Motivation and What Really Drives Human Behavior
Curated from: positivepsychology.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
11 ideas
·2.41K reads
16
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Drive Human Behaviour
Our motivation is our most valuable commodity. Multiplied only by action, its value fluctuates with how we invest our attention. In our world of exponential change and ever-increasing complexity, the power rests with those who act with self-determination and persistence.
47
364 reads
Why is it that we are all born with limitless potential, yet few people fulfill those possibilities?
ABRAHAM MASLOW
42
366 reads
Types of Motivation
Motivation can be experienced as either internal in the form of push motivation or external as in the case of pull motivation
Push motivation is described in terms of biological variables originating in a person’s brain and nervous system and psychological variables that represent the properties of a person's mind.
Pull motivation is understood as environmental variables that describe external sources of motivation, like incentives or goals
Our evolutionary history and our individual personal histories shed light on how our lifelong experiences shape our motives.
47
269 reads
Drive Motivation
Needs are internal motives that energize, direct and sustain behaviour.
They generate strivings necessary for the maintenance of life as in physiological needs, and for the promotion of growth and wellbeing as in psychological and implicit needs.
The drive theory of motivation tells us that physiological needs originate in our bodies.
As our physiological system attempts to maintain health, it registers in our brain a psychological drive to satisfy a physiological craving and motivates us to bring the system from deficiency toward homeostasis.
43
225 reads
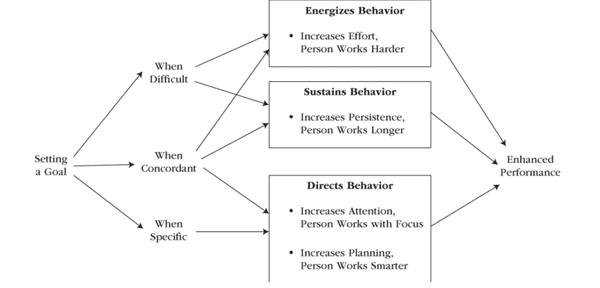
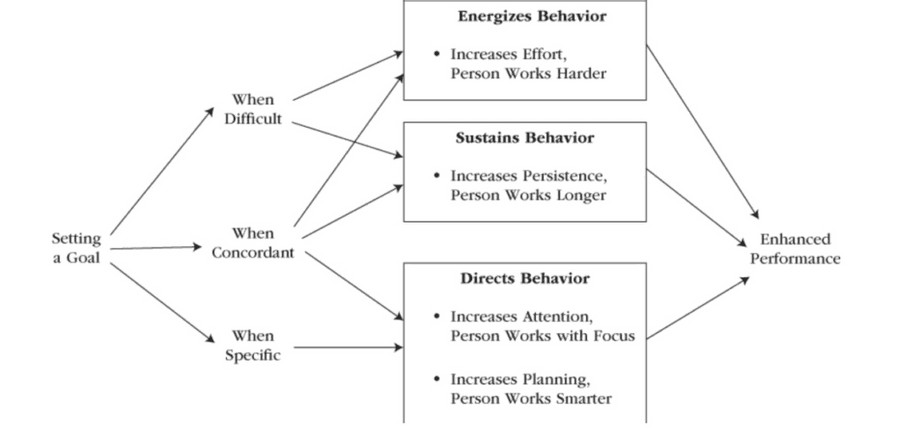
Goal Motivation
Goals, like mindset, beliefs, expectations, or self-concept, are sources of internal motives and are together referred to as cognition.
As a cognitive mental event, a goal is a "spring to action" that functions like a moving force that energizes and directs our behaviour in purposive ways
Goal setting translates into performance only when the goals are challenging, specific, and congruent with the self.
Motivation at its best is spontaneous.
Other factors such as ability and resources also influence performance, and there is no direct correspondence between goals and performance.
45
193 reads
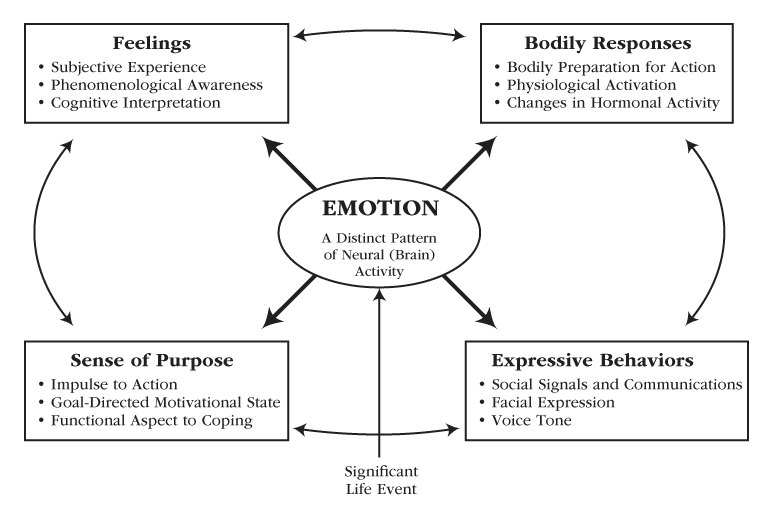
Motivation and Emotion
Emotions are considered motivational states because they generate bursts of energy that get our attention and cause our reactions to significant events in our lives
They synchronize four interrelated aspects of experience:
- Feelings
- Arousal
- Purpose
- Expression
Different emotions elicit different action tendencies
44
199 reads
Motivation and Personality
Personality theory and research show that we are, in fact, motivated in different ways based on our personality traits.
A high level of a particular trait will often make us act as the trait implies: we will be more open to experience, conscientious, extraverted, agreeable, and neurotic.
We will be motivated by different incentives, goals, and activities but also choose to be in different situations
If we exhibit characteristics at one end of a personality dimension we will seek out, create, or modify situations differently than do individuals at the other end of the spectrum.
44
154 reads
Motivation for Change
Change is rarely simple or linear.
It is difficult to find the motivation to engage in activities that are not intrinsically motivating.
What we need is to move away from extrinsically motivated action, e.g., when we have to do something because we fear consequences, and toward introjected and fully self-determined regulation, where we value the new behaviour and align it with other aspects of our life.
Stage-based approaches to behavioural changes have proven to be particularly effective in increasing motivation toward the pursuit of difficult and non-intrinsically motivating goals.
42
137 reads
The Motivations Of Abraham Maslow
- Abraham Maslow believed that all psychological problems stemmed from a lack of meaning and anxiety about these needs not being met.
- He warned us that when we set low aims for ourselves and do only as much as necessary to be competent, we set ourselves up for deep unhappiness in life.
- When his students shivered with weakness at the thought of becoming remarkable, Maslow would recall Nietzsche's idea of the law of eternal recurrence.
42
158 reads
Happiness Motivation
- Positive psychology brings attention to the proactive building of personal strengths and competencies, and these cannot be bad for motivation
- The good life consists of deriving happiness by using your signature strengths every day in the main realms of living.
- A meaningful life adds one more component: using these same strengths to forward knowledge, power or goodness.
43
156 reads
A Take-Home Message
Understanding the principles of motivation gives us the capacity to find workable solutions to real-world motivational problems.
Studying and applying motivational science can also help us reverse or cope with impulsive urges, habitual experiences, goal failure, counterproductive functioning, negative emotion, boredom, maladaptive or dysfunctional development, and a fragile sense of self.
44
190 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Ishank R's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about motivationandinspiration with this collection
How to make rational decisions
The role of biases in decision-making
The impact of social norms on decision-making
Related collections
Similar ideas
9 ideas
15 Key Motives Drive Human Behavior
neurosciencenews.com
2 ideas
Personality Traits Linked to Physical Activity and Sedentary Patterns
neurosciencenews.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates