Glycolysis
When glucose reaches the cytoplasm of the cell, it undergoes a series of reactions to extract energy from its chemical bonds.
Glucose, a 6-carbon compound, reacts with ATP in this process, resulting in the formation of Glucose-6-phosphate.
12
162 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
Important for studies.
“
Similar ideas to Glycolysis
First Step - Glucose Phosphorylation
The first step as soon as the glucose enters the cell is that it undergoes immediate phosphorylation. So that it cannot diffuse out of the cell. This is because, on phosphorylation, the glucose becomes polar and hence cannot flow across the plasma membrane passively.
This step functions at ...
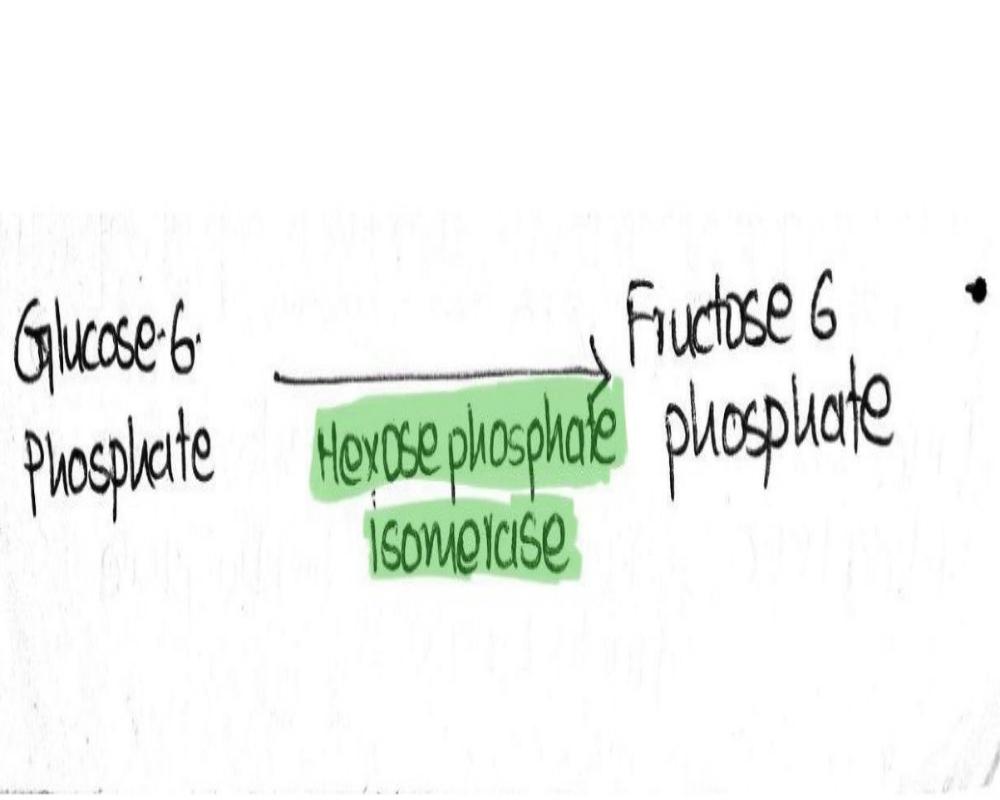
Second Step - Isomerization Of Glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P)
Once glucose is converted into glucose 6-phosphate, it is then isomerized into fructose 6-phosphate. The basic reason behind this conversion is that the addition of one more phosphate into glucose is not possible, due to its cyclic structure. Where only one carbon atom is present outside of the r...
6. Partial Oxidation of PGAL—Phosphoglyceraldehyde.
The phosphoglyceride hence obtained undergoes partial oxidation. It reacts with an inorganic phosphate and results in the formation of 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid along with the synthesis of an NADH+H+.
Enzyme-
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates