Cryptographic Hashing
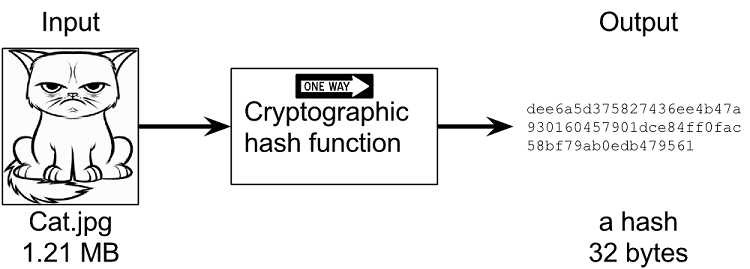
Hashing involves an algorithm (a “hash function”) generating a fixed output (hash) from a data input of any size. In most blockchains, the hash is an alphanumeric string of fixed length.
Because a hash is dependent on block data, hashes serve as unique identifiers for blocks on the chain. Running the same data through the hash function will produce the same hash no matter how many times you perform the operation.
A change in a block’s data automatically triggers the generation of a new hash. Which is why it’s easy to know if a block containing transactions has been altered.
19
100 reads
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about crypto with this collection
The differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
The future of the internet
Understanding the potential of Web 3.0
Related collections
Similar ideas to Cryptographic Hashing
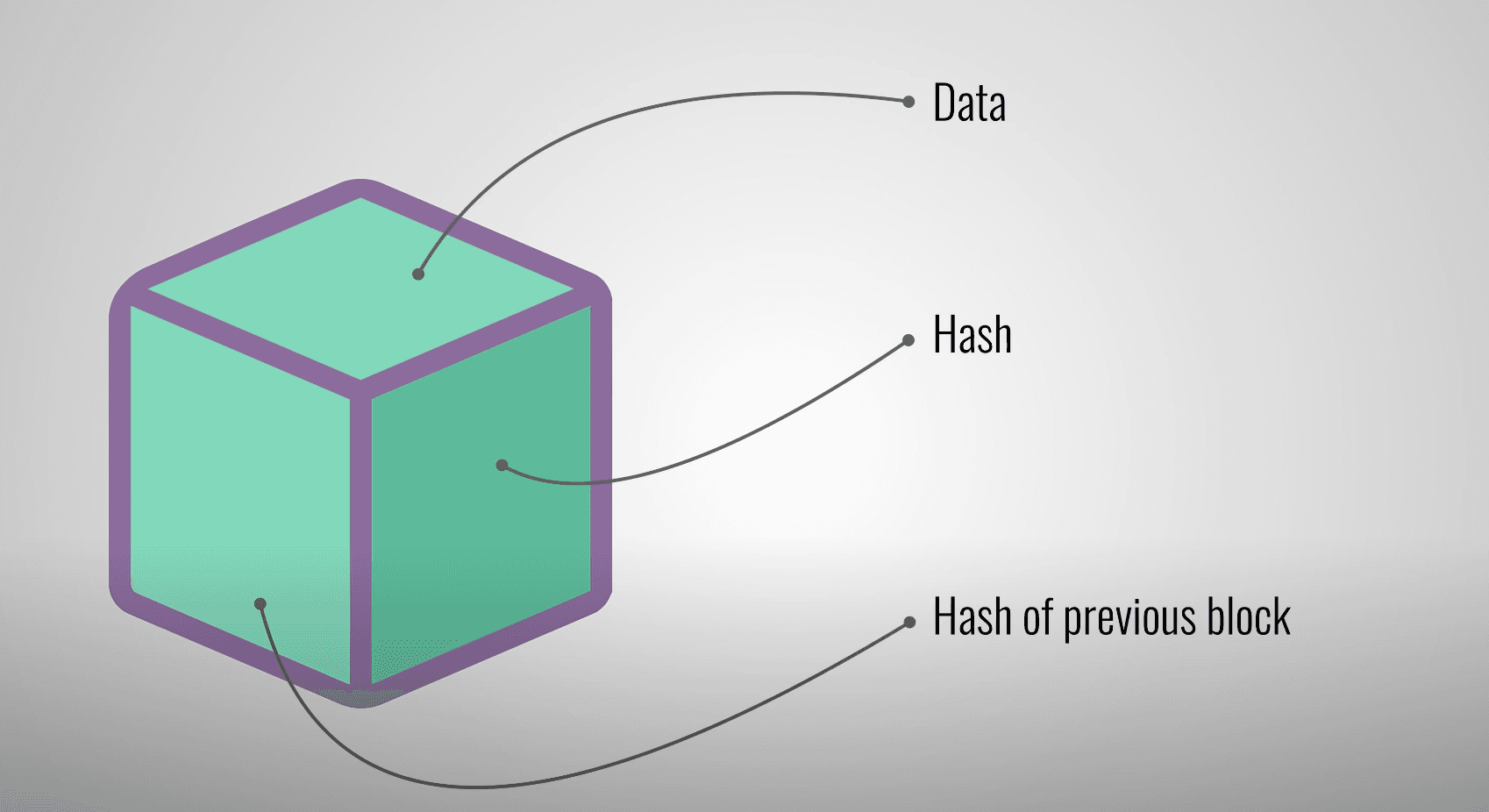
What's in a Blockchain BLOCK?
Each blockchain block contains:
- Data: depends on the type of chain. Bitcoin stores the sender, receiver, and amount.
- Hash: a fingerprint that identifies the block. If the content changes the hash will not match and the interference will be dete...
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates