Structure of circular reasoning
The most simple form of begging the question: A is true because A is true.
Circular reasoning can also be a bit longer:
- A is true because B is true, and B is true because A is true.
- A is true because B is true, and B is true because C is true. C is correct because A is true.
140
735 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about problemsolving with this collection
How to handle conflicts
How to identify and regulate emotions
How to develop self-awareness
Related collections
Similar ideas to Structure of circular reasoning
Begging the question
Begging the question is an example of a fallacy of presumption, also known as a circular argument: The conclusion appears at the beginning and the end of the argument. A is true because A is true.
A valid argument in support of a claim will of...
Begging The Question
This logical fallacy occurs when one’s own assumptions are used to establish their argument and prove it to be true.
Also called circular reasoning, this fallacy leads the person to follow the logic because a certain logic (which may be subjective or even entirely false) i...
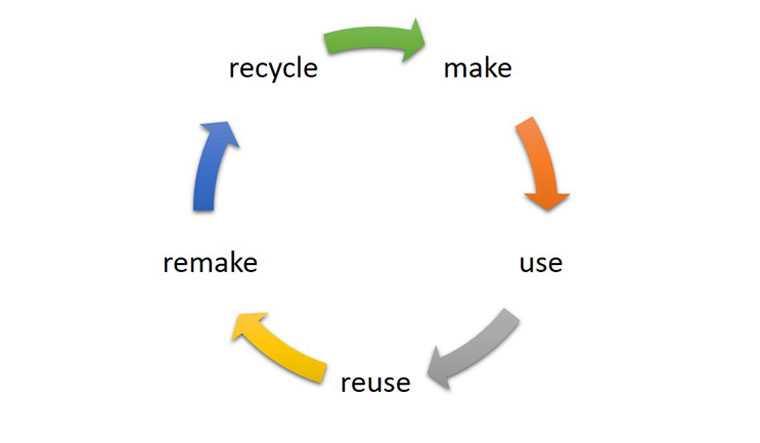
Circular economy
The purpose of circular economy is to prevent waste while promoting sustainable economic growth. Manufacturers have to design reusable products. The model follows the production-use-recycling-production cycle.
The circular economy is more profitable and less harmful to the...
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates