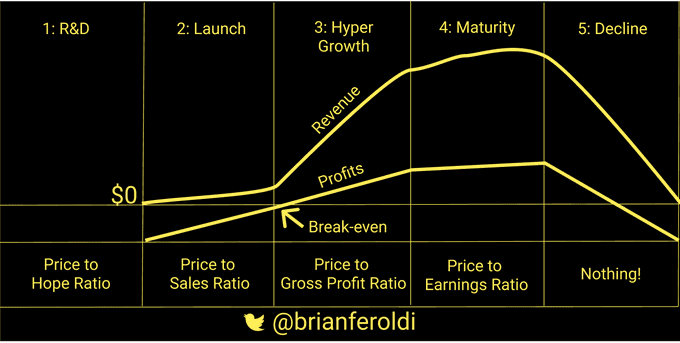
6.
The P/E ratio is only useful when a company is fully optimized for profits (stage 4)
It's most deceiving in stages 3 & 5
49
374 reads
CURATED FROM
10 critical investing lessons I wish I could teach my younger self
mobile.twitter.com
10 ideas
·4.24K reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
I've been investing for 18+ years I've made TONS of mistakes along the way here are 10 critical investing lessons I wish I could teach my younger self:
“
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about moneyandinvestments with this collection
How to apply new knowledge in everyday life
Why continuous learning is important
How to find and evaluate sources of knowledge
Related collections
Similar ideas to 6.
Some Famous Numbers
THE PRICE/EARNINGS RATIO
We’ve gone on about this already, but here’s a useful refinement: The p/e ratio of any company that’s fairly priced will equal its growth rate.
I’m talking about growth rate of earnings here. How do you find that out? Ask your broker what’s the growth rate, a...
What's a good P/E ratio to buy a stock at?
Unfortunately, there's no P/E ratio set in stone that makes a stock a buy if it's below, or a sell if it's above.
Often value investors and growth investors will look for different things in a P/E ratio.
- Value Investors - the lower the P/E ratio the better.
- Growth Inves...
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates