Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Background
If you’ve ever spent a night tossing and turning, you already know how you’ll feel the next day — tired, cranky, and out of sorts. But missing out on the recommended 7 to 9 hours of shut-eye nightly does more than make you feel groggy and grumpy.
The long-term effects of sleep deprivation are real.
It drains your mental abilities and puts your physical health at real risk. Science has linked poor slumber with a number of health problems
31
163 reads
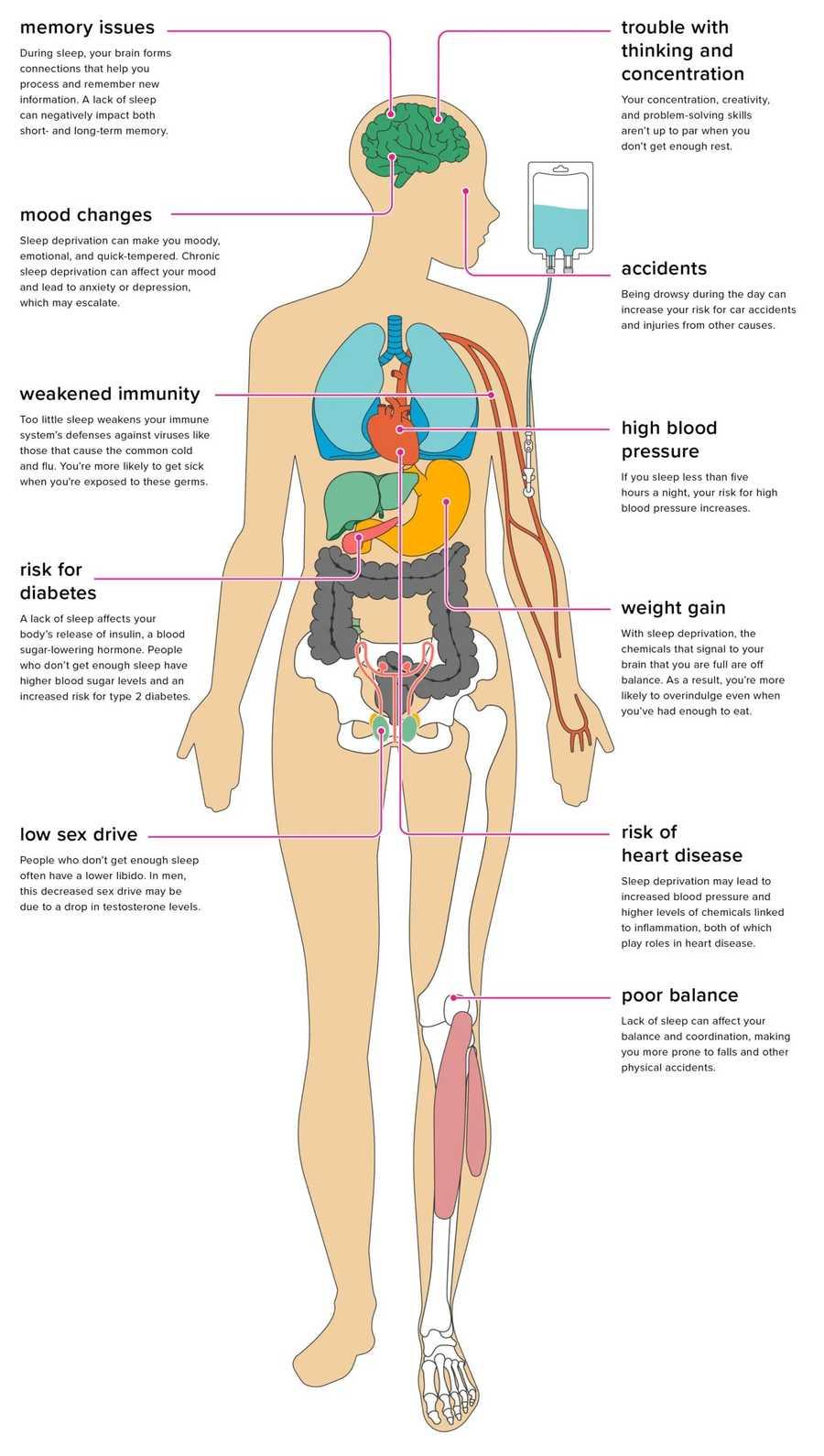
Image Of Sleep Deprivation Effects
Read on to learn the causes of sleep deprivation and exactly how it affects specific body functions and systems.
31
192 reads
Central Nervous System
Your central nervous system is the main information highway of your body. Sleep is necessary to keep it functioning properly, but chronic insomnia can disrupt how your body usually sends and processes information.
During sleep, pathways form between nerve cells (neurons) in your brain that help you remember new information you’ve learned. Sleep deprivation leaves your brain exhausted, so it can’t perform its duties as well, such as memory after studying
32
124 reads
Mood And Memory
You may also find it more difficult to concentrate or learn new things. The signals your body sends may also be delayed, decreasing your coordination and increasing your risk for accidents.
You may feel more impatient or prone to mood swings . It can also compromise decision-making processes and creativity.
If sleep deprivation continues long enough, you could start having hallucinations — seeing or hearing things that aren’t really there. Other psychological risks include:
impulsive behavior
anxiety
depression
paranoia
suicidal thoughts
32
98 reads
Microsleep
You may also end up experiencing microsleep during the day. During these episodes, you’ll fall asleep for a few to several seconds without realizing it.
Microsleep is out of your control and can be extremely dangerous if you’re driving. It can also make you more prone to injury if you operate heavy machinery at work and have a microsleep episode.
30
103 reads
Immune System
While you sleep, your immune system produces protective, infection-fighting substances like antibodies and cytokines. It uses these substances to combat foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses.
Certain cytokines also help you to sleep, giving your immune system more efficiency to defend your body against illness.
Sleep deprivation prevents your immune system from building up its forces. If you don’t get enough sleep, your body may not be able to fend off invaders, and it may also take you longer to recover from illness.
30
80 reads
Disease Risk
Long-term sleep deprivation also increases your risk for chronic conditions, such as diabetes mellitus and heart disease.
30
91 reads
Respiratory System
The relationship between sleep and the respiratory system goes both ways. A nighttime breathing disorder called obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can interrupt your sleep and lower sleep quality.
As you wake up throughout the night, this can cause sleep deprivation, which leaves you more vulnerable to respiratory infections like the common cold and flu . Sleep deprivation can also make existing respiratory diseases worse, such as chronic lung illness.
30
79 reads
Digestive System
Sleep deprivation is another risk factor for becoming overweight and obese. Sleep affects the levels of two hormones, leptin and ghrelin, which control feelings of hunger and fullness.
Leptin tells your brain that you’ve had enough to eat. Without enough sleep, your brain reduces leptin and raises ghrelin , which is an appetite stimulant. The flux of these hormones could explain nighttime snacking or why someone may overeat later in the night.
31
83 reads
Physical Activity
A lack of sleep can also make you feel too tired to exercise . Over time, reduced physical activity can make you gain weight because you’re not burning enough calories and not building muscle mass.
Sleep deprivation also causes your body to release less insulin after you eat. Insulin helps to reduce your blood sugar (glucose) level.
Sleep deprivation also lowers the body’s tolerance for glucose and is associated with insulin resistance. These disruptions can lead to diabetes mellitus and obesity
30
73 reads
Cardiovascular System
Sleep affects processes that keep your heart and blood vessels healthy, including those that affect your blood sugar, blood pressure , and inflammation levels. It also plays a vital role in your body’s ability to heal and repair the blood vessels and heart.
People who don’t sleep enough are more likely to get cardiovascular disease. One analysis linked insomnia to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke .
30
61 reads
Endocrine System
Hormone production is dependent on your sleep. For testosterone production, you need at least 3 hours of uninterrupted sleep, which is about the time of your first R.E.M. episode. Waking up throughout the night could affect hormone production.
This interruption can also affect growth hormone production , especially in children and adolescents. These hormones help the body build muscle mass and repair cells and tissues, in addition to other growth functions.
The pituitary gland releases growth hormone throughout each day, but adequate sleep and exercise also help the release of this hormone.
30
66 reads
Prevent Sleep Deprivation? 😴
Best way: ensure you get adequate sleep, recommended is 7-9 hours for adults aged 18 to 64.
Other ways:
- limit/ avoid daytime naps
- refrain from caffeine past noon/ at least a few hours prior to bedtime
- go to bed and wake up at the same time every day
- stick to your bedtime schedule in weekends and holidays
- spend an hour before bed doing relaxing activities, e.g read, meditate, or take a bath
- avoid heavy meals within a few hours of bedtime
- refrain from using electronic devices just before bed
- exercise regularly, but not in the evening hours close to bedtime
- reduce alcohol intake
31
77 reads
Most Common Types Of Sleep Disorders
- insomnia
- circadian rhythm disorders
- obstructive sleep apnea
- narcolepsy
- restless leg syndrome
31
96 reads
Ending
If you continue to have problems sleeping at night and are fighting daytime fatigue, talk to your doctor. They can test for underlying health conditions that might be getting in the way of your sleep schedule.
30
87 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
CURATOR'S NOTE
Recently, having not enough sleep made me search this up to inspire me to sleep better, no matter how busy I am- that's an issue with my time planning and not sleep deprivation. Otherwise it becomes one big cycle 🔄
“
M 's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about health with this collection
How to create a positive work environment
Techniques for cultivating gratitude and mindfulness at work
How to find purpose in your work
Related collections
Similar ideas
12 ideas
10 Top Health Benefits of Sleep
verywellhealth.com
3 ideas
Why sleep is so important for losing weight
theconversation.com
5 ideas
A dark night is good for your health
theconversation.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates