Working Memory
Curated from: scotthyoung.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
13 ideas
·16.6K reads
70
3
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
The working memory
Working memory temporarily stores the information you are working on. But it is not just a simple storage. The working memory enables you to create new thoughts, change them, combine them, search them, or any other function that helps you navigate your life.
By enabling these functions, working memory upholds your thinking, planning, learning, and decision-making.
314
3.15K reads
A working memory model
The working memory model of Alan Baddeley divides the working memory into four components:
- The phonological loop. It is mostly the temporary storage of sounds.
- The visuospatial sketchpad. The sketchpad stores two- and three-dimensional images of objects.
- The central executive. It is responsible for directing attention and manipulating information. It re-arranges ideas and applies the rules of grammar, logic or algebra to find a solution.
- The Episodic buffer.
307
1.98K reads
Learning depends on your working memory
To learn, you must first understand. To understand,
- your phonological loop must keep track of the sounds of the words;
- your central executive must continually update the sequences as you go along;
- the meanings need to be integrated, so you understand.
If any of these processes fail, you'll get confused.
309
1.61K reads
Working memory is a skill
If you practice this skill, you can improve it. To set out how to improve your working memory, it is useful to know how you can measure it.
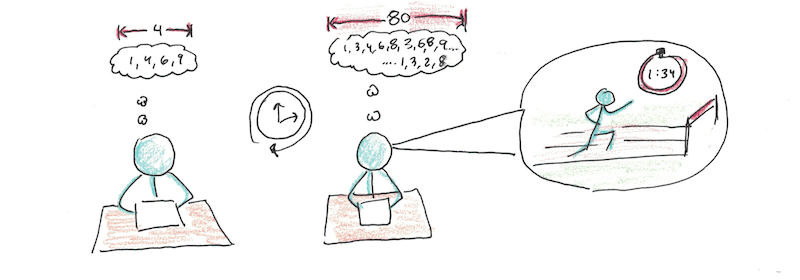
There is a difference between short-term memory capacity and working memory capacity.
- Short-term capacity is your ability to temporarily store small amounts of information - digits, letters, words, symbols, etc. The average human span is 4 items; the digit span is 7 digits.
- Working memory capacity is your combined ability to store and manipulate information.
304
1.31K reads
The phonological loop stores sound
A phonological loop is a kind of short-term memory storage that stores sound. A conversation, listening to music, and understanding a lecture depends on your phonological loop.
As you read, your phonological loop uses sub vocalisation (your internal voice) to translate visual information (what you read) into auditory information, which is then processed to extract meaning. If your internal voice is disrupted, you will find it hard to maintain information in your phonological loop, and your comprehension will suffer.
299
1.12K reads
Music interferes with your studies
- Music interferes with your digit span. Studies found that students performed better when they revised in a quiet environment than the students who listened to music.
- Many students listen to music while learning because it helps reduce anxiety. Music could also drown out external noise.
- The recommendation is that is you avoid music when studying in a quiet environment. If you don't have a quiet environment, reduce noise by using earplugs.
301
1.19K reads
Visuospatial sketchpad
The visuospatial sketchpad is essential for understanding mathematical, science, technology and engineering subjects.
You can improve your visuospatial working memory. There are two broad strategies for approaching visuospatial problems.
- A holistic strategy demands the most working-memory.
- An analytic strategy consists of noticing the relationship between patterns in a step-by-step way. Break complex tasks into smaller steps and write the steps onto paper.
297
1.01K reads
Improve learning with visualisation and drawing
You can use your visuospatial sketchpad to help your phonological loop and vice versa.
- Instead of remembering a shopping list, you can throw it into one picture. A list of peppers, milk, chicken and mustard can be visualised as a mustard-covered chicken swimming in milk with peppers.
- Instead of remembering scientific text from chemistry by summarising the main points, using a drawing-construction strategy is more effective. But the quality of drawings is essential for the technique to be effective.
302
988 reads
The functions of the central executive
- Allocation of attention. Multitasking can generally harm our performance. Each time you switch tasks, it takes some time and energy. (You have to shift your goals and reactivate the rules for the activity.) Lots of task switching will add up to lost time during a day.
- Manipulation of information. Extra manipulation of information can make your understanding suffer. If you study from multiple sources (several textbooks), it might be good to integrate the information in one place.
298
881 reads
Chunking is the secret to expertise
The idea behind chunking is to group underlying items by some sort of meaning or structure. For example, RTCTAIILFSO is easier remembered when it is regrouped to FRAC-TO-LIS-TIC.
- You can use chunking to memorise phone numbers, passwords or PIN codes by dividing the given sequence into chunks containing a maximum of 4 items each. A phone number could be split with dashes like this: 743-293-045
- One chunking technique to help your learning is organisation. This is where you categorise unstructured study material into meaningful groups.
303
933 reads
How to master any subject
Chunking is the secret behind mastering any subject. Chunking draws on your long-term memory resources. The more knowledge you have stored, the less information you need to process with your working memory, and the easier it will be to understand and remember your study material.
To master any subject:
- First, build solid foundations of the basics (the elementary chunks such as meanings and concepts)
- Then master the underlying sub-skills.
- Then attempt to form increasingly more complex chunks.
321
892 reads
Cognitive load: Understanding learning difficulties
Cognitive load is the effort used by the working memory to process information. The working memory capacity is limited: If it is overloaded with information, you will fail to understand.
There are three types of cognitive load:
- Intrinsic load. It is the level of difficulty of the subject. Reduce the intrinsic load by gaining more knowledge of the underlying chunks.
- Extrinsic load. It is associated with the way the study material is presented. Use a goal-free approach by first playing with the parts.
- Germane load. It is the effort you have to make to construct integrated chunks of information from the concepts in your study material.
300
741 reads
Turn anxiety into excitement
Anxiety is a major cause of cognitive load. Instead of your working memory focusing on the task at hand, your short-term memory is filled with irrelevant information. i.e. maths is hard; I hate math; I want to give up.
- The effect that anxiety has on your performance depends on the beliefs you have about it. If you believe math anxiety will help you perform better, then your performance will not be impacted.
- Reframe your mindset to excitement. "I'm excited."
317
818 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Carter X.'s ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about personaldevelopment with this collection
Ways to improve productivity
Strategies for reducing stress
Tips for managing email overload
Related collections
Similar ideas
4 ideas
9 ideas
Chunking: A Student's Best Weapon for Exams - EdEfficiency
edefficiency.com
5 ideas
Discover the Power of Handwriting
psychologytoday.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates