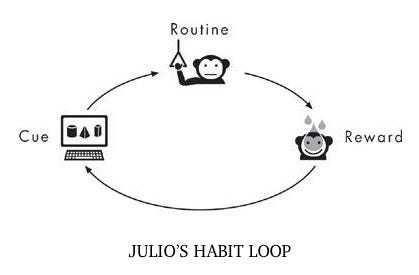
6. Habit Formation (Charles Duhigg)
- Principle: Understanding and leveraging the habit loop (cue, routine, reward).
- Application: By identifying cues and rewards, one can change routines to form new, beneficial habits, thus rewiring the brain for success.
75
476 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
The brain network operates through two primary memory modes: short-term memory and long-term memory.
“
Similar ideas to 6. Habit Formation (Charles Duhigg)
How to CHANGE your habits
To understand your own habits, you need to identify the components of your habit loops. Once you’ve diagnosed the habit loop of a particular behaviour, you can look for ways to supplant old vices with new routines.
There are four steps to doing this:
1. Identify the rout...
6. How triggers work
- The sequence known as a habit loop are described by three terms: cue, routine and reward.
- The golden rule of habit change design by Duhigg is to keep the cue and reward ande change the routine.
- A modified, more complete way to view this is: trigger -> impulse...
1. How Habits Work
Habits can be changed if we understand their mechanisms.
The basal ganglia, a part of the brain, stores and executes our habits independently of other brain functions, allowing us to perform routines without conscious thought.
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates