Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Explainable AI
Explainable AI is a critical element of the broader discipline of responsible AI. Responsible AI encompasses ethics, regulations, and governance across a range of risks and issues related to AI including bias, transparency, explicability, interpretability, robustness, safety, security, and privacy.
5
40 reads
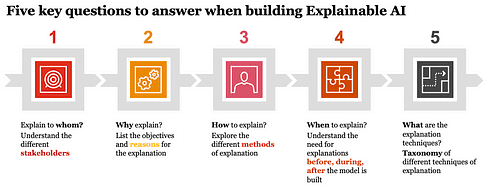
Interpretability and explainability are closely related topics . Interpretability is at the model level with an objective of understanding the decisions or predictions of the overall model. Explainability is at an individual instance of the model with the objective of understanding why the specific decision or prediction was made by the model. When it comes to explainable AI we need to consider five key questions — Whom to explain? Why explain? When to explain? How to explain? What is the explanation?
5
15 reads
Whom to Explain?
The audience for the explanation or whom to explain should be the first question to answer. Understanding the motivation of the audience, what action or decision the audience is planning to make, their mathematical or technical knowledge and expertise are all important aspects that should be considered during the formulation of the explanation. Based on our experience we propose four main categories of audience:
- End users
- Business sponsors
- Data Scientists
- Regulators
This list of four types is by no means exhaustive, but it does capture some of the key differences between different groups.
6
11 reads
Why Explain?
End users require an explanation of the decision or action recommended made by the AI system in order to carry out the recommendation.
Business users require an explanation to ensure corporate governance and manage reputational risk to their group or company.
Data scientists require explanations to validate models and also perform trade-offs between accuracy of the model and performance criteria.
Regulators require explanations to ensure compliance to existing regulations and ensuring that no harm comes to consumers.
6
10 reads
When to Explain?
Explanations may be generated before the model is built, also called ex-ante or the model is trained and tested first and then the explanation may be generated, also called post-hoc.
6
12 reads
How to Explain?
Visual or graphical explanations, tabular data-driven explanation, natural language descriptions or voice explanations are some of the existing modes of explanation.
A salesperson might be comfortable with an explanation that shows a graph of increasing sales and how the increase in sales is achieved.
The instructions for a construction worker and the explanations for why those instructions are being given may be better provided through a voice interface as opposed to a detailed written explanation.
6
12 reads
What is the Explanation (technique)?
There are six broad approaches as it relates to post-hoc explainability.
- Feature relevance: These approaches to explainability focus on the inner functioning of the model and highlight the features that best explain the outcome of the model.
- Model simplification: These approaches focus on building a new model that is a simplification of a more complex model that is to be explained.
- Local explanations: These approaches segment the solutions space and provide explanations for smaller segments that are less complex.
- Explanations by example
- Visualization
- Text explanations
7
11 reads
What is the Explanation (technique)?
There are six broad approaches as it relates to post-hoc explainability.
- Feature relevance: These approaches to explainability focus on the inner functioning of the model and highlight the features that best explain the outcome of the model.
- Model simplification: These approaches focus on building a new model that is a simplification of a more complex model that is to be explained.
- Local explanations: These approaches segment the solutions space and provide explanations for smaller segments that are less complex.
- Explanations by example
- Visualization
- Text explanations
8
13 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Decebal Dobrica's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about artificialintelligence with this collection
Find out the challenges it poses
Learn about the potential impact on society
Understanding the concept of Metaverse
Related collections
Similar ideas
4 ideas
1 idea
7 ideas
Our approach to building transparent and explainable AI systems
engineering.linkedin.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates