About Kapila: Vedic sage, of the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy |
Curated from: peoplepill.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
15 ideas
·705 reads
5
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
8. Rishi Kapila
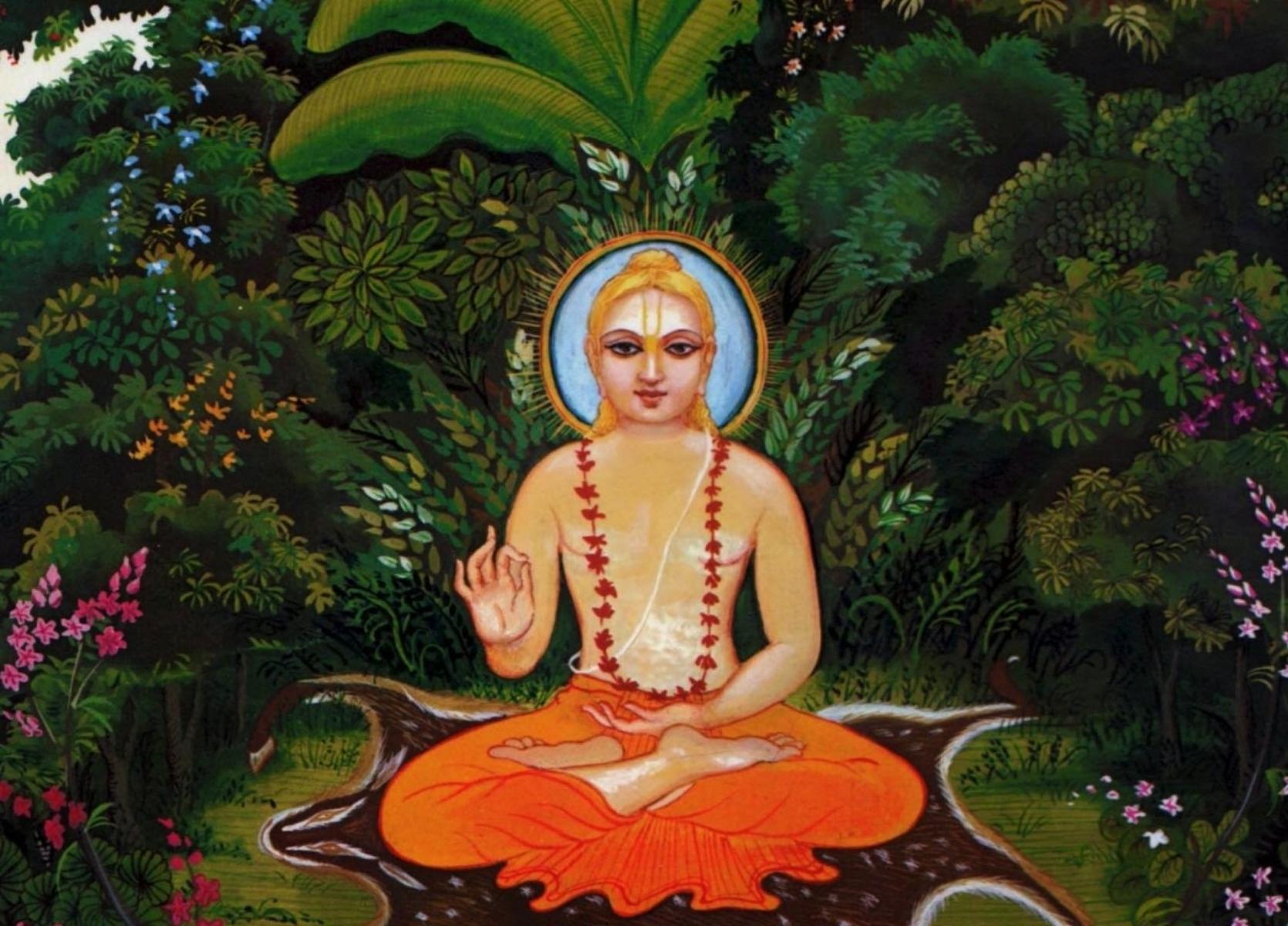
Kapila was a Vedic sage who lived around the 6th century BCE and is considered a founder of Samkhya, the oldest of the six orthodox schools of Indian philosophy, or darshans. His name comes from the Sanskrit meaning “reddish brown” and is translated as “the red one.”
Kapila is considered an incarnation of Vishnu who came to earth to restore spiritual order. He is also known for teaching Bhakti yoga, the spiritual path of liberation or enlightenment.
11
139 reads
Biography
Kapila is a given name of different individuals in ancient and medieval Indian texts, of which the most well-known is the founder of the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy. Kapila of Samkhya fame is considered a Vedic sage, estimated to have lived in the 6th-century BCE, or the 7th-century BCE.
Rishi Kapila is credited with authoring the influential Samkhya-sutra, in which aphoristic sutras present the dualistic philosophy of Samkhya. Kapila's influence on Buddha and Buddhism have long been the subject of scholarly studies.
10
95 reads
Kapila And Ahimsa
Many historic personalities in Hinduism and Jainism, mythical figures, pilgrimage sites in Indian religion, as well as an ancient variety of cow went by the name Kapila.
Kapila is credited with authoring an influential sutra, called Samkhya-sutra(also called Kapila-sutra),which aphoristically presents the dualistic philosophy of Samkhya.These sutras were explained in another well studied text of Hinduism called the Samkhyakarika. Beyond the Samkhya theories,he appears in many dialogues of Hindu texts, such as in explaining and defending the principle of Ahimsa (non-violence) in the Mahabharata.
10
74 reads
In Vedic texts
The Rigveda X.27.16 – estimated to have been composed between 1500 and 1200 BCE – mentions Kapila (daśānām ekam kapilam ) which the 14th-century Vedic commentator Sayana thought refers to a sage; a view which Chakravarti in 1951 and Larson in 1987 consider unreliable, with Chakravarti suggesting that the word refers to one of the Maruts, while Larson and Bhattacharya state kapilam in that verse means "tawny" or "reddish-brown"; as was also translated by Griffith.
10
68 reads
Jainism
Kapila is mentioned in chapter VIII of the Uttaradhyayana-sutra , states Larson and Bhattacharya, where a discourse of poetical verses is titled as Kaviliyam , or "Kapila's verses".
The name Kapila appears in Jaina texts. For example, in the 12th century Hemacandra's epic poem on Jain elders, Kapila appears as a Brahmin who converted to Jainism during the Nanda Empire era.
According to Jnatadharmakatha , Kapila was a contemporary of Krishna and the Vasudeva of Dhatakikhanda . The text further mentions that both of them blew their shankha (counch) together.
11
52 reads
Buddhism
Buddhists literature, such as the Jataka tales, state the Buddha was Kapila in one of his previous lives.
Scholars have long compared and associated the teachings of Kapila and Buddha. For example, Max Muller wrote (abridged),
There are no doubt certain notions which Buddha shares in common, not only with Kapila, but with every Hindu philosopher.It has been said that Buddha borrowed his atheism from Kapila. But atheism is an indefinite term, and may mean very different things. In one sense, every Indian philosopher was an atheist,
for they all perceived that the gods of the populace could not
11
41 reads
...
claim the attributes that belong to a Supreme Being (Absolute,the source of all that exists or seems to exist,Brahman).
Kapila,when accused of atheism,is not accused of denying the existence of an Absolute Being.He is accused of denying the existence of an Ishvara.
As Buddhist art often depicts Vedic deities, one can find art of both Narayana and Kapila as kings within a Buddhist temple, along with statues of Buddhist figures such as Amitabha, Maitreya, and Vairocana.
In Chinese Buddhism, the Buddha directed the Yaksha Kapila and fifteen daughters of Devas to become the patrons of China.
10
33 reads
Works
The following works were authored by Kapila, some of which are lost, and known because they are mentioned in other works; while few others are unpublished manuscripts available in libraries stated:
- Manvadi Shrāddha - mentioned by Rudradeva in Pakayajna Prakasa .
- Dṛṣṭantara Yoga - also named Siddhāntasāra available at Madras Oriental Manuscripts Library.
- Kapilanyayabhasa - mentioned by Alberuni in his works.
- Kapila Purana - referred to by Sutasamhita and Kavindracharya. Available at Sarasvati Bhavana Library, Varanasi.
10
29 reads
....
•Kapila Samhita - there are 2 works by the same name. One is the samhita quoted in the Bhagavatatatparyanirnaya and by Viramitrodaya in Samskaras . Another is the Samhita detailing pilgrim centers of Orissa.
•Kapilasutra - Two books, namely the Samkya Pravacana Sutra and the Tattvasamasasutra, are jointly known as Kapilasutra.Bhaskararaya refers to them in his work Saubhagya-bhaskara.
•Kapila Stotra - Chapters 25 to 33 of the third khanda of the Bhagavata Mahapurana are called Kapila Stotra.
•Kapila Smriti - Available in the work Smriti-Sandarbha, a collection of Smritis, from Gurumandal Publica.
10
20 reads
.....
•Kapilopanishad - Mentioned in the Anandasrama list at 4067 (Anandasrama 4067).
•Kapila Gita - also known as Dṛṣṭantasara or Siddhāntasāra .Kapila Pancharatra - also known as Maha Kapila Pancharatra. Quoted by Raghunandana in Saṃskāra Mayukha .
Ayurveda books mentioning Kapila's works are:
Vagbhatta mentions Kapila's views in chapter 20 of Sutrasthana .Nischalakara mentions Kapila's views in his commentary on Chikitsa Sangraha .Kapila's views are quoted in Ayurvedadipika .The Kavindracharya list at 987 mentions a book named Kapila Siddhanta Rasayana .
10
17 reads
......
Hemadri quotes Kapila's views in Ashtangahradaya (16th verse) of the commentary Ayurveda Rasayana .Sarvadarsanasamgraha (Sarva-darśana-saṃgraha ) mentions Kapila's views on Raseśvara school of philosophy.
Teachings
Kapila's Samkhya is taught in various Hindu texts:
10
27 reads
Mahabharata
- "Kapila said, "Acts only cleanse the body. Knowledge, however, is the highest end (for which one strives). 5 When all faults of the heart are cured (by acts), and when the felicity of Brahma becomes established in knowledge, benevolence, forgiveness, tranquillity, compassion, truthfulness, and candour, abstention from injury, absence of pride, modesty, renunciation, and abstention from work are attained. These constitute the path that lead to Brahma. By those one attains to what is the Highest."
- "Bhishma said (to Yudhishthira), 'Listen, O slayer of foes! The Sankhyas or followers of Kapila,
10
30 reads
...
who are conversant with all paths and endued with wisdom, say that there are five faults, O puissant one, in the human body.
They are Desire and Wrath and Fear and Sleep and Breath. These faults are seen in the bodies of all embodied creatures.
Those that are endued with wisdom cut the root of wrath with the aid of Forgiveness. Desire is cut off by casting off all purposes.
By cultivation of the quality of Goodness (Sattwa) sleep is conquered, and Fear is conquered by cultivating Heedfulness.
Breath is conquered by abstemiousness of diet. (Book 12: Santi Parva: Part III, Section CCCII.)
10
25 reads
Bhagavata Purana
- "My appearance in this world is especially to explain the philosophy of Sankhya, which is highly esteemed for self-realization by those desiring freedom from the entanglement of unnecessary material desires. This path of self-realization, which is difficult to understand, has now been lost in the course of time. Please know that I have assumed this body of Kapila to introduce and explain this philosophy to human society again."
- "When one is completely cleansed of the impurities of lust and greed produced from the false identification of the body as "I" and bodily possessions as "mine,"
10
25 reads
Recognition
Continued above - one's mind becomes purified. In that pure state he transcends the stage of so-called material happiness and distress."
Kapila, the founder of Samkhya, has been a highly revered sage in various schools of Hindu philosophy. Gaudapada (~500 CE), a Advaita Vedanta scholar, in his Bhasya called Kapila as one of the seven great sages along with Sanaka, Sananda, Sanatana, Asuri, Vodhu and Pancasikha. Vyasa, the Yoga scholar, in his Yogasutra-bhasya wrote Kapila to be the "primal wise man, or knower".
10
30 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
卐 || एकं सत विप्रा बहुधा वदन्ति || Enthusiast || Collection Of Some Best Reads || Decentralizing...
अर्हम् Arham's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about artsandculture with this collection
Leonardo da Vinci's creative process
How to approach problem-solving like da Vinci
The importance of curiosity and observation
Related collections
Similar ideas
7 ideas
Narasimha Avatar - Fourth Avatar Of Vishnu | Dashavatar
THE HINDU SAGA
4 ideas
Parashuram Avatar - Sixth Avatar Of Vishnu | Dashavatar
THE HINDU SAGA
1 idea
Meditation: Overview, Research, and Effectiveness - The Human Condition
thehumancondition.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates