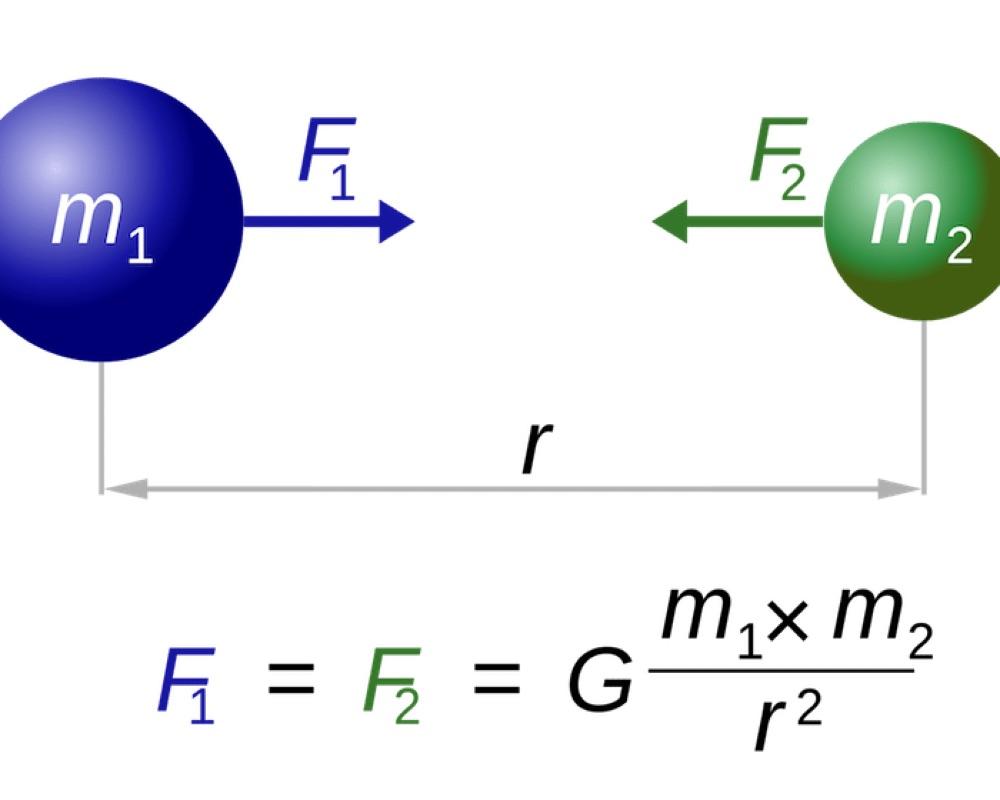Prince Rahul's Key Ideas from Six Easy Pieces
by Richard Phillips Feynman
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
21 ideas
·33.6K reads
104
5
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
“Everything we know is only some kind of approximation, because we know that we do not know all the laws as yet. Therefore, things must be learned only to be unlearned again or, more likely, to be corrected.”
RICHARD FEYNMAN
436
5.55K reads
Jiggling Motion In Atoms
- The jiggling motion is what we represent as heat: when we increase the temperature, we increase the motion.
- If we heat the water, the jiggling increases and the volume between the atoms increases, and if the heating continues there comes a time when the pull between the molecules is not enough to hold them together and they do fly apart and become separated from one another.
- Of course, this is how we manufacture steam out of water.
355
3.59K reads
Why We Blow The Soup To Cool It
- When a molecule leaves it is due to an accidental, extra accumulation of a little bit more than ordinary energy, which it needs if it is to break away from the attractions of its neighbors.
- Therefore, since those that leave have more energy than the average, the ones that are left have less average motion than they had before. So the liquid gradually cools if it evaporates.
- When they leave they take away heat; when they come back they generate heat.
- Hence, blow on soup to cool it!
352
3.03K reads
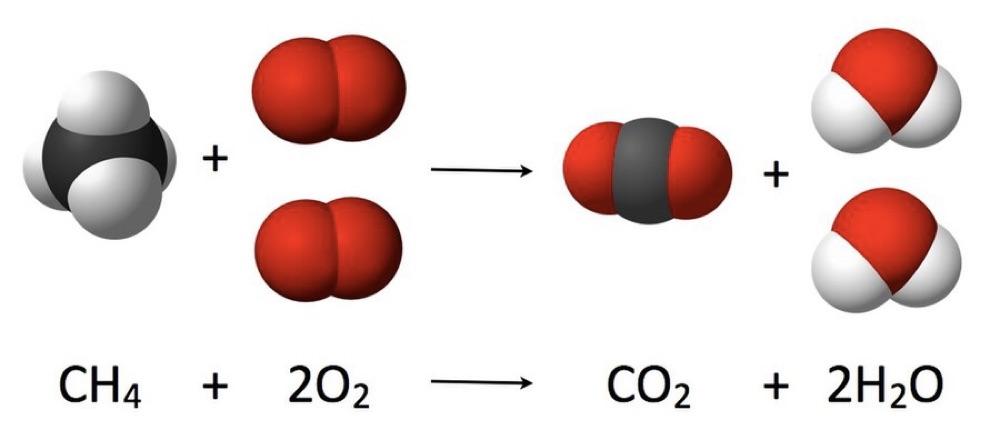
Chemical reactions
- A process in which the rearrangement of the atomic partners occurs is what we call a chemical reaction.
- The heat is ordinarily in the form of the molecular motion of the hot gas, but in certain circumstances it can be so enormous that it generates light. That is how one gets flames.
- If we look at very tiny particles (colloids) in water through amicroscope, we see a perpetual jiggling of the particles, which is the result of the bombardment of the atoms. This is called the Brownian motion.
349
2.15K reads
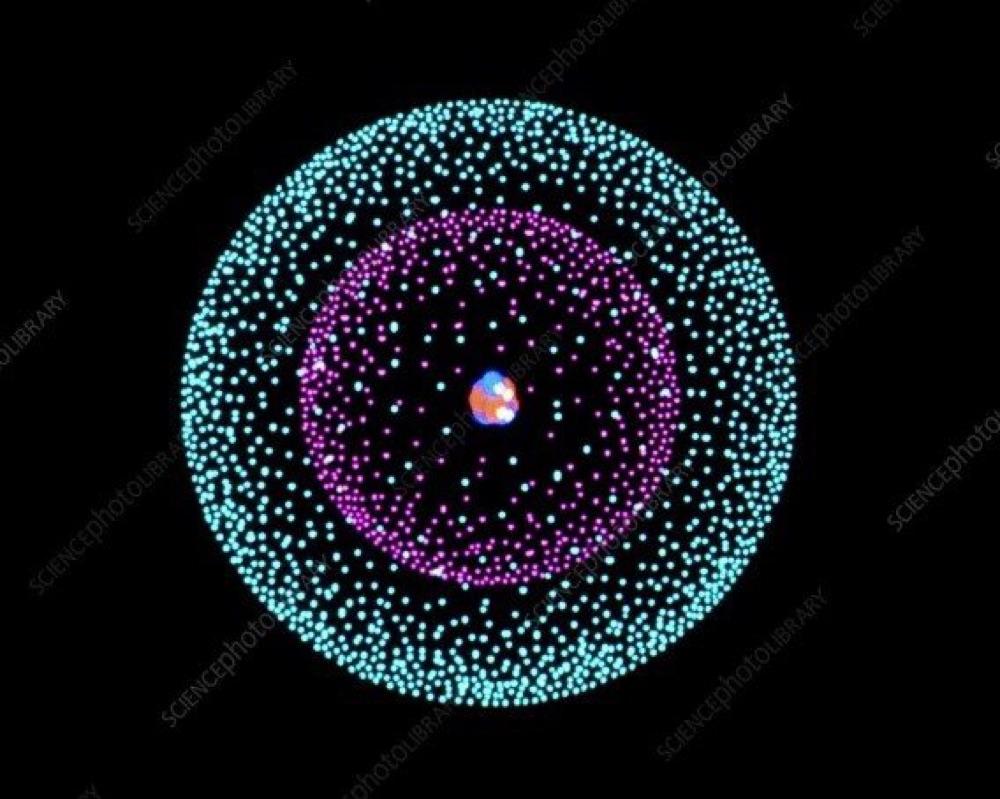
BASIC PHYSICS
- Nucleus consist of two kinds of particles, protons and neutrons, almost of the same weight and very heavy.
- The protons are electrically positive charged and the neutrons are neutral.
- An atom has a diameter of about 10^-8 cm. The nucleus has a diameter of about 10^-13 cm.
- If we have an atom with six protons inside its nucleus, and this is surrounded by six electrons , this would be atom number six in the chemical table, and it is called carbon.
- So the chemical properties of a substance depend only on the number of electrons.
352
1.87K reads
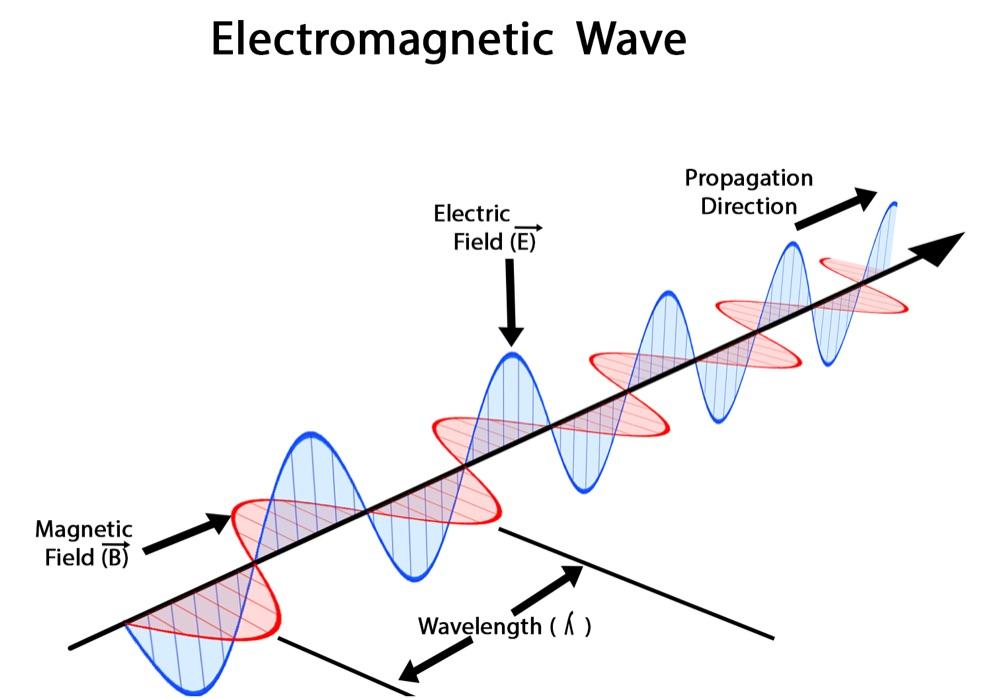
Electromagnetic Waves
- If we shake a charge back and forth more and more rapidly, and look at the effects, we get a whole series of different kinds of waves, which are all unified by specifying the number of oscillations per second.
- The electromagnetic field can carry waves; some of these waves are light, others are used in radio broadcasts, but the general name is electromagnetic waves. These oscillatory waves can have various frequencies.
- A changing electric field cannot exist without magnetism.
351
1.63K reads
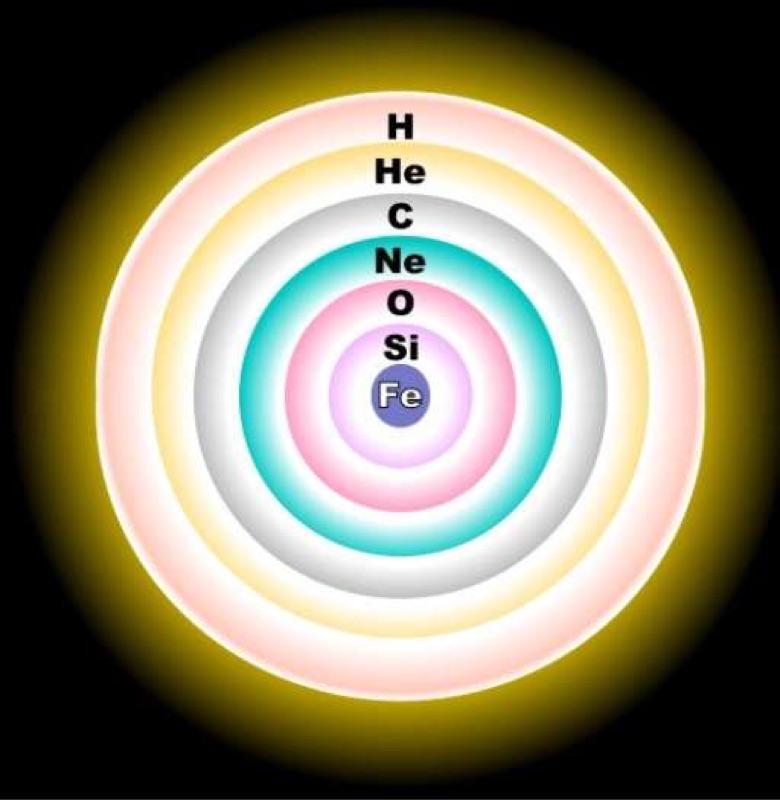
We Are Cooked From Stars ⭐️
- It is the nuclear “burning” of hydrogen which supplies the energy of the sun; the hydrogen is converted into helium.
- Furthermore, ultimately, the manufacture of various chemical elements proceeds in the centers of the stars, from hydrogen.
- The stuff of which we are made was “cooked” once, in a star, and spit out. 😮
354
1.57K reads
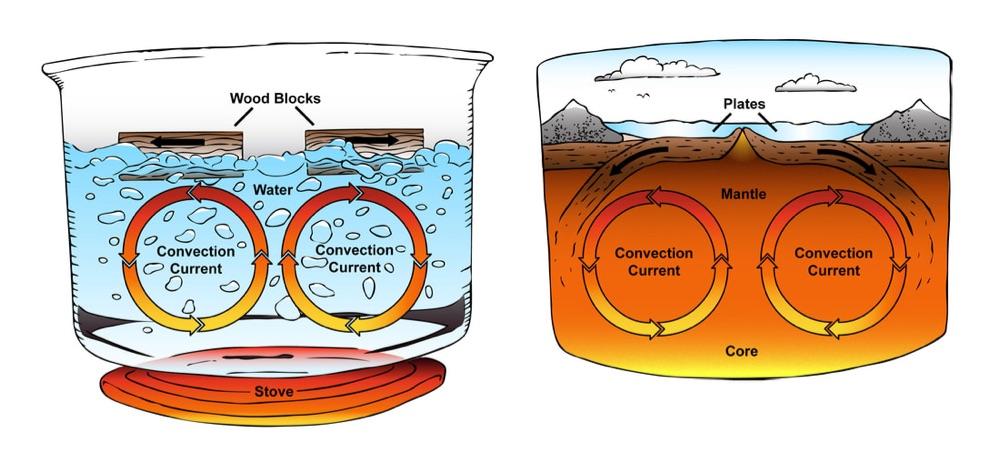
How Mountains, Volcanoes And Earthquake Are Made?
- The theory is that there are currents inside the earth—circulating currents, due to the difference in temperature inside and outside—which, in their motion, push the surface slightly.
- Thus if there are two opposite circulations next to each other, the matter will collect in the region where they meet and make belts of mountains which are in unhappy stressed conditions, and so produce volcanoes and earthquakes.
348
1.44K reads
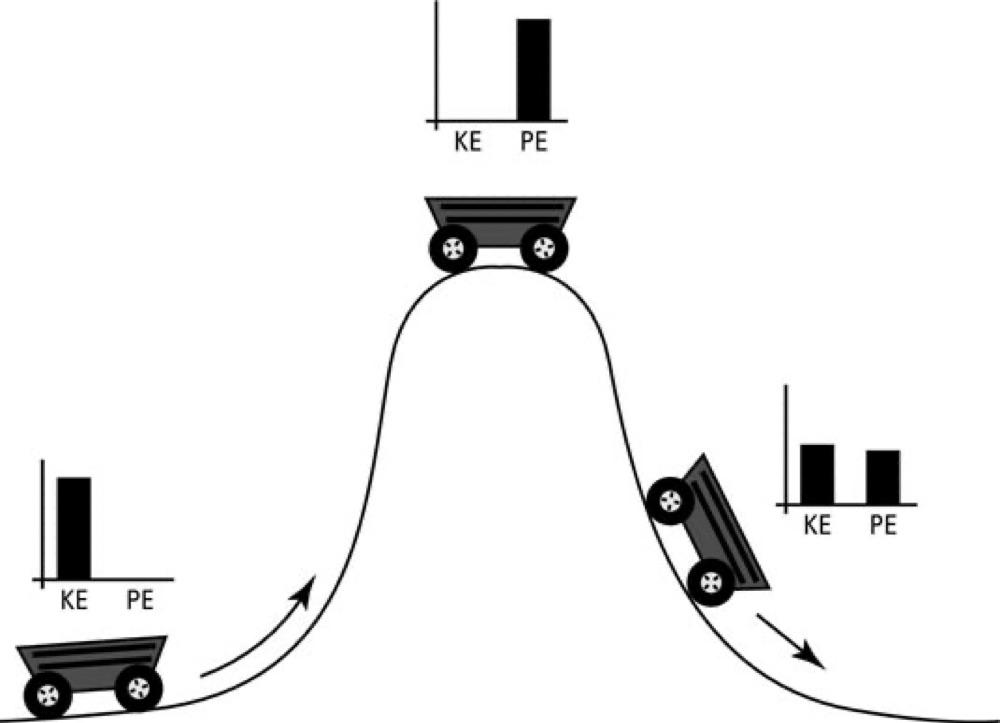
CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
- The energy has a large number of different forms, and there is a formula for each one. These are gravitational energy, kinetic energy, heat energy, elastic energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, radiant energy, nuclear energy, mass energy.
- If we total up the formulas for each of these contributions, it will not change except for energy going in and out.
349
1.22K reads
Types Of Energy
- Heat energy= kinetic energy of atoms—internal motion.
- Electrical energy, which has to do with pushing and pulling by electric charges.
- Radiant energy, the energy of light, which we know is a form of electrical energy because light can be represented as wigglings in the electromagnetic field.
- Chemical energy, the energy which is released in chemical reactions.
- Nuclear energy, the energy which is involved with the arrangement of particles inside the nucleus
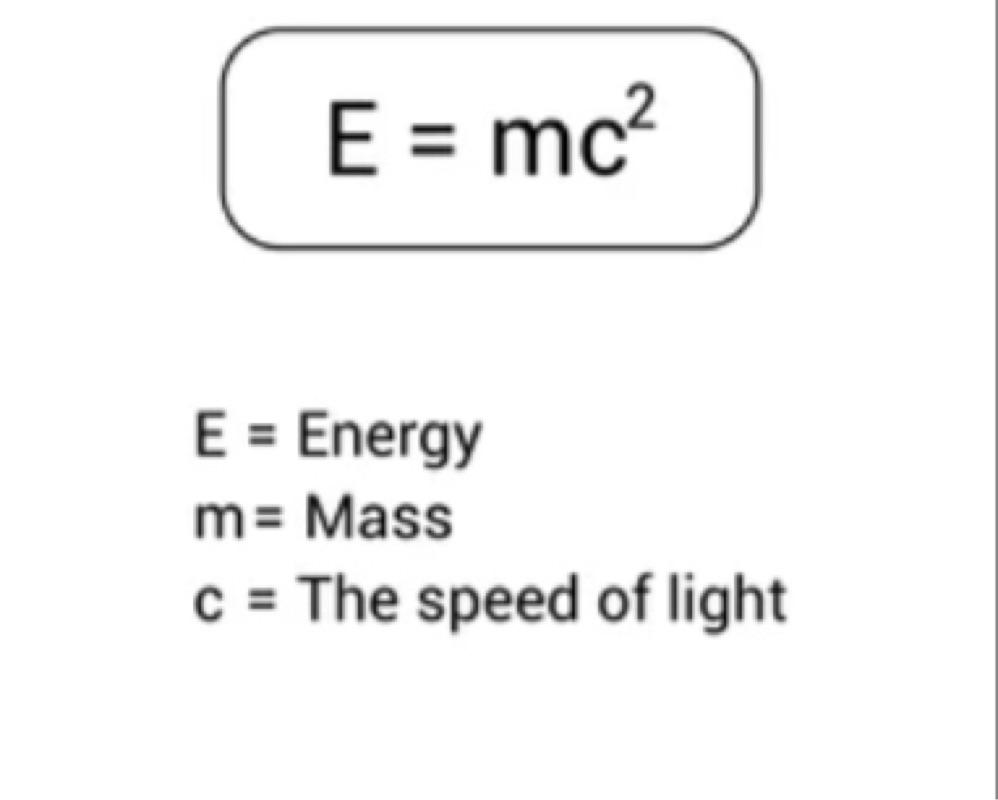
- An object has energy from its sheer existence.(E=mc^2)
353
1.13K reads
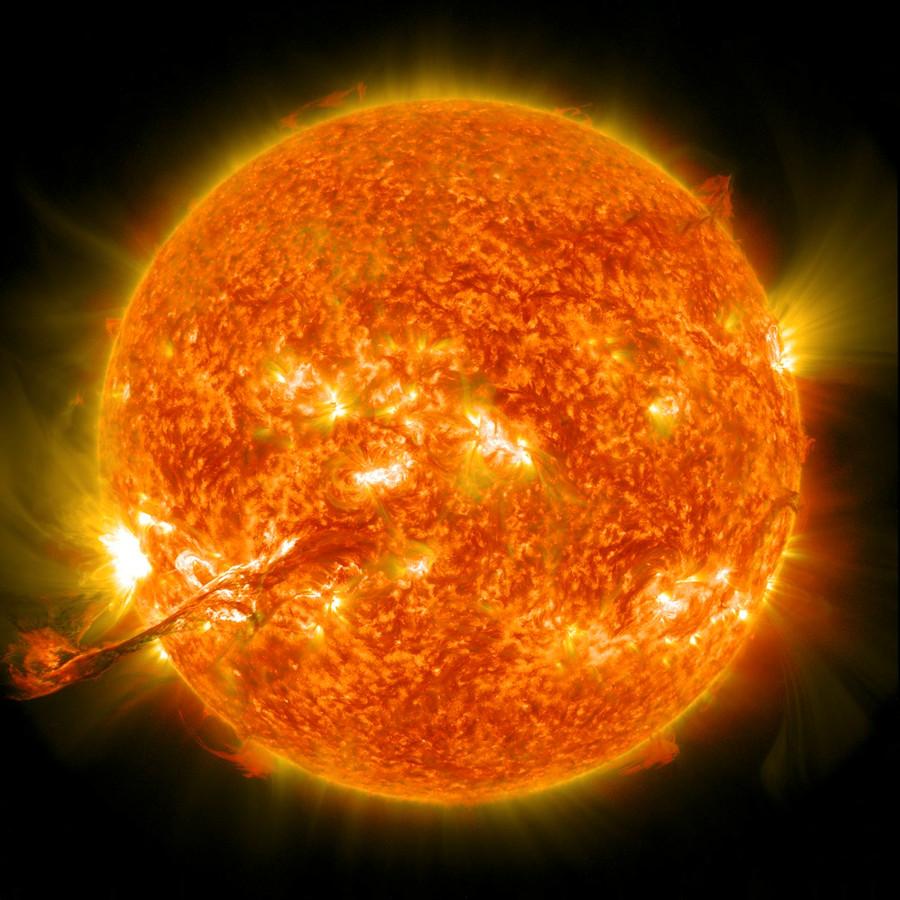
Sun ☀️ - The Ultimate Source Of Energy
- Our supplies of energy are from the sun, rain, coal, uranium, and hydrogen.
- The sun makes the rain, and the coal also, so that all these are from the sun.
- Although energy is conserved, nature does not seem to be interested in it; she liberates a lot of energy from the sun, but only one part in two billion falls on the earth. Nature has conservation of energy, but does not really care; she spends a lot of it in all directions.
347
1.06K reads
THE THEORY OF GRAVITATION
What is this law of gravitation? It is that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which for any two bodies is proportional to the mass of each and varies inversely as the square of the distance between them.
F=GMm/r^2
where G=6.6743 × 10-11 m^3 kg^-1 s^-2
346
1.02K reads
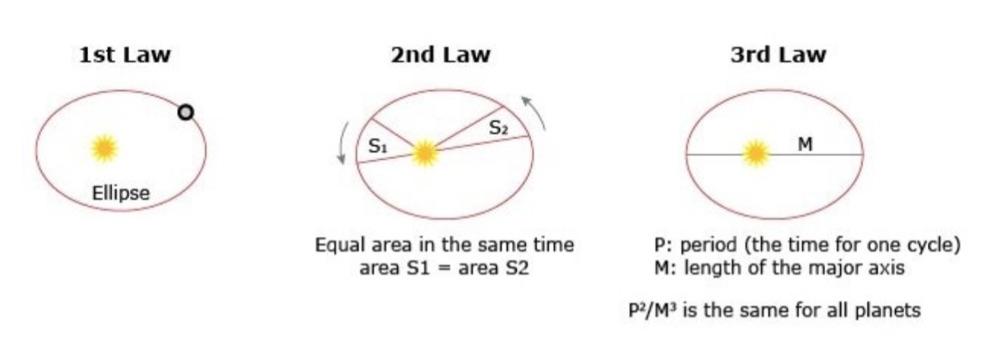
Kepler’s Laws
- Each planet moves around the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus.
- The radius vector from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time.
- The squares of the periods of any two planets are proportional to the cubes of the semimajor axes of their respective orbits: T ∝ a^3/2.
346
1.02K reads
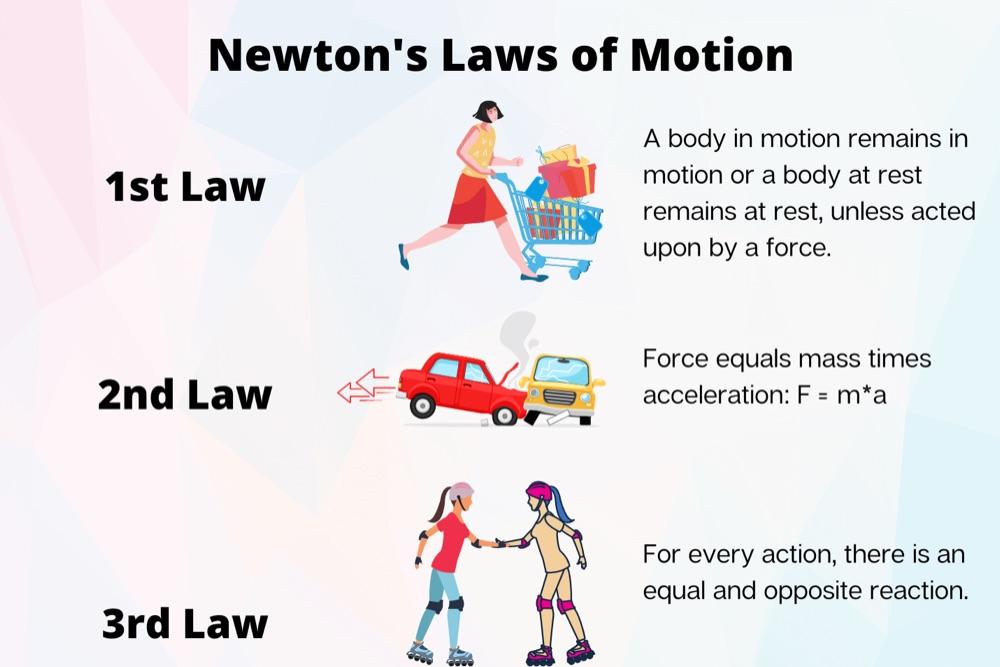
Newton’s Laws Of Motion
- Principle of inertia—if something is moving, with nothing touching it and completely undisturbed, it will go on forever, coasting at a uniform speed in a straight line.
- Newton modified this idea, saying that the only way to change the motion of a body is to use force. Newton thus added the idea that a force is needed to change the speed or the direction of motion of a body. The force is proportional to the mass times the acceleration.
- Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
349
919 reads
Why is the earth round?
That is easy; it is due to gravitation. The earth can be understood to be round merely because everything attracts everything else and so it has attracted itself together as far as it can! If we go even further, the earth is not exactly a sphere because it is rotating, and this brings in centrifugal effects which tend to oppose gravity near the equator.
344
955 reads
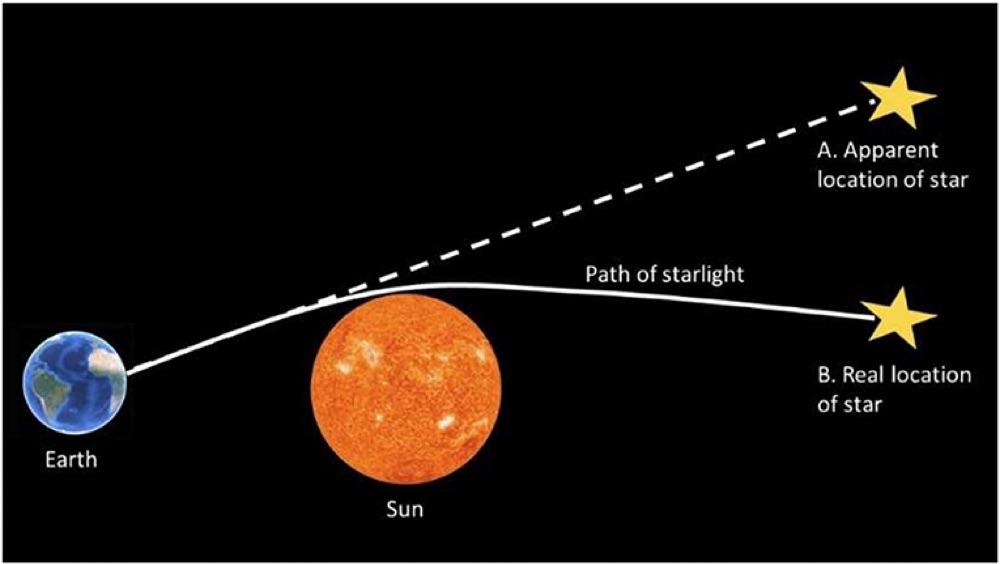
Einstein’s Theory Of Relativity
- In the Einstein relativity theory, anything which has energy has mass—mass in the sense that it is attracted gravitationally.
- Even light, which has an energy, has a “mass.” When a light beam, which has energy in it, comes past the sun there is an attraction on it by the sun.
- Thus the light does not go straight, but is deflected.
- During the eclipse of the sun, for example, the stars which are around the sun should appear displaced from where they would be if the sun were not there, and this has been observed.
349
962 reads
Quantum Electrodynamics
- The new view of the interaction of electrons and photons that is electromagnetic theory, but with everything quantum-mechanically correct, is called quantum electrodynamics.
- It predicted another very remarkable thing: besides the electron, there should be another particle of the same mass, but of opposite charge, called a positron, and these two, coming together, could annihilate each other with the emission of gamma rays.
345
889 reads
Wave-Particle Duality
- “Quantum mechanics” is the description of the behavior of matter in all its details and, in particular, of the happenings on an atomic scale.
- Historically, the electron, for example, was thought to behave like a particle, and then it was found that in many respects it behaved like a wave. So it really behaves like neither.
- One of the consequences is that things which we used to consider as waves also behave like particles, and particles behave like waves; in fact everything behaves the same way. There is no distinction between a wave and a particle.
347
817 reads
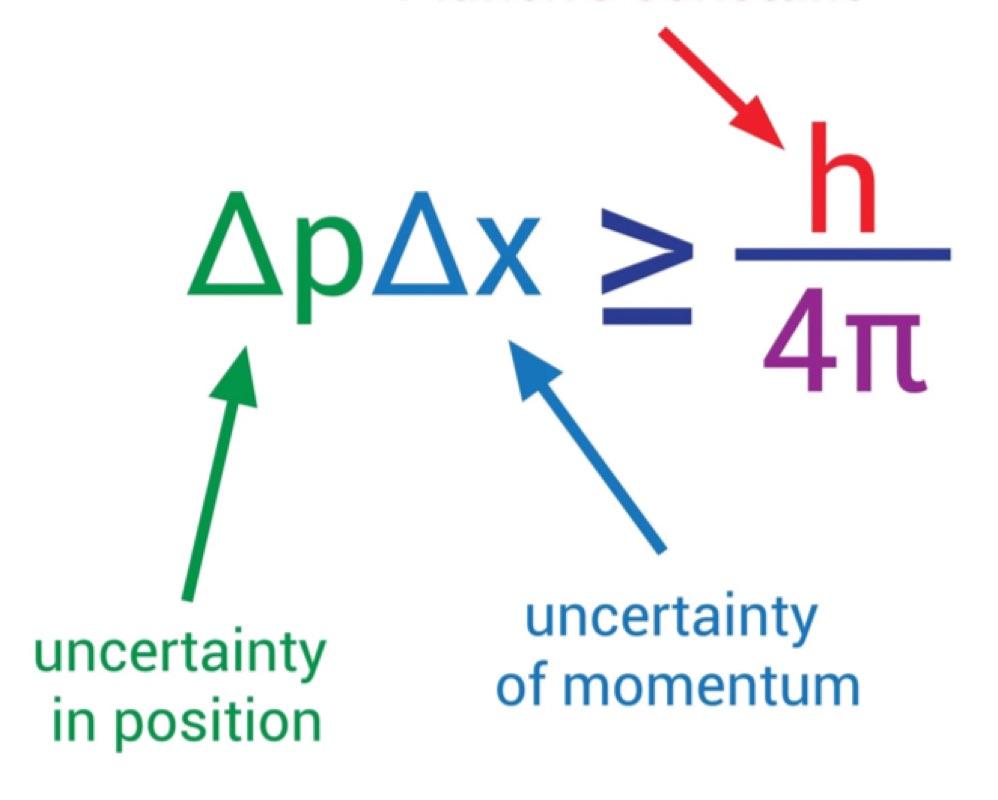
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
- “It is impossible to design an apparatus to determine which hole the electron passes through, that will not at the same time disturb the electrons enough to destroy the interference pattern.”
- “One cannot know both where something is and how fast it is moving.”
- The uncertainty of the momentum and the uncertainty of the position are complementary, and the product of the two is bounded by a small constant.
- We can write the law like this: Δx Δp ≥ h/4π.
346
844 reads
Even At 0 Kelvin, Atoms Jiggle 🤯
When a crystal is cooled to absolute zero (0 Kelvin) , we said that the atoms do not stop moving, they still jiggle. Why?
- If they stopped moving, we would know where they were and that they had zero motion, and that is against the uncertainty principle. We cannot know where they are and how fast they are moving, so they must be continually wiggling in there!
Zero Mass: The fact that a particle has zero mass means, in a way, that it cannot be at rest. A photon is never at rest; it is always moving at 186,000 miles a second.
348
829 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
The more one seeks to rise into height and light, the more vigorously do ones roots struggle earthward, downward, into the dark, the deep — into evil.
CURATOR'S NOTE
Richard Phillips Feynman (May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, as well as his work in particle physics for which he proposed the parton model. For his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 jointly with Julian Schwinger and Shin'ichirō Tomonaga.
“
Prince Rahul's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about books with this collection
How to create customer-centric strategies
The importance of empathy in customer success
The impact of customer success on business growth
Related collections
Different Perspectives Curated by Others from Six Easy Pieces
Curious about different takes? Check out our book page to explore multiple unique summaries written by Deepstash curators:
1 idea
Amarnath K's Key Ideas from Six Easy Pieces
Richard Phillips Feynman
Discover Key Ideas from Books on Similar Topics
7 ideas
Epistemology and Probability
Arkady Plotnitsky
20 ideas
Lost Knowledge of the Ancients
Glenn Kreisberg
3 ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates