Composition
This is a method where we take simple functions and combine them into a more complex function. Let's say we have two methods f(x) = x * 2 //(timesTwo) and f(x) = x - 1 // (minusOne) . And we want to compute f(x) = 2x -1 . You call the timesTwo function first. With the output of timesTwo , you call the minusOne function. How would you code this?
The requirement here is that the next function takes as argument the same type that the previous function returns.
23
130 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
Not your object oriented programming
“
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about computerscience with this collection
Understanding machine learning models
Improving data analysis and decision-making
How Google uses logic in machine learning
Related collections
Similar ideas to Composition
Running the Action Tree
Once we have the action tree, running the code is easy. Each action node has a function ‘execute’ which takes some input, does whatever the action should (including possibly calling sub action) and returns the action’s output. This is the interpreter in action.
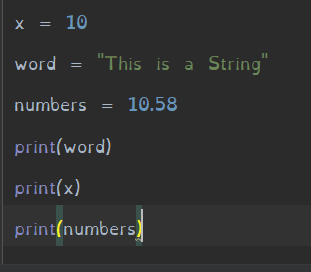
Learning Python: More on printing and variables
In this part we will be going over more on variables and printing them.
So let's make a variable and give it the value of 10, so it should look something like this X = 10, X could be any word really just not a reserved word, here is a link to a website with alot of reserved words that can't...
Ethereum is the Excel of Blockchains
Bitcoin is a database that does only 1 thing: track ownership of coins. Ethereum adds the computational capabilities that makes Excel more than a database:
- Turing Completeness. It means that it can solve any computational problem. With the introduction of formulas, E...
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates