How Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Explains Human Motivation
Curated from: verywellmind.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
9 ideas
·1.52K reads
14
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Abraham Maslow
Abraham Harold Maslow (1908 – 1970) was an American psychologist who was best known for creating Maslow's hierarchy of needs, a theory of psychological health predicated on fulfilling innate human needs in priority, culminating in self-actualization. Maslow was a psychology professor at Brandeis University, Brooklyn College, New School for Social Research, and Columbia University. He stressed the importance of focusing on the positive qualities in people, as opposed to treating them as a "bag of symptoms". (Wikipedia)
26
219 reads
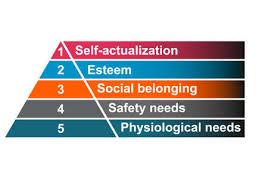
Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs is one of the best-known theories of motivation. Maslow's theory states that our actions are motivated by certain physiological and psychological needs that progress from basic to complex.
This hierarchy suggests that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other, more advanced needs.
There are five different levels of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is often displayed as a pyramid. The lowest levels of the pyramid of needs are made up of the most basic needs while the most complex needs are at the top.
32
176 reads
Physiological Needs (Level 1)
The physiological needs include those that are vital to survival. Some examples of physiological needs include:
· Food
· Water
· Breathing
· Homeostasis
In addition to the basic requirements of nutrition, air, and temperature regulation, physiological needs also include shelter and clothing.
28
187 reads
Security and Safety Needs (Level 2)
At the second level of Maslow’s hierarchy, the needs start to become a bit more complex. At this level, the needs for security and safety become primary.
People want control and order in their lives. Some of the basic security and safety needs include:
· Financial security
· Health and wellness
· Safety against accidents and injury
28
157 reads
Social Needs (Level 3)
The social needs in Maslow’s hierarchy include love, acceptance, and belonging. At this level, the need for emotional relationships drives human behavior. Some of the things that satisfy this need include:
· Friendships
· Romantic attachments
· Family relationships
· Social groups
· Community groups
In order to avoid loneliness, depression, and anxiety, it is important for people to feel loved and accepted by others.
30
131 reads
Esteem Needs (Level 4)
At the fourth level in Maslow’s hierarchy is the need for appreciation and respect. Once the needs at the bottom three levels have been satisfied, the esteem needs begin to play a more prominent role in motivating behavior.
At this level, it becomes increasingly important to gain the respect and appreciation of others. People have a need to accomplish things, then have their efforts recognized. In addition to the need for feelings of accomplishment and prestige, esteem needs include such things as self-esteem and personal worth.
28
135 reads
Self-Actualization Needs (Level 5)
At the very peak of Maslow’s hierarchy are the self-actualization needs. Self-actualizing people are self-aware, concerned with personal growth, less concerned with the opinions of others, and interested in fulfilling their potential.
28
167 reads
Impact of Maslow's Hierarchy
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs represented part of an important shift in psychology. Rather than focusing on abnormal behavior and development, Maslow's humanistic psychology was focused on the development of healthy individuals.
26
158 reads
Maslow Quote
“What is necessary to change a person is to change his awareness of himself.”
-Abraham Maslow
30
193 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
CURATOR'S NOTE
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
“
Tom Joad's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about communication with this collection
How to showcase your skills and experience
How to answer common interview questions
How to make a good first impression
Related collections
Similar ideas
1 idea
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Explained
thoughtco.com
3 ideas
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Explained
thoughtco.com
21 ideas
10 Common Traits Of Self-Actualized People
bigthink.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates