What is Cloud Computing?
Curated from: ibm.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
10 ideas
·858 reads
8
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is on-demand access, via the internet, to computing resources—applications, servers (physical servers and virtual servers), data storage, development tools, networking capabilities, and more—hosted at a remote data center managed by a cloud services provider (or CSP). The CSP makes these resources available for a monthly subscription fee or bills them according to usage.
Cloud computing has the following benefits:
- Lower IT costs
- Improved agility and Time-To-Value
- Better scaling.
20
176 reads
Virtualization Of IT Infrastructure
The term ‘cloud computing’ also refers to the technology that makes the cloud work. This includes some form of virtualized IT infrastructure—servers, operating system software, networking, and other infrastructure that’s abstracted, using special software, so that it can be pooled and divided irrespective of physical hardware boundaries.
17
90 reads
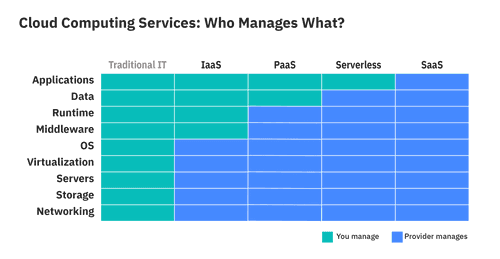
Cloud computing services
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service), and SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) are the three most common models of cloud services.
- IaaS provides on-demand access to fundamental computing resources–physical and virtual servers, networking, and storage—over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- PaaS provides software developers with an on-demand platform—hardware, complete software stack, infrastructure, and development tools.
- SaaS—also known as cloud-based software or cloud applications—is application software that’s hosted in the cloud accessible via a web browser or app.
20
91 reads
Serverless computing
Serverless computing (also called simply serverless) is a cloud computing model that offloads all the backend infrastructure management tasks–provisioning, scaling, scheduling, patching—to the cloud provider, freeing developers to focus all their time and effort on the code and business logic specific to their applications.
A subset of serverless. FaaS allows developers to execute portions of application code (called functions) in response to specific events.
19
95 reads
Types Of Cloud Computing: Public Cloud
Public cloud is a type of cloud computing in which a cloud service provider makes computing resources—anything from SaaS applications, to individual virtual machines (VMs), to bare metal computing hardware, to complete enterprise-grade infrastructures and development platforms—available to users over the public internet.
18
103 reads
A private cloud is a cloud environment in which all cloud infrastructure and computing resources are dedicated to, and accessible by, one customer only. Private cloud combines many of the benefits of cloud computing—including elasticity, scalability, and ease of service delivery—with the access control, security, and resource customization of on-premises infrastructure.
19
60 reads
Types Of Cloud Computing: Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud is just what it sounds like—a combination of public and private cloud environments. Specifically, and ideally, a hybrid cloud connects an organization's private cloud services and public clouds into a single, flexible infrastructure for running the organization’s applications and workloads.
18
60 reads
Types Of Cloud Computing: Multicloud and hybrid multicloud
Multicloud is the use of two or more clouds from two or more different cloud providers. Having a multicloud environment can be as simple as using email SaaS from one vendor and image editing SaaS from another.
Hybrid multicloud is the use of two or more public clouds together with a private cloud environment. Organizations choose multicloud to avoid vendor lock-in, to have more services to choose from and to access to more innovation.
19
55 reads
Cloud Security
Traditionally, security concerns have been the primary obstacle for organizations considering cloud services, particularly public cloud services. In response to demand, however, the security offered by cloud service providers is steadily outstripping on-premises security solutions.
Some cloud security best practices include:
- Shared responsibility for security
- Data encryption
- User identity and access management
- Collaborative management
- Security and compliance monitoring
19
54 reads
Cloud Use Cases
With 25% of organizations planning to move all their applications to the cloud within the next year, it would seem that cloud computing use cases are limitless.
Disaster recovery and business continuity:
The cloud provides cost-effective redundancy to protect data against system failures and the physical distance required to recover data and applications in the event of a local outage or disaster.
All of the major public cloud providers offer Disaster-Recovery-as-a-Service (DRaaS).
20
74 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Charlie 's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about computerscience with this collection
Understanding machine learning models
Improving data analysis and decision-making
How Google uses logic in machine learning
Related collections
Similar ideas
6 ideas
How to Use Massive AI Models (Like GPT-3) in Your Startup
future.a16z.com
2 ideas
5 ideas
How to Use Massive AI Models (Like GPT-3) in Your Startup
future.a16z.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates