Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Thermochemistry basics
The law of Conservation of Energy refers to an isolated system in which there is no net change in energy and where energy is neither created nor destroyed. Although there is no change in energy, energy can change forms, for example from potential to kinetic energy. In other words, potential energy (V) and kinetic energy (T) sum to a constant total energy (E) for a specific isolated system.
E = T + V
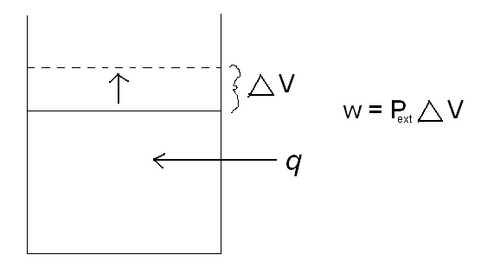
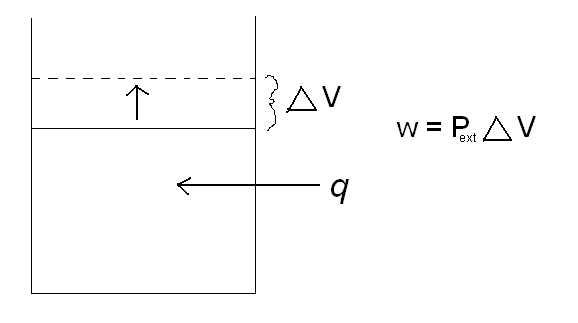
Another way that energy can change forms is heat (q) and work (w). As heat is applied to a closed system, the system does work by increasing its volume.
w = P e x t Δ V
12
108 reads
Equation explained
where Pext is the external pressure, and 🔺V is the change in volume. A classic example of this is a piston. As heat is added to the cylinder, the pressure inside the cylinder increases. The piston then rises to relieve the pressure difference between the pressure inside the cylinder and the external pressure. By increasing the volume in the cylinder, the piston has just done work. Reference the picture below.
The sum of heat and work is the change in internal energy, Δ U .
In an isolated system, q = − w . Therefore, Δ U = 0 .
12
35 reads
Quantum mechanics' equation
In quantum mechanics, the equation
- H^ψn=Enψn
Where,
- E = the energy corresponding to a wave function
- V = the potential
- H^ = the Hamiltonian operator
The equation is analogous to the equation:
E=T+V
15
179 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Highschool Student who has passionate interest in different sciences and World history.
Ziad Mohsen's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about scienceandnature with this collection
The differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
The future of the internet
Understanding the potential of Web 3.0
Related collections
Similar ideas
3 ideas
These Are the Different Forms of Energy in Science
thoughtco.com
10 ideas
Principles of evidence based medicine
adc.bmj.com
8 ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates