Basic Music Theory for Beginners - The Complete Guide – Icon
Curated from: iconcollective.edu
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
11 ideas
·26.2K reads
296
2
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Musical theory: a tool to understand music
Music theory will give you a better understanding of music. It is not a set of rules but a tool to help you understand, create, and communicate music.
The best is to learn music fundamentals first. The building blocks of musical compositions include:
- Harmony - When multiple notes play at the same time to produce a harmonious new sound.
- Melody - Notes in succession that are arranged into a musical phrase.
- Rhythm - A recurring movement of notes and rests and a pattern of strong and weak notes.
682
4.46K reads
Harmony in music
Harmony combines chords and chord progressions. Not all harmonies sound pleasing to the ear.
- Dissonant harmony doesn't sound pleasant when played together. It adds tension and makes the chord sound unstable.
- Consonant harmony sounds balanced and pleasant.
Musicians combine consonant and dissonant harmonies to make music more interesting.
614
3.66K reads
The melody in music
The melody of the song is often the most recognisable part. Most compositions have multiple melodies that repeat.
Two primary elements of a melody:
- Pitch is how high or low a note will sound.
- Rhythm is the duration of each pitch.
There are two types of melodic motion that musicians combine to give melodies more variation:
- Conjunct motion is when notes move by whole or half steps with shorter leaps between the notes.
- Disjunct motion has larger leaps between the notes.
616
2.88K reads
Basic elements of rhythm in music
Rhythm is the backbone for other musical elements. Understanding rhythm can help you make great music.
- Beat: A repeating pulse.
- Meter: A specific pattern of strong and weak pulses.
- Time Signature: The number of beats per measure.
- Tempo: How fast or slow the music plays.
- Strong and Weak Beats: The downbeats are the strong beats, and the offbeats are the weak beats.
- Syncopation: Rhythms that accent or emphasize the offbeats.
- Accents: Where the emphases are placed on the notes.
623
2.5K reads
The fundamentals of music theory
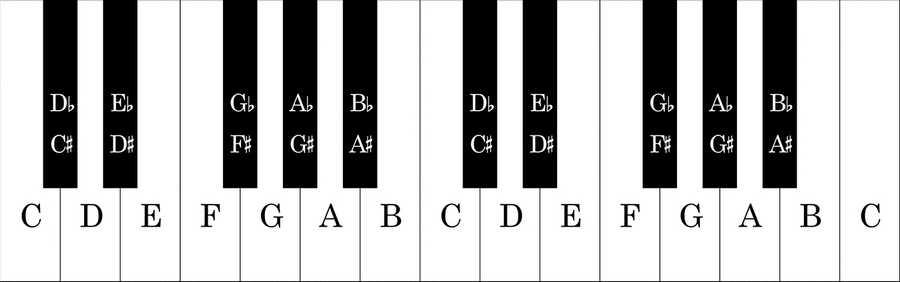
- The musical alphabet consists of seven letters: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and repeat. They are the white keys, and each note has a specific pitch.
- There are 12 notes on the piano keyboard: A, A#/B♭, B, C, C#/D♭, D, D#/E♭, E, F, F#/G♭, G, G#/A♭. The sharps (#) and flats (♭) are often the black keys on a piano.
- Octaves are the next highest or lowest pitch of the same note.
- Key signatures indicate what notes in a scale are sharp (♯) or flat (♭).
631
2.39K reads
Intervals - the distance between two notes
There are five types of intervals in music: major (M), minor (m), perfect (P), augmented (A), and diminished (d). They are measured by the number of half steps and whole steps, and their position in the scale.
Intervals are the foundation of harmony (paying two or more notes together) and melody (playing single notes in sequence).
611
2.18K reads
Music scales
A music scale is a set of notes within an octave and arranged by their pitch. The notes from a scale form melodies and harmonies.
The two main types of scales are major and minor scales and can start from any note.
- Major scales are happy sounding and follow the same interval pattern of whole-whole-half-whole-whole-whole-half.
- Minor scales sound dark and sad and follow the same interval pattern of whole-half-whole-whole-half-whole-whole.
There are twelve minor scales with three variations: natural, harmonic, and melodic.
624
1.89K reads
Music modes
Musical modes are scales and are made from a parent scale. They use the same notes and interval patterns, but the scale is started on a different note.
The seven musical modes are:
- I – Ionian: major scale
- ii – Dorian: major scale starting on the 2nd degree
- iii – Phrygian: major scale starting on the 3rd degree
- IV – Lydian: major scale starting on the 4th degree
- V – Mixolydian: major scale starting on the 5th degree
- vi – Aeolian: natural minor scale or major scale starting on the 6th degree
- vii – Locrian: major scale starting on the 7th degree
634
1.67K reads
Basic chords in music
Chords are the harmonious building blocks of music. Knowing how to build chords and how they interact is essential when learning music theory.
There are four basic types of chords in music:
- Major – It has a major third and a perfect fifth above the root
- Minor – It has a minor third and a perfect fifth above the root
- Diminished – It has a minor third and a diminished fifth above the root
- Augmented – It has a major third and an augmented fifth above the root.
620
1.49K reads
Different types of chords
- The most basic chords are triads - a chord made of three notes.
- The seventh chords add a note above the basic triad. For example, C major seventh has the notes C-E-G-B.
- Major chords have a root note, a major third, and a perfect fifth, for example, a C major triad has the notes C-E-G.
- Minor chords have a root note, a minor third and a perfect fifth, for example, a C minor triad consists of the notes C-E♭-G.
- Diminished chords sound tense. They have a root note, minor third, and diminished fifth. For example, a C diminished triad has the notes: C-E♭-G♭.
622
1.47K reads
Chord extensions, inversions and progressions
- Chord extensions add notes to the basic triad beyond the seventh. They extend into the next octave and are richer than basic triads.
- Chord inversions are variations of the same chord. Transferring the bottom note in a chord to the next octave makes an inversion.
- Chord progressions is an ordered series of chords and support the melody and the rhythm.
600
1.64K reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Aiden Mejia's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about personaldevelopment with this collection
How to set achievable goals
How to manage time for personal and professional life
How to avoid distractions
Related collections
Similar ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates