How Does Blockchain Security Work, Anyway?
Curated from: hackernoon.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
6 ideas
·603 reads
3
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
How Do Blockchains Work?
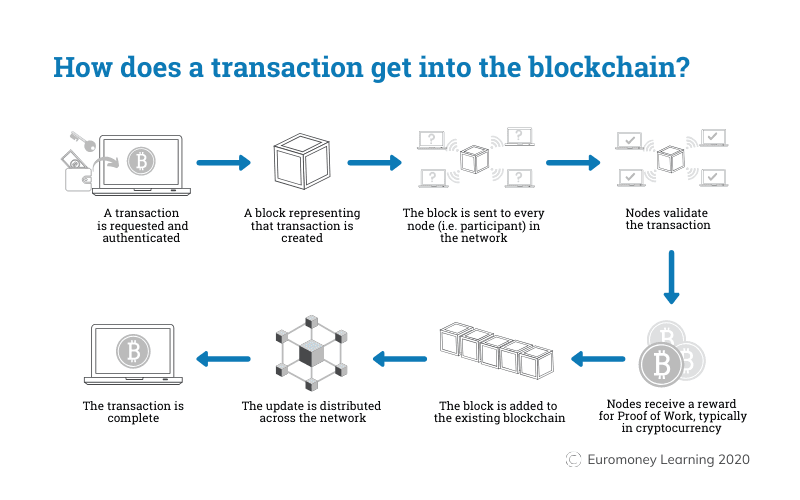
The blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records all transactions conducted by participants in the network.
Networks are sustained by a group of computers (called nodes) distributed across the world. Each node can initiate transactions or validate new transactions, which is why blockchain networks are seen as "peer-to-peer" systems.
Each new transaction gets added to a block, which is then added to the blockchain. Once other nodes agree to the transaction's validity, the new block is added to other blocks, creating a chain—hence the name.
21
168 reads
How is Blockchain Security Achieved?
Blockchains are extremely secure, making them ideal for transactions requiring high levels of data integrity and safety. For example, blockchains can be used to securely transfer money, track charity donations, safeguard records, and conduct voting.
Blockchain security is achieved through a mix of cryptography, game theory, consensus mechanisms, and failure-resistant design.
19
109 reads
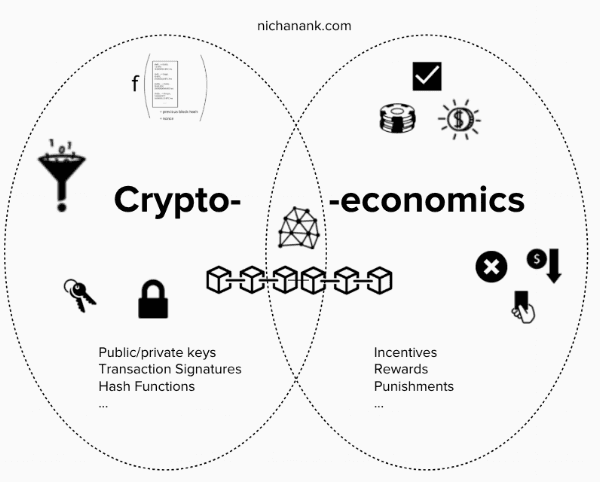
Cryptographic Hashing
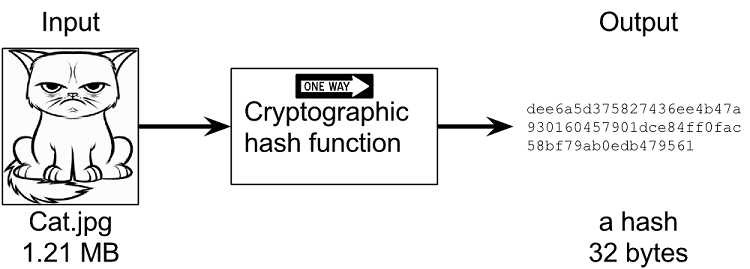
Hashing involves an algorithm (a “hash function”) generating a fixed output (hash) from a data input of any size. In most blockchains, the hash is an alphanumeric string of fixed length.
Because a hash is dependent on block data, hashes serve as unique identifiers for blocks on the chain. Running the same data through the hash function will produce the same hash no matter how many times you perform the operation.
A change in a block’s data automatically triggers the generation of a new hash. Which is why it’s easy to know if a block containing transactions has been altered.
19
100 reads
Public-Key Cryptography
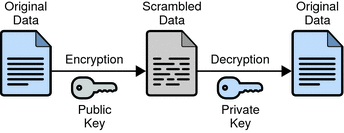
Cryptography is useful for safeguarding blockchain wallets.
Wallets are used to store digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), or any other items created and transferred on the blockchain.
When users create a wallet, they get a public key and a private key. The private key is to your wallet what a password is to your bank account. Every transaction must be signed with a private key to prove ownership of the assets.
The existence of a private key means that no one can gain access to your wallet and move funds and other assets without your approval.
20
79 reads
Consensus Algorithms
Consensus algorithms allow participants on the blockchain to agree on the validity of transactions and the true state of the blockchain. In other words, a consensus is what makes the blockchain ledger a reliable and secure record of information.
In a blockchain network, every node must confirm the validity of each transaction. This makes it harder for anyone to perform the malicious activity and get away with it. No two versions of a blockchain can exist, making it impossible to alter records without getting noticed.
Blockchain networks use different consensus mechanisms.
19
69 reads
Cryptoeconomics (Game Theory)
Cryptoeconomics is based on game theory, a field of study that attempts to predict the interactions between different participants in a situation with defined rules and outcomes. When applied to blockchain networks, game theory can be used to encourage honest activity by providing adequate incentives.
Cryptoeconomics works differently depending on the blockchain. Bitcoin uses a Proof-of-Work system where nodes (called miners) must expend some resource (electricity, in this case) before confirming transactions. Blockchains like Ethereum 2.0, Solana, and Cardano use the Proof-of-Stake system.
18
78 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Oscar Moss's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about crypto with this collection
The differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
The future of the internet
Understanding the potential of Web 3.0
Related collections
Similar ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates