What is Ethereum Gas? [The Most Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide Ever!]
Curated from: blockgeeks.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
9 ideas
·1.52K reads
10
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
From Bitcoin to Smart Contracts
Bitcoin created a decentralized monetary system which can transfer money from one person to another. That only allowed for monetary transactions, there was no way to add conditions to those transactions:
Alice can send Bob 5 BTC, but she couldn’t tell Bob that he will get the money only if he performed certain tasks.
These conditions are a smart contract: self-executing with specific instructions written in its code which get executed when certain conditions are made.
Say Alice wants to buy a house. The seller will receive the funds only if property rights are cleared and after the rights have been transferred over.
53
477 reads
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
Ether is made of a blockchain (an immutable database) and a world decentralised computer (EVM), a virtual machine in which all the smart contracts function in Ethereum.
The EVM is a simple yet powerful Turing Complete 256-bit virtual machine. Turing Complete means that given the resources and memory, any program executed in the EVM can solve any problem.
43
197 reads
The attributes of a Smart Contract
A smart contract functionality needs to be 3 things:
Deterministic: it gives the same output to a given input every single time.
Terminable: contracts by definition, must be capable of termination in a given time limit.
Isolated: a contract will be kept isolated in a sandbox to save the entire ecosystem from negative effects.
42
157 reads
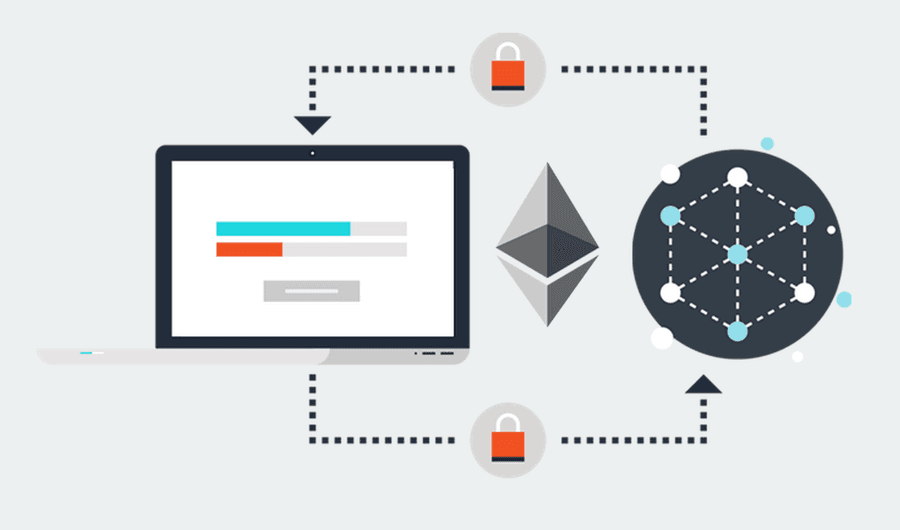
Ethereum Gas
Gas is a unit that measures the amount of computational effort that it will take to execute certain operations. Each and every line of code in an Ethereum smart contract requires a certain amount of gas to be executed.
Suppose you are going on a road trip:
- You go to the gas station & specify how much gas you want to fill up in your car.
- You get that gas-filled up in your car.
- You pay the gas station the amount of money you owe them for the gas.
In Ether world:
- Driving the car is the smart contract.
- The gas is well….gas.
- The gas station is your miner.
- The paid money is miner fees.
41
148 reads
Purpose of Ethereum Gas system
Incentivization. Like any proof-of-work peer-to-peer system, Ethereum is heavily dependent on the computational power of its miners. More miners, more computational power, more secure and fast the system.
To attract more miners Ether needs to make the system as profitable and alluring as possible for the miners. In Ethereum, there are two ways that miners can earn money:
- By mining blocks and getting block rewards.
- By running smart contracts. The gas system allows them to charge a certain fee for doing so.
40
113 reads
Ethereum as electricity
If bitcoin is digital gold, Ethereum is alike the power grid, powering an ecosystem of worldwide decentralized applications.
The gas is the metering system for the consumed power. And ETH is the currency used to pay for running the software and maintaining the network.
41
130 reads
Gas Limits & Gas Price
To get an operation done in Ethereum, the sender of the transaction must specify a gas limit before they submit it to the network & a gas price:
- The gas limit is the maximum amount of gas the sender is willing to pay for this transaction. If an operation has LOW gas, then the miners won’t even pick it up because it doesn’t have enough gas to finish the computation.
- The price is the amount of gas the sender is willing to pay. If an operation has LOW fees, then it might have just enough gas to cover it but still, the miners won’t be chomping at the bits to pick it up because an operation with low fees isn’t economically appealing for them.
41
101 reads
Ethereum Gas Refund
If an operation runs out of gas, then it is reverted back to its original state like nothing actually happened, however, the operation generator must STILL pay the miners the fee for their computational costs and the operation gets added to the blockchain (even if it has not been executed).
40
88 reads
Ethereum Gas is EXPENSIVE
When two numbers are added a million times in Ethereum it costs ~$26.55 in fees. On Amazon AWS system it costs $0.000000066.
This means that computation in Ethereum is 400 million times more expensive!
However:
- A well-written contract would likely move such computational complexity off-chain and deal more with updating state in the contract.
- A well-written contract would likely move such computational complexity off-chain and deal more with updating state in the contract.
41
114 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Life-long learner. Passionate about leadership, entrepreneurship, philosophy, Buddhism & SF. Founder @deepstash.
Vladimir Oane's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about crypto with this collection
How to start a successful business
How to build a strong team
How to market your business
Related collections
Similar ideas
7 ideas
Ethereum upgrades: A beginner’s guide to ETH 2.0
cointelegraph.com
6 ideas
Ethereum is the future of our economics
notboring.co
8 ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates
![What is Ethereum Gas? [The Most Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide Ever!]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fd3t70bohx4vuj7.cloudfront.net%2Ft16B__ifyHsbzZanrXmC9w9Tz-66h-V7Xs2_yaU98-Q%2Fresize%3Afill%3A600%3A0%2Fgravity%3Asm%2Fquality%3A90%2FaHR0cHM6Ly9pbWFnZXMudW5zcGxhc2guY29tL3Bob3RvLTE2NDEzNzA2MDQzNzMtYTgxYWJkNmNlYzJlP2Nyb3A9ZW50cm9weSZjcz10aW55c3JnYiZmaXQ9bWF4JmZtPWpwZyZpeGlkPU1ud3hNRGN4TVRWOE1Id3hmSE5sWVhKamFId3hmSHhYYUdGMEpUSXdhWE1sTWpCRmRHaGxjbVYxYlNVeU1FZGhjeVV6UmlVeU1DVTFRbFJvWlNVeU1FMXZjM1FsTWpCRGIyMXdjbVZvWlc1emFYWmxKVEl3VTNSbGNDMUNlUzFUZEdWd0pUSXdSM1ZwWkdVbE1qQkZkbVZ5SlRJeEpUVkVmR1Z1ZkRCOGZIeDhNVFkyT0RZeE9UQTJNdyZpeGxpYj1yYi00LjAuMyZxPTgwJnc9NDAw&w=3840&q=75)