Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
“Startup success is not a consequence of good genes or being in the right place at the right time. Startup success can be engineered by following the right process, which means it can be learned, which means it can be taught.”
ERIC RIES
1.44K
15.8K reads
Why Do startups fail ??
According to Eric Ries, there are two main reasons for startup failures:
- Traditional management methods do not work for a highly uncertain startup
- The second reason may seem completely opposite to the first one
- seeing that traditional management approaches do not work, entrepreneurs let things go by themselves and are guided by the "just do it" principle.
Even such a chaotic and unpredictable phenomenon as a startup (can) should be managed. And this is what we document in this stash
1.34K
9.52K reads
What is a Lean Startup?
- Many people share the opinion that entrepreneurial success is a combination of perseverance, intelligence, a good product, and the luck of being in the right place at the right time.
- Routine, small things, and boring details do not matter.
- it is nothing more than just a myth, partly imposed by pop culture.
It's exactly the boring little things that are critical to a startup's success.
1.39K
8.76K reads
Five Principles of the Lean Startup:
- Entrepreneurs are everywhere.
- Irrespective of the size of the venture if you guys are working on a product that solves a problem in a new and better way then you are entrepreneurs
- Entrepreneurship is management. Startups need a new type of management that will handle the conditions of extreme uncertainty.
- Confirmation by facts. A startup needs continuous learning through a scientific approach and empirical hypothesis testing.
1.41K
7.47K reads
Continuation of the above topic
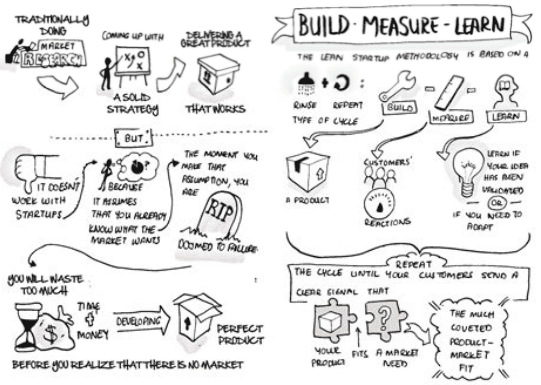
- The cycle "build-measure-learn". First, create an MVP of the product, evaluate consumers' reaction,
- And then decide whether to continue on the chosen course or change your direction.
- Innovation Accounting. This is what is commonly referred to as dull detail.
- But accounting for innovations is essential to improving startup performance.
- Innovation Accounting is a system of criteria and indicators that help evaluate a startup's success (or failure).
1.38K
6K reads
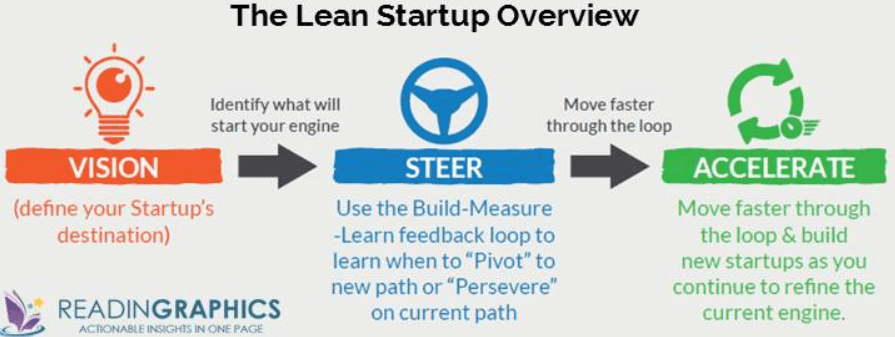
- Instead of making complex plans based on many assumptions,
- you can make constant adjustments with a steering wheel called the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop.
- Startups are greatly analogous to driving a car to our office as we know the destination but we may change the routes according to our ease
1.35K
6.11K reads
How to determine what people need without wasting time and money
- As an entrepreneur, the core aim is to build a product or a solution to a burning problem
- And even though the user experience matters a lot but mainly what matters is whether your product is solving the core itch of the user
- And in every solution, there are a set of assumptions that we base our solution upon
- So to test those key assumptions build an MVP and test it with the people who need it the most
- Learning from their feedback and keep on improving the product or service
- Which is a way better approach than directly building a great product that no one needs
1.4K
4.18K reads
How to go into practice?
The feedback that a startup receives in its experiments
can be qualitative (which product options they like and which they don't)
or quantitative (how many customers use the product, the number of registered users).
The Lean Startup concept is based on a Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop.
The most important challenge of startup management is to strive to reduce the feedback cycle time. But all the elements of this cycle deserve equal attention.
1.33K
3.61K reads
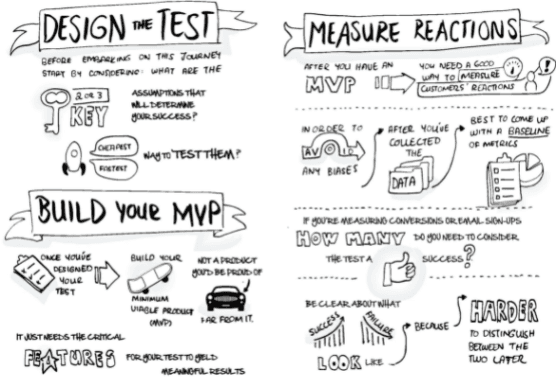
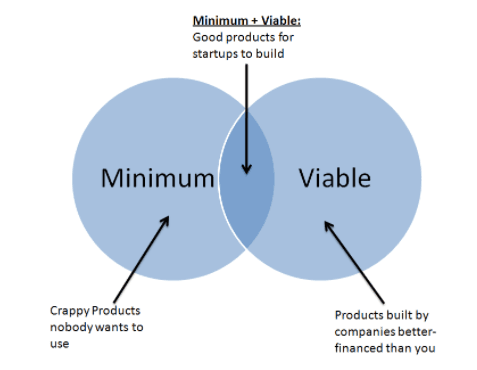
Build #step-1
- For a startup, you need to start creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) as soon as possible.
- MVP is a version of a product that allows you to start the Build-Measure-Learn cycle with minimal effort, spending as little development time as possible.
- Such a crude product may be devoid of the options that will be most appreciated by customers in the future.
- Still, at the same time, enough to be usable and understandable by first users.
1.34K
3.31K reads
Types of MVP
- Video MVP {A video that explains your product or solution to measure traction}
- The Concierge MVP {idea that when you’re just starting out you don’t need to be able to handle thousands of customers, you just need to make one customer happy} great way to validate your hypothesis
- The Wizard of Oz MVP. In a Wizard of Oz MVP customers believe they are interacting with your technology product; however, the reality is that behind the scenes a human is doing the work
- Landing Page MVP: make a landing page with an explanation of your solution if people are showing interest and interacting its a good sign
1.39K
2.78K reads
Measure #step-2
- "Measure" means determining whether the efforts to create a product are producing the desired results.
- And this is the key difference between Lean Startup valuation and standard methods, where deadlines and budget utilization are assessed,
- but it may not be considered that the startup has created a useless product.
- The primary assessment method in a Lean startup is innovation accounting.
- This is a quantitative approach that allows us to find out how successful our attempts to trigger the growth mechanism are. It also helps identify intermediate learning outcomes.
1.32K
2.56K reads
Learn #step-3
- It means to figure out whether the chose path lead to success or we need to pivot
- When an entrepreneur sees that the chosen path does not lead to success,
- he must be ready to find a new strategic hypothesis and stop spending money on following the unnecessary direction.
1.32K
2.42K reads
Genchi Genbutsu
- Genchi Genbutsu, which is translated as "go and see." This principle is guided, in particular, in Toyotа.
- A manager responsible for the development of the Sienna minivan travelled around all the US states and talked with families,
- finding out which minivan Americans want to see and taking into account their children's opinion, which had a positive effect on the sales of this car brand.
- There are always people behind the numbers.
- You need to get knowledge first-hand, literally going out into the street.
1.33K
2.3K reads
Do what scares perfectionists
- It is not uncommon for entrepreneurs to first create a product and then find out consumers' reactions. But the point is to do the opposite.
- The goal of creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is to start learning and testing in practice as soon as possible.
- An MVP is needed to test the hypotheses of entrepreneurs. It should not be perfect. It should be quality enough to attract the first customers, but no more.
1.33K
2.33K reads
Innovation accounting
- As we have already mentioned, Innovation accounting is a systematic approach to figuring out if you are making progress and getting evidence from the facts.
- It is an alternative to the traditional reporting system for companies operating in conditions of uncertainty.
- This is a new type of reporting system that allows you to assess whether changes lead to improvements or not.
- Keeping track of innovation allows startup founders to make sure they are actually getting a business going.
- You need to start by turning leaps of faith into a working financial model.
1.3K
2K reads
Three stages of innovation accounting:
1. Create MVP and get feedback to understand the real state.
2. Try to bring metrics closer to ideal ones. It can take a lot of trying.
3. Decide whether to move in the same direction or make a pivot.
If you are close to the ideal metrics, you need to move in the same direction.
1.32K
1.95K reads
Cohort analysis
- One of the most important analysis tools for a startup is Cohort analysis.
- It may sound complicated, but it is based on one simple premise.
- Rather than looking at aggregate metrics such as total income and total customers,
- We should measure the metrics separately for each consumer group that interacts with the product independently of the rest of the groups. Each such group is called a cohort.
- For the techies, we are talking about A/B testing
1.33K
1.83K reads
Vanity metrics
- If nobody uses your product, then optimization or marketing will make no sense.
- A startup must be very clear about making clear and well-founded predictions to prove that a good business can be built with the product.
- The necessary indicators are often replaced by those that look nicer but are useless ("vanity metrics").
- These metrics usually include ad views, page visits, app installs, and more.
- Real metrics should prove the value of your project, that it really solves user problems.
1.31K
1.73K reads
Key aspects of Innovation Accounting
1. Effective indicators. show what needs to be done to get the results you want. They help to learn from the results of their actions.
2. Simplicity of presentation. Reports should be presented simply and clearly. It is worth remembering indicators are the results of people's work.
3. Data Verification and accountability.
1.29K
1.63K reads
When should you make a pivot?
- When it becomes clear that the initially chosen path will not lead to success,
- the entrepreneur is required to make a pivot - to radically change the strategy, create and test a new hypothesis about the product.
- The pivot's essence is to take into account everything that you have learned earlier, but at the same time radically change the strategy to get even more grounded knowledge.
- It is a combination of the scientific method of hypothesis testing and vision, intuition, and creativity.
1.3K
1.47K reads
Startup runway
- if a startup has a million dollars in the bank and spends $100k per month, its runway is 10 months.
- Based on this definition, the "runway" can be extended in two ways: by reducing costs or raising additional funding.
- However, Eric Ries suggests defining the runway in a different way - through the number of pivots that a startup can make.
- Then, to extend it, you need to learn how to make turns as quickly as possible.
- The need to make a pivot is indicated by a decrease in the effectiveness of product experiments.
1.31K
1.97K reads
How to get traction?
Small batch approach
The Lean Startup methodology is based on a small batch approach, borrowed from the concept of lean manufacturing.
- When working in small batches, the finished product is produced every few seconds.
- When working in large batches, all the finished goods are produced simultaneously, at the very end.
- Imagine what this means when it comes to hours, days, weeks.
- What if a customer suddenly decides they don't need a product?
- Would we like to know about this earlier? In the small batches approach, this risk is minimized.
1.29K
1.51K reads
“The engine of growth is the mechanism that startups use to achieve sustainable growth. I use the word sustainable to exclude all one-time activities that generate a surge of customers but have no long-term impact, such as a single advertisement or a publicity stunt that might be used to jump-start growth but could not sustain that growth for the long term.”
1.29K
3.68K reads
1. The sticky engine of growth
- The rules that govern sticky growth are pretty simple: if the acquisition rate exceeds the loss rate, then the popularity of the product rises. Therefore, companies need to track consumer losses.
1.3K
1.67K reads
2. Viral engine of growth.
- It's called the viral loop, and its speed is determined by the viral rate.
- The higher this coefficient, the faster the product will gain popularity.
- The viral ratio shows how many more customers each new customer can bring.
- Each of his friends is also a potential client, and he can also bring his friends.
- If the viral rate is 1, then only 1 in every 10 customers will bring a friend with them.
- Such a cycle is not viable. Let's say 100 clients come to the company.
- They will bring 10 friends with them. These 10 friends will bring only one person, and this will end the cycle.
1.31K
1.39K reads
3. Paid engine of growth.
- For a company to grow steadily over a long time using a paid-growth tool, it needs a differentiated ability to 'monetize' a particular group of users.
- For example, at IMVU (Ries' ex-company), this was due to introducing the ability to get off funds from mobile phones, which helped the company attract more customers than competitors who focused only on bank cards.
1.28K
1.45K reads
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The lean startup is developing a product based on the expressed desires of the market.
- The lean startup uses validated learning, which is a process by which companies assess consumer interest.
- Lean startup methods focus heavily on customer-related information such as customer churn rate, lifetime customer value, and product popularity.
- In lean startup practices, experimentation is favored more than adherence to a rigid plan.
- Lean startup standards will involve releasing a small form or early concept products to assess the customer reaction to the product.
1.31K
1.38K reads
Adaptation
- A startup cannot afford to operate without a system.
- To be successful, a startup needs to be an adaptive organization in which processes and actions are quickly and automatically adjusted in response to reality.
- In addition to the speed, which was mentioned above, a startup needs to have its regulators, with which it can find the pace it needs.
1.31K
1.66K reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
We are just another couple of engineering students who love to explore new ideas in the fields of Tech, Productivity, Self improvement & Entrepreneurship
Curious about different takes? Check out our The Lean Startup Summary book page to explore multiple unique summaries written by Deepstash users.
Learnsters 's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about books with this collection
How to start a successful business
How to build a strong team
How to market your business
Related collections
Different Perspectives Curated by Others from The Lean Startup
Curious about different takes? Check out our book page to explore multiple unique summaries written by Deepstash curators:
8 ideas
6 ideas
16 ideas
Discover Key Ideas from Books on Similar Topics
6 ideas
This is How Effective Leaders Move Beyond Blame
firstround.com
14 ideas
Top Hacks from a PM Behind Two of Tech's Hottest Products
review.firstround.com
5 ideas
Why leadership-development programs fail
mckinsey.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates