5. Bernstein-Vazirani Algorithm
The Bernstein-Vazirani Algorithm was invented by Ethan Bernstein and Umesh Vazirani in 1992. It is a restricted version of the Deutsch–Jozsa algorithm.
The algorithm was created to solve a is
So, let’s just say that we are given a box . Hidden in the box is a secret number. This “secret number” is represented by six bits made up of 0’s and 1’s. We need to figure out what the “secret number” is.
Classically, a computer would find it most efficient to calculate the “secret number” by evaluating the function n times, where x = 2^i and i is the summation of 0, 1, … n-1.
55
190 reads
CURATED FROM
IDEAS CURATED BY
卐 || एकं सत विप्रा बहुधा वदन्ति || Enthusiast || Collection Of Some Best Reads || Decentralizing...
The idea is part of this collection:
Learn more about personaldevelopment with this collection
How to close the deal
How to handle objections
How to present your value to your employer
Related collections
Similar ideas to 5. Bernstein-Vazirani Algorithm
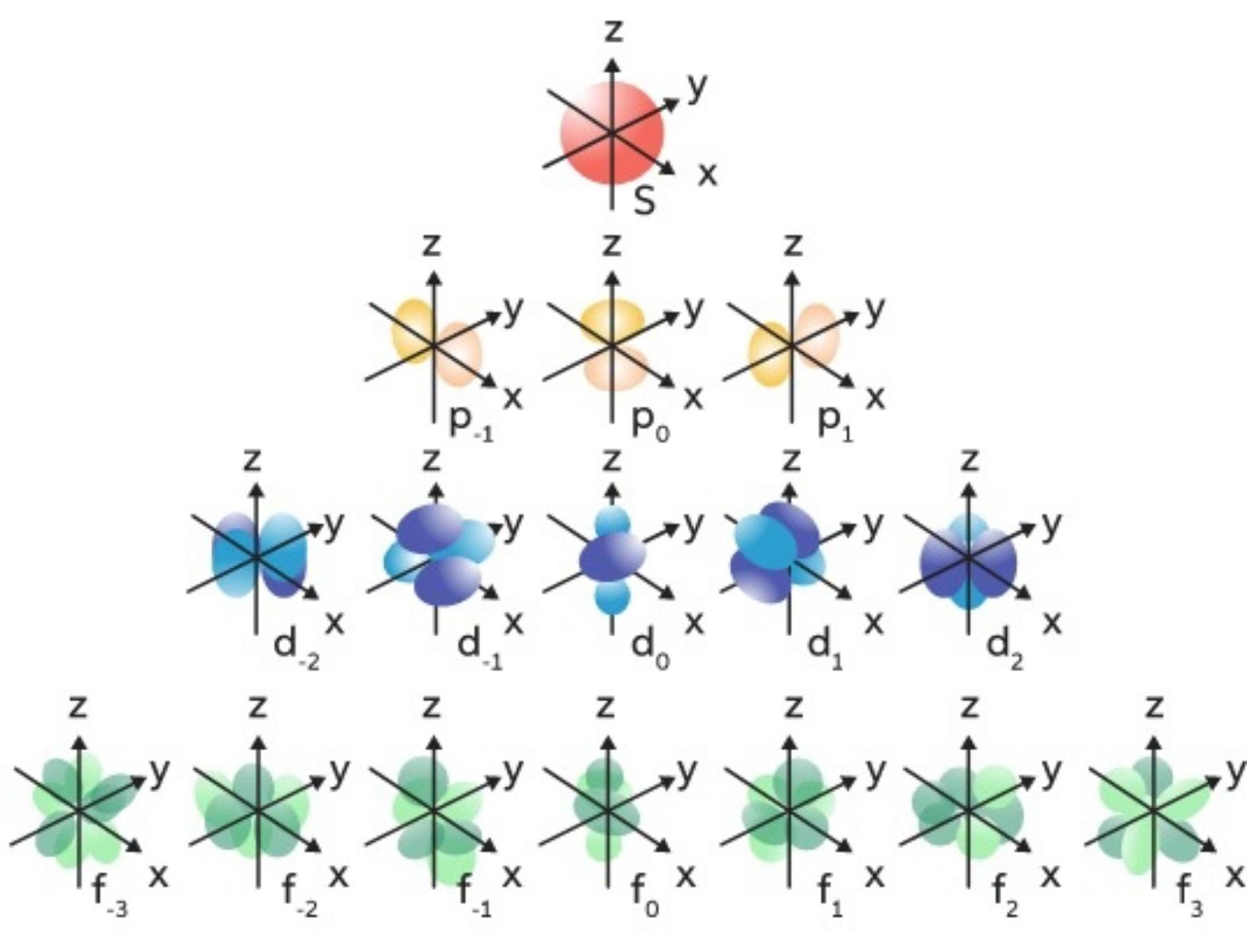
Magnetic quantum Numbers (mℓ)
Specifie the orientation in space of an orbital of a given energy (n) and shape (l). This number divides the subshell into individual orbitals which hold the electrons; there are 2l+1 orbitals in each subshell.
Every orbital capacity is 2 electrons
Magnetic ...
Mathematics of motivation
When Ivan Pavlov and his dogs led to the discovery of learned behaviour through repeated exposure, and Edward Thorndike discovered the Law of Effect that stated that rewarded behaviours tended to increase, many psychologists were impelled to separate psychology from armchair introspection and
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates