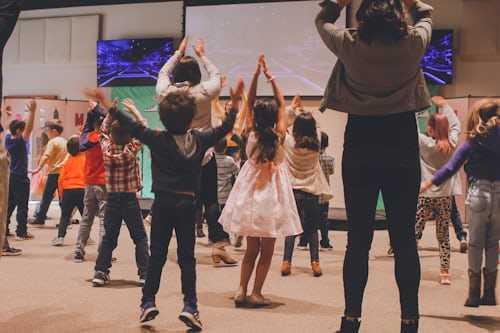Moving Together In Sync
- The synchronicity that is created while moving together in a simultaneous and coordinated manner results in strong social bonding, and well-being, according to new research.
- Activities like the parading, line dancing and crew rowing, which usually have synchronous movements, allows humans to bond together all at once.
- Even in the animal kingdom, birds, dolphins, and fireflies synchronize their actions, displaying coordinated behaviour.
84
432 reads
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about personaldevelopment with this collection
How to stay motivated
How to create a workout routine
Proper form and technique for home workouts
Related collections
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates