Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Gravity is one of the universe's fundamental forces
Scientists know four forces - things that attract or repel one object from another. The strong force and the weak force operate only inside the centres of atoms. The electromagnetic force rules objects with excess charge, and gravity directs objects with mass.
People have long speculated about gravity. While ancient Greek and Indian philosophers observed gravity, it was the insight from Isaac Newton that made it possible to measure and predict the phenomenon.
54
335 reads
The universal law of gravitation
In 1687, Isaac Newton's treatise Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica showed that every object in the universe, small and great, pulled on every other object, from a grain of sand to the planets.
Newton could compute the attraction: Doubling the mass of one object makes its pull twice as strong, and bringing two objects twice as close quadruples their mutual pull.
50
283 reads
Increased understanding of the gravitational pull
While Isaac Newton's description of gravity was good enough to detect Neptune's existence in the mid-1800s, Newton's law was not perfect. Astronomers discovered a mismatch between his law and the laws of nature.
This mismatch was resolved in 1915 when Albert Einstein published his theory of general relativity. Before this theory, physicists knew how to calculate a planet's gravitational pull, but they didn't understand why gravity behaved this way.
49
232 reads
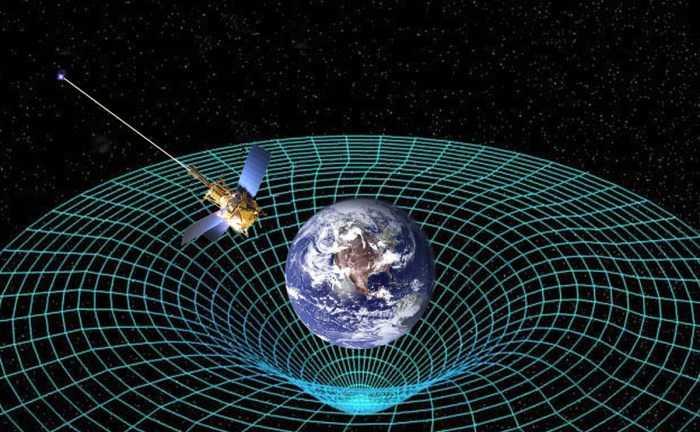
Einstein and the shape of spacetime
Albert Einstein held that space and time together made up the universe's fabric that could stretch and compress. Einstein suggested that the shape of spacetime is what gives rise to the force of gravity. A concentration of mass, like the earth or sun, bends space around it, like water that bends around the flow of a river. When other objects move closeby, they follow the curvature.
Einstein's field equations of general relativity, which show how matter and energy warp spacetime, gained acceptance when they successfully predicted the changes in Mercury's orbit.
56
260 reads
Gravity as a tool of discovery
The current description of gravity is so accurate that it has become a guide for cosmic discoveries.
American astronomers noticed in the 1960s that galaxies appear to rotate fast enough to spin-off stars. However, they did not whirl apart, and something seems to help them stick together. Most physicists now suspect that "dark matter" warps spacetime enough to keep galaxies and galaxy clusters intact.
51
256 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Homer Cordaro's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about books with this collection
The benefits of a bedtime routine
How to improve your sleep quality
How to create a relaxing sleep environment
Related collections
Similar ideas
1 idea
Theory of relativity
en.wikipedia.org
9 ideas
Why Gravity Is Not Like the Other Forces
quantamagazine.org
12 ideas
Einstein, Symmetry and the Future of Physics
quantamagazine.org
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates