Experimentation Background
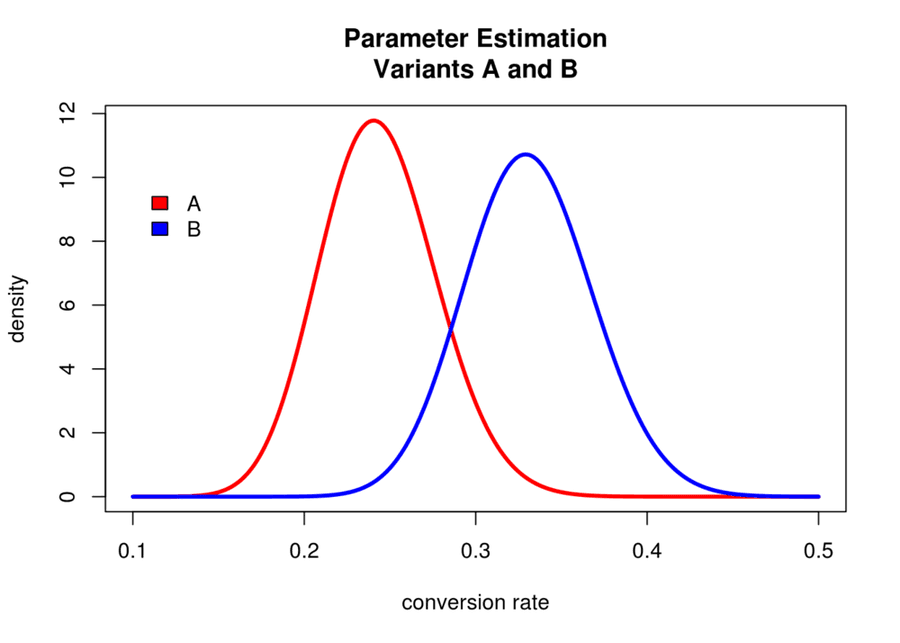
In any A/B test, we use the data we collect from variants A and B to compute some metric for each variant (e.g. the rate at which a button is clicked). Then, we use a statistical method to determine which variant is better.
5
48 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about product with this collection
How to analyze churn data and make data-driven decisions
The importance of customer feedback
How to improve customer experience
Related collections
Similar ideas to Experimentation Background
Bayesian Methods
In Bayesian A/B testing, we model the metric for each variant as a random variable with some probability distribution.
By accepting variants that offer a small improvement, Bayesian A/B testing asserts that the false positive rate — the proportion of times we accept the treatment when the t...
How Do You Plan an A/B Test?
Decide what to test, create two versions, decide on how long to run the test, collect enough data, analyze.
If you’re running an on-site test, you’ll want to think of all the sales-related pieces of your website, and then figure out which elements to split test:
- headlines
Before you start, consider your destination
We can't know what is worth doing if we don't know where we are going.
- Before touching any clutter, visualise what it would mean to have a clutter-free to-do list. Maybe you want to have a successful business, or get in shape.
- Then i...
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates