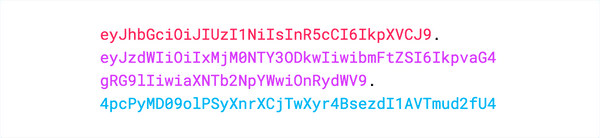Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
JWT stands for JSON Web Token and represents an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret (with the HMAC algorithm) or a public/private key pair using RSA or ECDSA.
9
124 reads
Why should JWTs be used?
- Authorization: The most common scenario for using JWT. Once the user is logged in, each subsequent request will include the JWT, allowing the user to access routes, services, and resources that are permitted with that token.
- Information exchange: JSON Web Tokens are a good way of securely transmitting information between parties. Because JWTs can be signed—for example, using public/private key pairs—you can be sure the senders are who they say they are. Additionally, as the signature is calculated using the header and the payload, you can also verify that the content hasn't been tampered with.
7
66 reads
JWTs structure
In its compact form, JSON Web Tokens consist of three parts separated by dots (.), which are:
- Header
- Payload
- Signature
Therefore, a JWT typically looks like the following.
aaaaa.bbbbb.ccccc
I'll break down every part in the upcoming ideas.
7
60 reads
JWT Headers
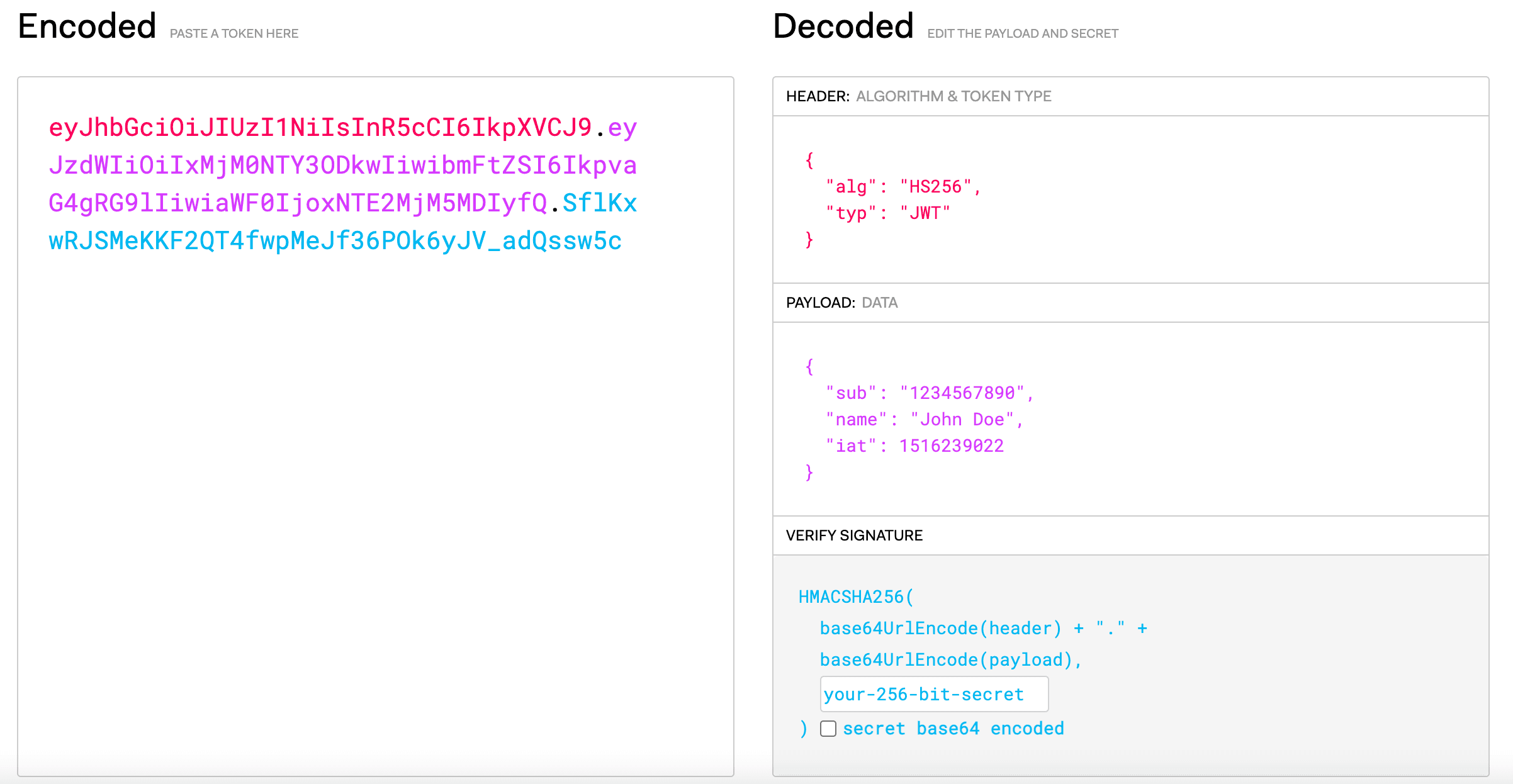
The header is the first part of a JWT token and it usually consists of two parts: the type of the token, and the signing algorithm being used. (see picture above - type is "JWT" and the signing algorithm is HMAC SHA256 ).
This JSON is then Base64Url encoded.
6
43 reads
JWT Payload
The payload is the second part of a JWT token and it contains the claims - statements about an entity (usually the user) and additional data. There are three types of claims:
- Registered - recommended predefined claims that provide a set of useful, interoperable claims. Some of them are: iss (issuer), exp (expiration time), sub (subject), aud (audience) etc. Names are short because a goal of JWTs is for the representation to be compact.
- Public - can be defined at will by those using the JWT
- Private - custom claims created to share information between parties
This JSON is then Base64Url encoded.
6
28 reads
JWT Signature
The signature is the third part of a JWT token. In order to create it we have to take the encoded header, the encoded payload, a secret, the algorithm specified in the header, and sign that (see picture).
The signature is used to verify the message wasn't changed along the way, and, in the case of tokens signed with a private key, it can also verify that the sender of the JWT is who it says it is.
6
27 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Mircea-Ioan Oprea's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about computerscience with this collection
The importance of networking in podcasting
How to grow your podcast audience
How to monetize your podcast
Related collections
Similar ideas
2 ideas
A beginner's guide to social tokens
linda.mirror.xyz
10 ideas
What Is a Digital Signature? | Binance Academy
academy.binance.com
5 ideas
What is UTF-8 Encoding? A Guide for Non-Programmers
blog.hubspot.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates