Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
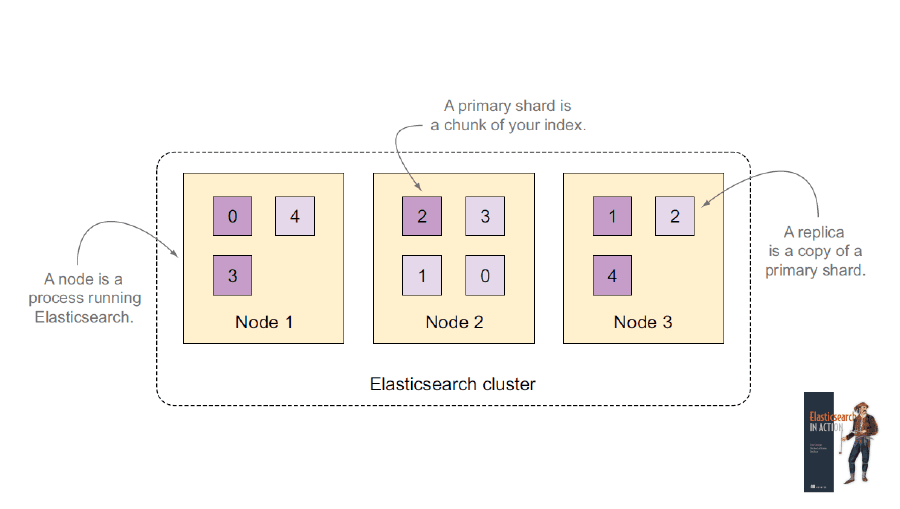
Terminology
- Node = An Elasticsearch process. It's recommended to run each node on a separate server.
- Cluster = Set of one or more nodes.
- Shard = Part of an index, used for distributing data across the cluster.
5
99 reads
Shards
Elasticsearch divides each index into shards, which are standalone Lucene indices. These can be either primary shards or replicas.
The number of shards and replicas per shard is set when a new index is created. After that, Elasticsearch takes care of evenly distributing the shards across the cluster. For maximum availability and performance, it ensures that replica shards are not on the same node as their correspondent primary shard.
4
20 reads
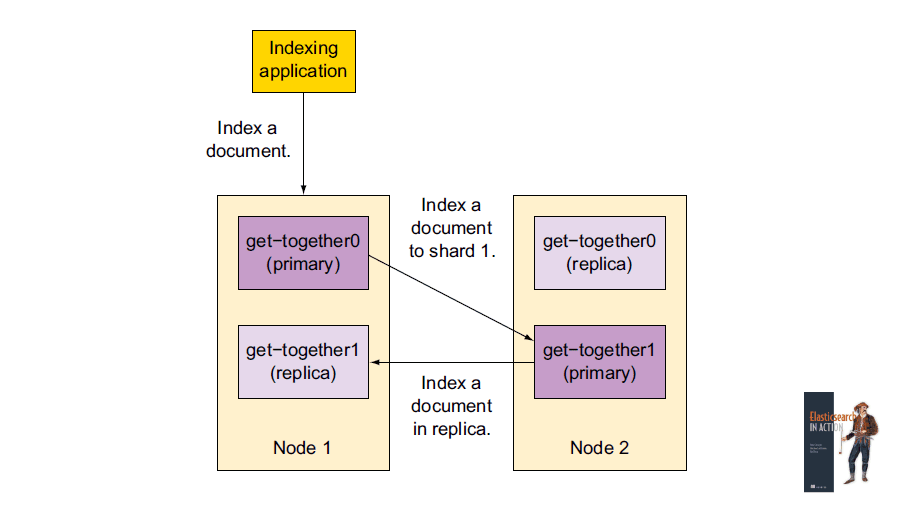
Distributed indexing
Indexing process
- When you index a document, the node that receives your HTTP request determines which shard should contain your document, based on a hash of the document’s ID.
- Then, it forwards the document to the node holding that primary shard.
- Once the shard is updated, the document is sent to be indexed in all replicas of that shard.
- Finally, the indexing command returns after all replicas are updated.
This process keeps replicas in sync and allows them to serve searches and to be promoted to primary shards in case the original primary is unavailable.
4
13 reads
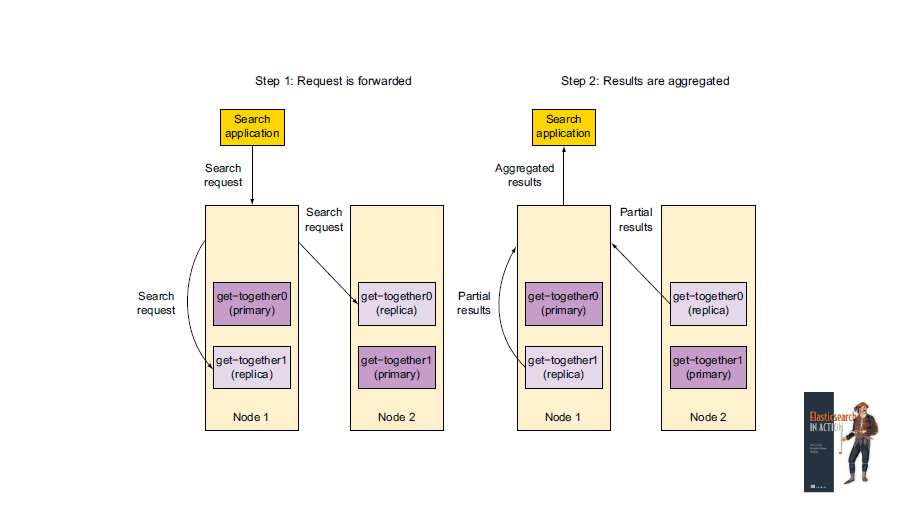
Distributed search
Searching an index requires Elasticsearch to query a set of shards that contain all your data. Since shards are distributed across multiple nodes, this query will be forwarded to multiple nodes.
Search process
- When you make a search request, the node that receives it forwards it to a set of shards that contain all your data. These can be either primary shards or replicas, and are chosen in a round-robin fashion.
- Then, the coordinator node gathers the results from those shards, aggregates and sorts them, and sends the results back to the client.
4
15 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Alt account of @ocp. I use it to stash ideas about software engineering
CURATOR'S NOTE
📖 Elasticsearch in Action
“
Similar ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates