Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
How to Make Money Trading Forex
As a forex trader, you are speculating on whether one currency will rise or fall in price against another currency.
So “forex trading” can be defined as the process of speculating on currency prices to try and make a profit.
The objective of forex trading is to exchange one currency for another in the expectation that the price will change.
More specifically, the currency you bought will increase in value compared to the one you sold.
An exchange rate is simply the ratio of one currency valued against another currency.
29
272 reads
How to Read a Forex Pairs
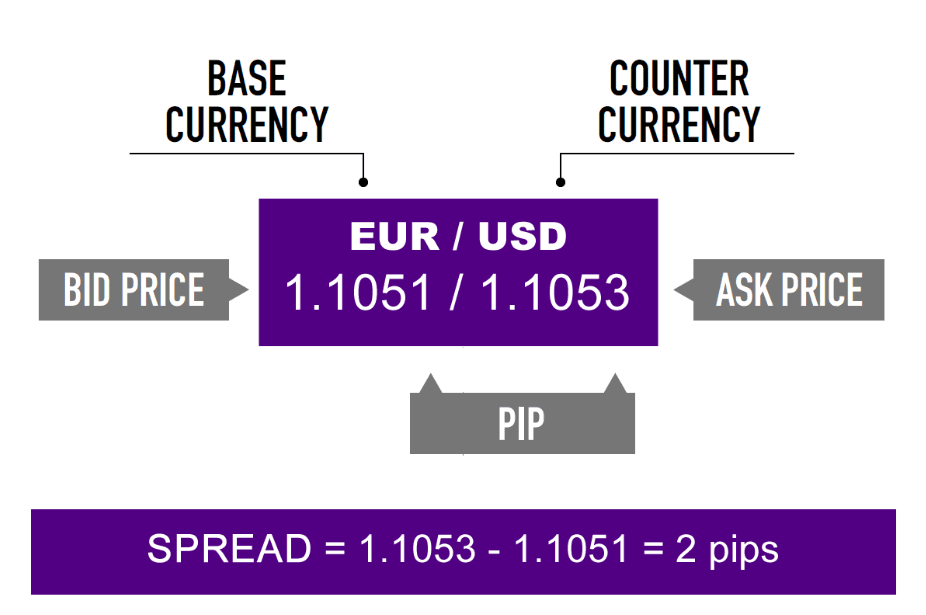
Currencies are always in pairs, such as GBP/USD or USD/JPY.
The reason they are in pairs is that, in every foreign exchange transaction, you are simultaneously buying one currency and selling another.
Whenever you have an open position in forex trading, you are exchanging one currency for another.
- Base currency (The first listed currency as the reference element for the exchange rate of the currency pair. It always has a value of one)
- Counter/Quote currency (The second listed currency)
28
186 reads
Buying or Selling Currencies
When buying, the exchange rate tells you how much you have to pay in units of the quote currency to buy ONE unit of the base currency.
When selling, the exchange rate tells you how many units of the quote currency you get for selling ONE unit of the base currency.
- You would buy the pair if you believe the base currency will appreciate (gain value) relative to the quote currency.
- You would sell the pair if you think the base currency will depreciate (lose value) relative to the quote currency.
28
151 reads
Terms in Taking and Closing Position
If you want to buy (which actually means buy the base currency and sell the quote currency), you want the base currency to rise in value and then you would sell it back at a higher price.
- long = buy.
If you want to sell (which actually means sell the base currency and buy the quote currency), you want the base currency to fall in value and then you would buy it back at a lower price.
- short = sell.
28
131 reads
The Bid, Ask and Spread
All forex quotes are quoted with two prices: the bid and ask.
- The bid is lower than the ask price.
- The bid: Price at which your broker is willing to buy the base currency in exchange for the quote currency.
- The ask or offer price: Price at which your broker will sell the base currency in exchange for the quote currency.
- Spread: The difference between the bid and the ask price.
28
137 reads
Know When to Buy or Sell a Currency Pair
Forex trading involves trying to predict which currency will rise or fall versus another currency.
The supply and demand for a currency changes due to various economic factors, which drive currency exchange rates up and down.
Example: EUR/USD
If you believe that the US economy will continue to weaken, which is bad for the USD, you would execute a BUY EUR/USD order with the expectation that it will rise versus the USD.
If you believe that the US economy is strong & the euro will weaken against the USD, you would execute a SELL EUR/USD order with the expectation that it will fall versus the USD.
28
111 reads
Trading in “Lots”
In forex, it would be just as foolish to buy or sell 1, so they usually come in “lots” of 100,000 units (standard lot) depending on your broker and the type of account you have.
When you trade with leverage, no need to pay the 100,000 upfront. Instead, you’d put down a small “deposit” or margin.
- Leverage: ratio of the transaction size (“position size”) to the actual cash (“trading capital”) used for margin.
- Margin trading lets you open large position sizes using only a fraction of the capital you’d normally need.
You can conduct relatively large transactions with a small amount of initial capital.
28
96 reads
Trading Using Leverage
When you decide to close a position, the deposit (“margin”) that you originally made is returned to you and a calculation of your profits or losses is done.
A small margin deposit can lead to large losses as well as gains.
It also means that a relatively small movement can lead to a proportionately much larger movement in the size of any loss or profit which can work against you as well as for you.
When trading on margin, it’s important to be aware that your risk is based on the full value of your position size. You can quickly blow your account if you don’t understand how margin works.
28
80 reads
Rollover
For positions open at your broker’s “cut-off time” (usually 5:00 pm ET), there is a daily “rollover fee“ or “swap fee” that a trader either pays or earns, depending on the positions you have open.
If you do not want to earn or pay interest on your positions, simply make sure they are all closed before cut-off time, the established end of the market day.
Since every currency trade involves borrowing one currency to buy another, interest rollover charges are part of forex trading.
- Interest is PAID on the currency that is borrowed.
- Interest is EARNED on the one that is bought.
28
75 reads
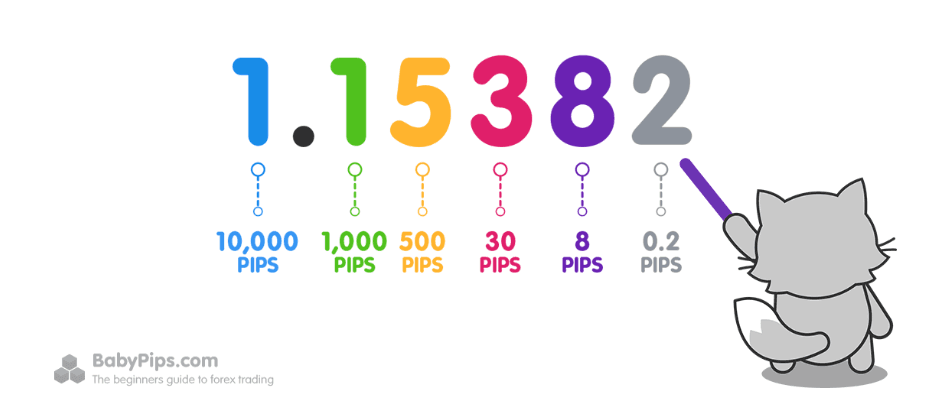
What is a Pip in Forex?
The unit of measurement to express the change in value between two currencies is called a “pip.”
A pip is usually the last decimal place of a price quote.
28
85 reads
What is a Pipette?
There are forex brokers that quote currency pairs beyond the standard “4 and 2” decimal places to “5 and 3” decimal places.
They are quoting FRACTIONAL PIPS, also called “points” or “pipettes.”
A “point” or “pipette” or “fractional pip” is equal to a “tenth of a pip“.
28
69 reads
How to Calculate the Value of a Pip
As each currency has its own relative value, it’s necessary to calculate the value of a pip for that particular currency pair.
What is the pip value in terms of my trading account’s currency?
Not everyone has their account denominated in the same currency.
This means that the pip value will have to be translated to whatever currency our account may be traded in.
Simply multiply/divide the “found pip value” by the exchange rate of your account currency and the currency in question.
28
64 reads
What is a Lot in Forex?
A “lot” is a unit measuring a transaction amount.
When you place orders on your trading platform, orders are placed in sizes quoted in lots.
The standard size for a lot is 100,000 units of currency, and now, there are also mini, micro, and nano lot sizes that are 10,000, 1,000, and 100 units.
The change in a currency value relative to another is measured in “pips,” which is a very, very small percentage of a unit of currency’s value.
Lot size depends on the account you registered in your broker.
28
60 reads
Leverage
Think of your broker as a bank who basically fronts you $100,000 to buy currencies.
The amount of leverage you use will depend on your broker and what you feel comfortable with.
Typically the broker will require a deposit, also known as “margin“.
Once you have deposited your money, you will then be able to trade. The broker will also specify how much margin is required per position (lot) traded.
Any losses or gains will be deducted or added to the remaining cash balance in your account.
The minimum security (margin) for each lot will vary from broker to broker.
28
50 reads
Bid/Ask Spread
Forex brokers will quote you two different prices for a currency pair: the bid and ask price.
- The “bid” is the price at which you can SELL the base currency.
- The “ask” is the price at which you can BUY the base currency.
The difference between these two prices is known as the spread.
This spread is the fee for providing transaction immediacy. This is why the terms “transaction cost” and “bid-ask spread” are used interchangeably.
Instead of charging a separate fee for making a trade, the cost is built into the buy and sell price of the currency pair you want to trade.
28
51 reads
How is the Spread in Forex Trading Measured?
The spread is usually measured in pips, which is the smallest unit of the price movement of a currency pair.
For most currency pairs, one pip is equal to 0.0001.
28
55 reads
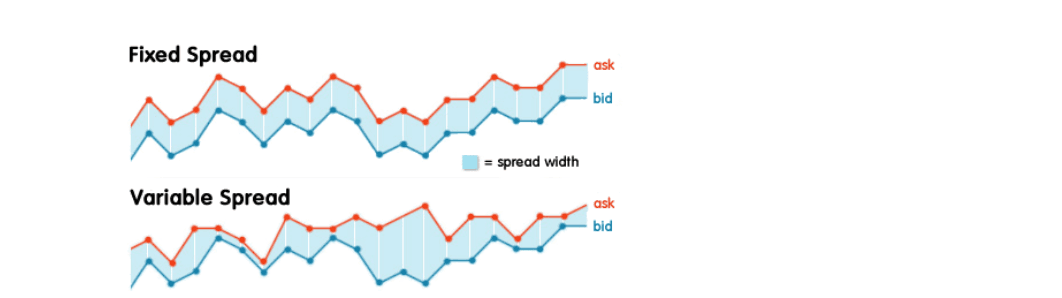
What Types of Spreads are in Forex?
The type of spreads that you’ll see on a trading platform depends on the forex broker and how they make money.
There are two types of spreads:
- Fixed: usually offered by brokers that operate as a market maker or “dealing desk” model. Fixed spreads stay the same regardless of what market conditions are at any given time.
- Variable (also known as “floating”): offered by brokers operating a “non-dealing desk” model. The difference between the bid and ask prices of currency pairs is constantly changing.
28
50 reads
Pros and Cons of Fixed Spreads
Fixed spreads use a dealing desk; the broker buys large positions from their liquidity provider(s) and offers these positions in smaller sizes to traders.
Pros
- Smaller capital requirements, ideal for new traders
- Make calculating transaction costs more predictable
Cons
- Requotes can occur frequently since pricing is only coming from your broker. It means the broker will “block” the trade and ask you to accept a new price. You will be “re-quoted” with a new price.
- Slippage. The price that you finally end up after entering a trade will be totally different than the intended entry price.
28
53 reads
Pros and Cons of Variable Spreads
Variable spreads are offered by non-dealing desk brokers who get their pricing of currency pairs from multiple liquidity providers & pass on these prices to the trader without the intervention of a dealing desk. Spreads will widen or tighten based on the supply and demand of currencies and the overall market volatility.
Pros
- No requotes since the variation in the spread factors in changes in price due to market conditions (News or Breaking News)
- More transparent pricing
Cons
- Not ideal for scalpers. Spread may widen so much from profitable to unprofitable quickly.
- Not friendly for new traders
28
45 reads
Fixed vs Variable Spreads: Which is Better?
Better with Fixed:
- Traders with smaller accounts and who trade less frequently will benefit from fixed spread pricing.
Better with Variable:
- Traders with larger accounts who trade frequently during peak market hours (when spreads are the tightest).
- Traders who want fast trade execution and need to avoid requotes.
28
50 reads
Spread Costs and Calculations
How the spread relates to actual transaction costs. You need two things:
- The value per pip
- The number of lots you’re trading
To figure out the total cost, you would multiply the cost per pip by the number of lots you’re trading.
The pip cost is linear. This means that you will need to multiply the cost per pip by the number of lots you are trading.
If you increase your position size, your transaction cost, which is reflected in the spread, will rise as well.
28
44 reads
Types of Forex Orders
An order is an offer sent using your broker’s trading platform to open or close a transaction if the instructions specified by you are satisfied or in other words, how you will enter or exit a trade.
Be sure that you know which types of orders your broker accepts.
Different brokers accept different types of forex orders.
Orders fall into two buckets:
Market order: an order instantly executed against a price that your broker has provided. Consisting of:
- Buy
- Sell
Pending order: an order to be executed at a later time at the price you specify.
- Buy Limit
- Sell Limit
- Buy Stop
- Sell Stop
28
40 reads
Market Order
A market order is an order to buy or sell at the best available price.
Please keep in mind that depending on market conditions, there may be a difference between the price you selected and the final price that is executed (or “filled”) on your trading platform.
When you place a market order, you do not have any control over what price your market order will actually be filled at.
This order type ensures that the trade is executed quickly, which can be crucial in fast-moving markets.
Pros:
- Fast execution
- High probability of trade execution
Cons:
- No control over the execution price
- Potential slippage
28
45 reads
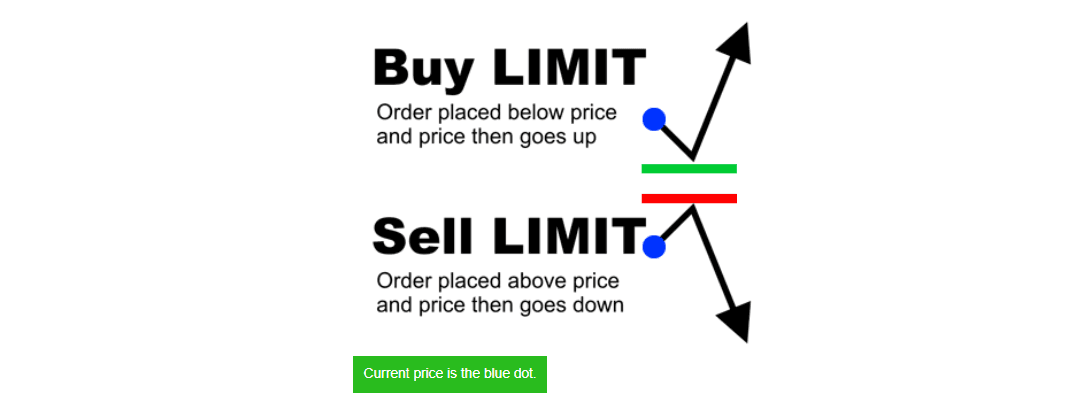
Limit Order
A limit order is an order placed to either buy below the market or sell above the market at a certain price.
- You place a “Buy Limit” order to buy at or below a specified price.
- You place a “Sell Limit” order to sell at a specified price or better.
A limit order can only be executed when the price becomes more favorable to you.
- A limit order to BUY at a price below the current market price will be executed at a price equal to or less than the specified price.
- A limit order to SELL at a price above the current market price will be executed at a price equal to or more than the specific price.
28
41 reads
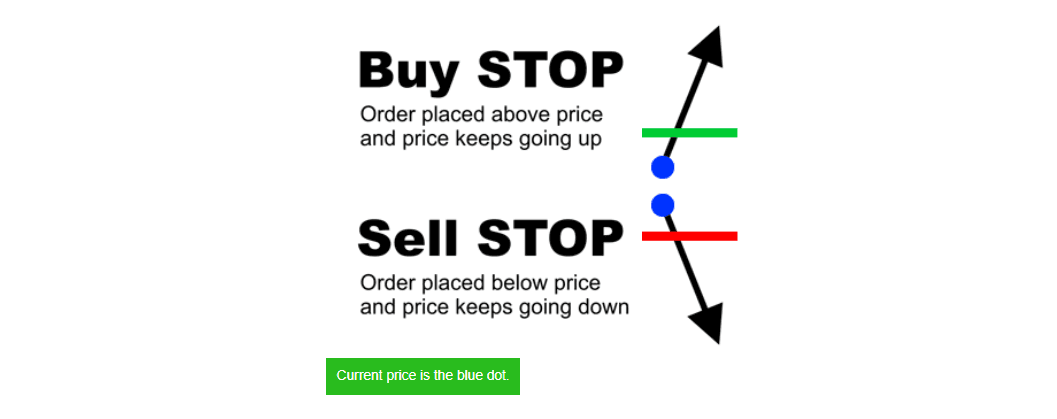
Stop Entry Order
A stop order “stops” an order from executing until price reaches a stop price.
A stop entry order is an order placed to buy above the market or sell below the market at a certain price.
- You place a “Buy Stop” order to buy at a price above the market price, and it is triggered when the market price touches or goes through the Buy Stop price.
- You place a “Sell Stop” order to sell when a specified price is reached.
A stop order can only be executed when the price becomes less favorable to you.
28
41 reads
Stop Loss Order
A stop loss order is a type of order linked to a trade for the purpose of preventing additional losses if the price goes against you.
A stop loss order remains in effect until the position is liquidated or you cancel the stop loss order.
A stop order is NOT guaranteed a specific execution price and in volatile and/or illiquid markets, may execute significantly away from its stop price. Stop orders may be triggered by a sharp move in price that might be temporary.
28
39 reads
Trailing Stop
A stop loss order which is always attached to an open position and which automatically moves once profit becomes equal to or higher than a level you specify.
A trailing stop is a type of stop loss order attached to a trade that moves as the price fluctuates.
Your stop will STAY at this new price level. It will not widen if the market goes higher against you.
Once the market price hits your trailing stop price, a market order to close your position at the best available price will be sent and your position will be closed.
28
40 reads
Limit Orders vs Stop Orders
All of orders allow traders to tell their brokers at what price they’re willing to trade in the future.
The difference lies in the purpose of the specified price
- A stop order activates an order when the market price reaches/passes a specified stop price. Think of a stop price as a threshold for your order to execute. At what exact price that your order will be filled at depends on market conditions.
- A limit order can only be executed at a price equal to/better than a specified limit price. Think of a limit price as a price guarantee. You are guaranteed to only get executed at your limit price.
28
41 reads
Demo Trade
You can open a demo account for FREE with most forex brokers. These “pretend” accounts have most of the capabilities of a “real” account.
The demo account allows you to learn about the mechanics of forex trading and test your trading skills and processes with ZERO risk.
Do NOT open a live trading account until you are CONSISTENTLY trading PROFITABLY on a demo account.
Stick with 1 of the majors because they are the most liquid which usually means tighter spreads and less chance of slippage.
Plus, in the beginning, you need time to focus on improving your trading processes and creating good habits.
28
41 reads
Can You Get Rich By Trading Forex?
- All forex traders, and ALL traders, LOSE money on some trades.
- Trading forex is not for the unemployed, those on low incomes, are knee-deep in credit card debt or who can’t afford to pay their electricity bill or afford to eat.
- Forex Trading is NOT a Get-Rich-Quick Scheme. Forex trading is a SKILL that takes TIME to learn.
Practice trading on a DEMO ACCOUNT until you find a method that you know inside and out, and can comfortably execute objectively.
28
44 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
CURATOR'S NOTE
I want to make summary of what I have learned about Forex so that I can refresh it again.
“
Similar ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates