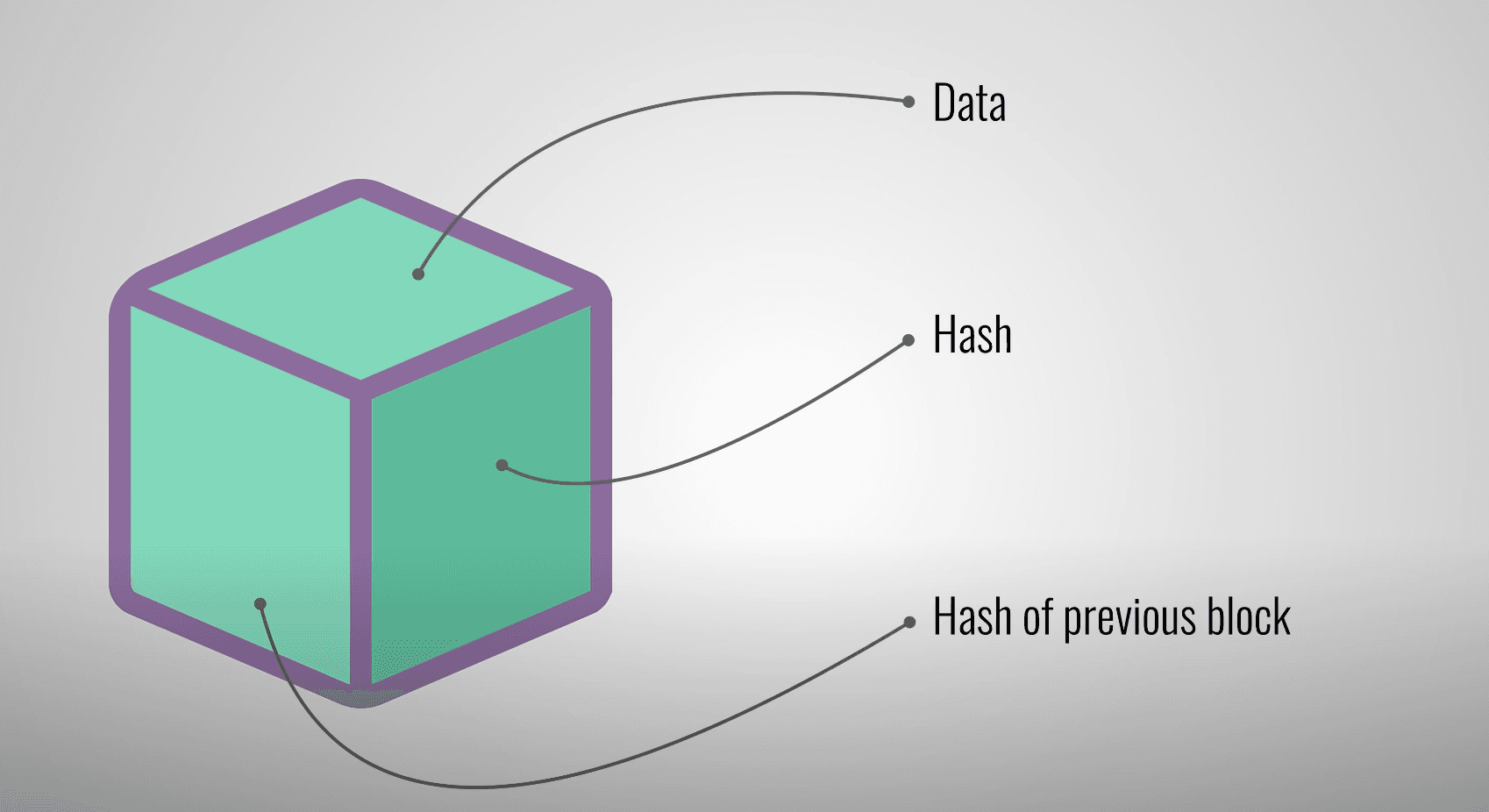
Blocks and Hashing
Bitcoin transactions are grouped into blocks, each with a unique cryptographic hash, a number that serves as a secure “check value” for the data in that block.
Any change in the block’s data will produce a completely different hash. This concept secures Bitcoin, as every block is linked to the one before it, forming a chain (hence, blockchain, a chain of blocks).
This structure creates a tamper-evident, public ledger that is "secured by math."
52
187 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
Web3 Tutor⛓️ Demo Trader🩺 Web3 White Hat♟️ Dr. In-view🥋 Web2Web3 TextCurator☯️ CowryWise & Bitget Ambassador🫂 SMM (GIDA)🕺 News Writer (DiutoCoinNews)🛡️ Cover Enthusiast🦯 Dancing🇳🇬 Martial arts♣️ Creator L2, UNEC Lead
Ummm, I don't know what to say but bear this in mind : the curations here are just from 12% of this book. I read from MoonReader, so the EPUB version is numbered as percentages and not pages.
“
Similar ideas to Blocks and Hashing
What's in a Blockchain BLOCK?
Each blockchain block contains:
- Data: depends on the type of chain. Bitcoin stores the sender, receiver, and amount.
- Hash: a fingerprint that identifies the block. If the content changes the hash will not match and the interference will be dete...
Blockchain
Although most people think of blockchain technology in relation to cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, blockchain offers security that is useful in many other ways. In the simplest of terms, blockchain can be described as data you can only add to, not take away fr...
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates