Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
To solve Ethereum’s scalability problems, Buterin and the ETH crew have outlined a network upgrade called Ethereum 2.0, or Eth2. Ethereum 2.0 brings foundation-altering changes to how Ethereum works, but it will take years to implement. Since 2020, Ethereum developers have worked tirelessly on bringing the network’s upgrade to fruition, hoping to make Ethereum faster, more secure and more accessible than ever before.
4
60 reads
Breakdown of Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 2.0 marks a significant shift in the network’s consensus algorithm. Instead of Ethereum running an energy-intensive proof-of-work algorithm, the Eth2 upgrade means switching to a proof-of-stake algorithm.
A PoS algorithm brings many benefits over a PoW one, adjusting various aspects of a network like scalability, security and accessibility.
4
42 reads
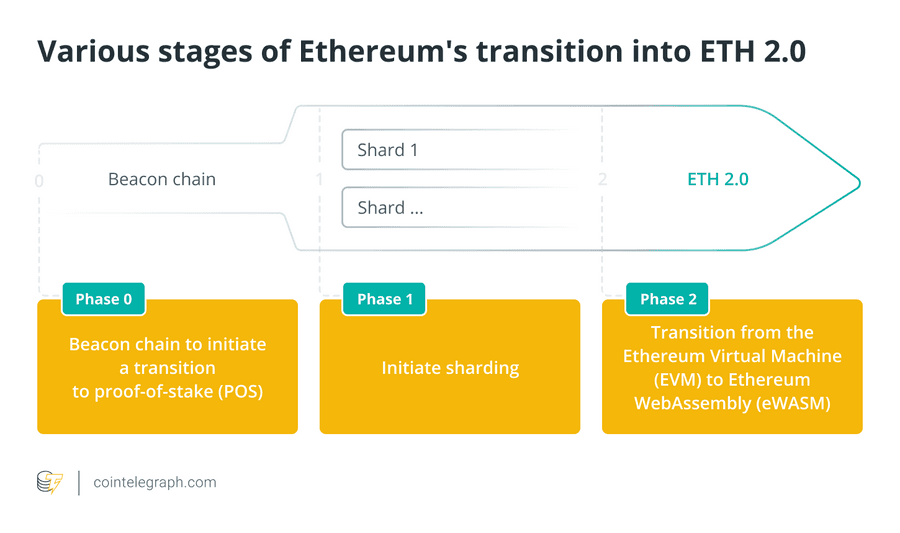
Transitioning to Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum’s transition into 2.0 is broken down into various stages.
4
48 reads
Phase 0
Phase 0 of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade introduces what’s called the Beacon Chain. Launched on December 1, 2020, the Beacon Chain marks the shift to PoS, enabling users to stake (lock away) their Ethereum and become validators. That said, Phase 0 does not affect the main Ethereum blockchain, the Beacon Chain exists alongside Ethereum’s mainnet. However, both the Beacon chain and mainnet will eventually be linked. The objective is to “merge” Mainnet into the Beacon Chain-controlled and coordinated proof-of-stake system.
4
43 reads
Phase 1
With Ethereum 2.0, validators and other users can run their own shards, validating transactions and keeping the mainchain from seeing too much congestion. A proof-of-stake consensus method is required for shard networks to enter the Ethereum ecosystem safely. Staking will be introduced on the Beacon Chain, preparing the stage for the shard chain update to come later.
4
32 reads
Phase 2
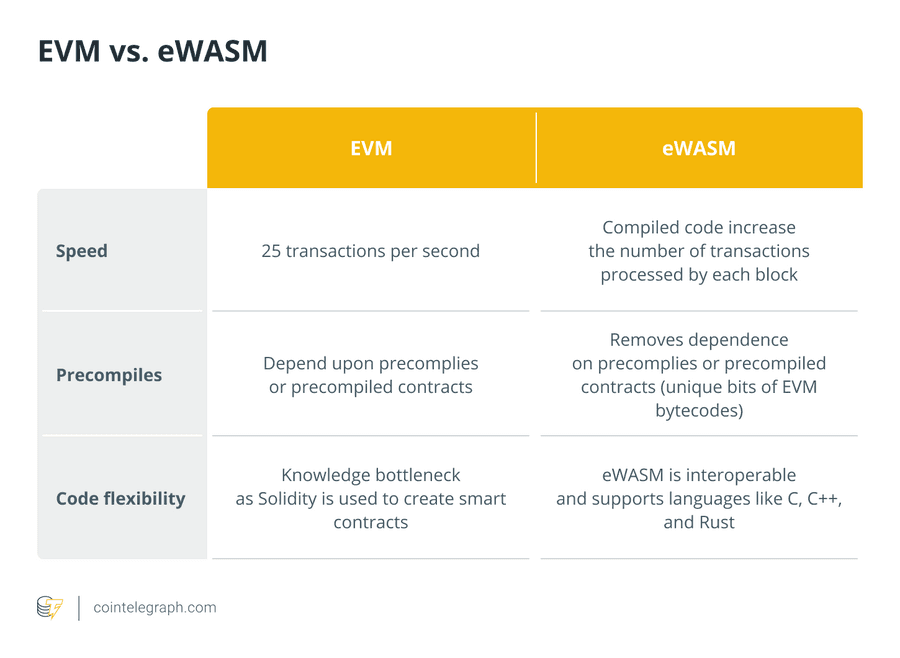
Finally, Phase 2 will see the introduction of Ethereum WebAssembly or eWASM.
The eWASM compiles code much faster than the EVM, speeding up processes within the network. Gas works more efficiently via the eWASM, and the eWASM is compatible with various traditional coding languages like C and C++.
4
40 reads
What comes next?
Basic transactions on Ethereum aren’t the only factors affected by the network’s lack of scalability. Ethereum’s problems affect nonfungible tokens (NFTs) and aspects of decentralized finance like loaning and borrowing. For example, building and trading NFTs on Ethereum can cost hundreds of dollars in gas fees due to network congestion.
4
33 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Decebal Dobrica's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about crypto with this collection
Find out the challenges it poses
Learn about the potential impact on society
Understanding the concept of Metaverse
Related collections
Similar ideas
2 ideas
What is the Ethereum Arrow Glacier upgrade?
cointelegraph.com
6 ideas
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake: Basic Mining Guide
blockgeeks.com
8 ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates