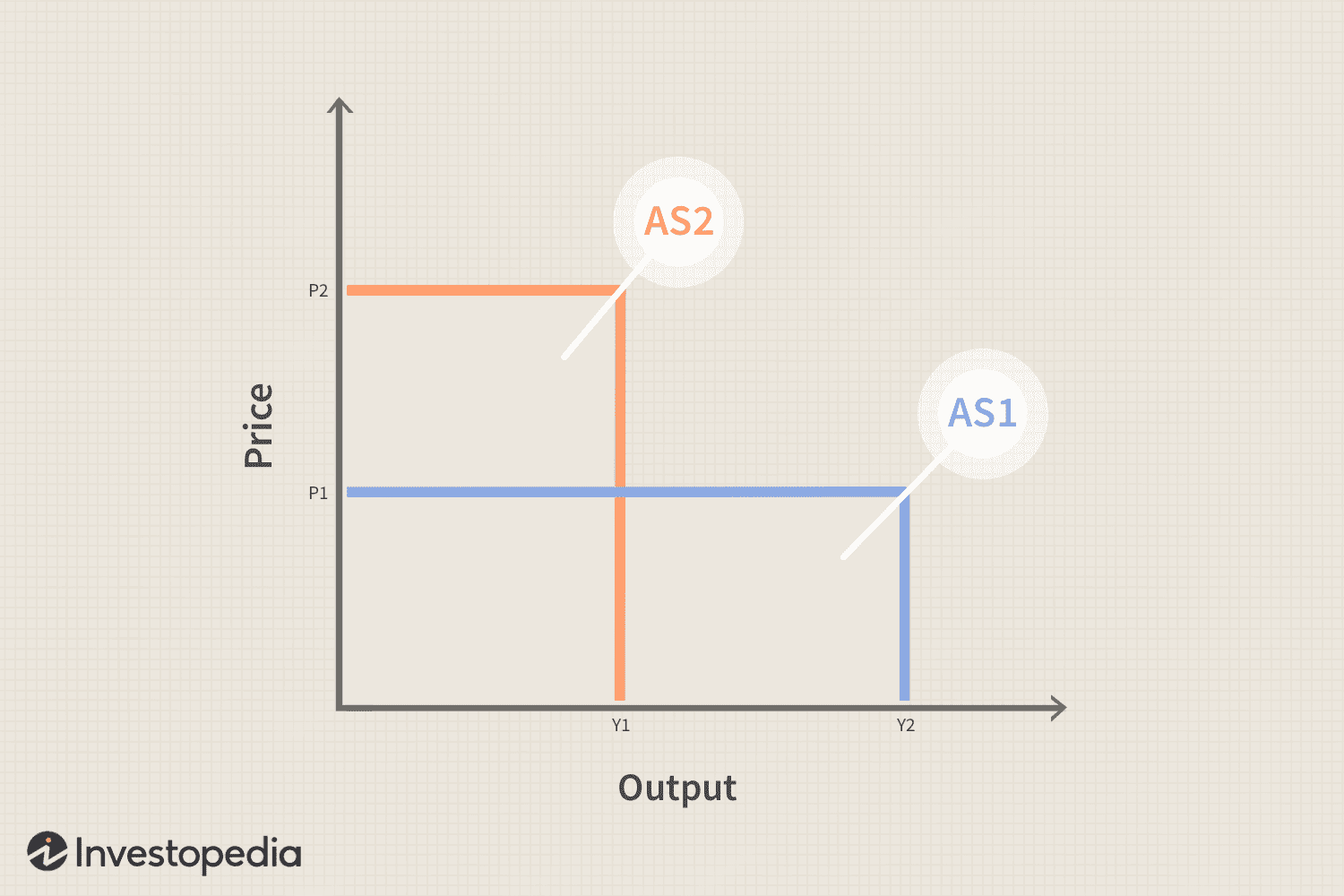
Cost-Push Inflation
Cost-push inflation is the decrease in the aggregate supple of goods and services stemming from an increase in the cost of production.
An increase in the costs of raw materials or labor can contribute to cost-pull inflation.
Pricing Power
If you double your prices, and lose less than half your customers, its probably a good move. Pricing power is your ability to raise the prices you are charging over time. It is related to "price elasticity" in economics.
Bus...
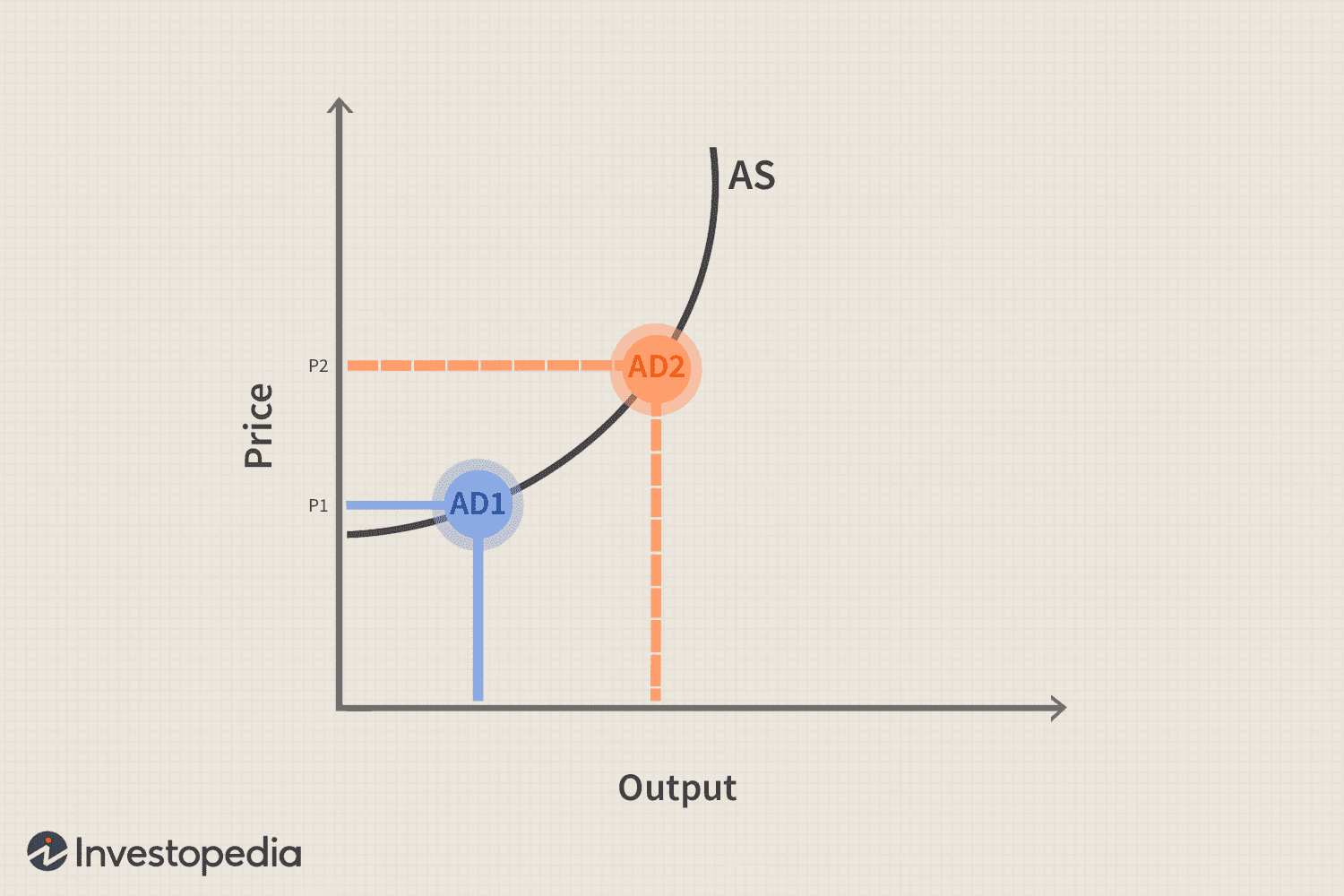
Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation is the increase in aggregate demand, categorized by the four sections of the macroeconomy: households, business. governments. and foreign buyers.
Demand-pull inflation can be cause by an expanding economy, increased government spending, or overseas growth.
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates