States of Consciousness
Curated from: sparknotes.com
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
18 ideas
·5.18K reads
52
2
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
A DEEP DIVE INTO SLEEPING
Sleep is just one of many types of consciousness we experience, and sleep itself comprises several states of consciousness. Even when we’re sleeping, our brains and bodies continue to work.
Sleep is affected by biological rhythms or periodic physiological changes. Biological rhythms are regular, periodic changes in a body’s functioning. There are three types of biological rhythms.
114
763 reads
3 Types Of Biological Rhythms
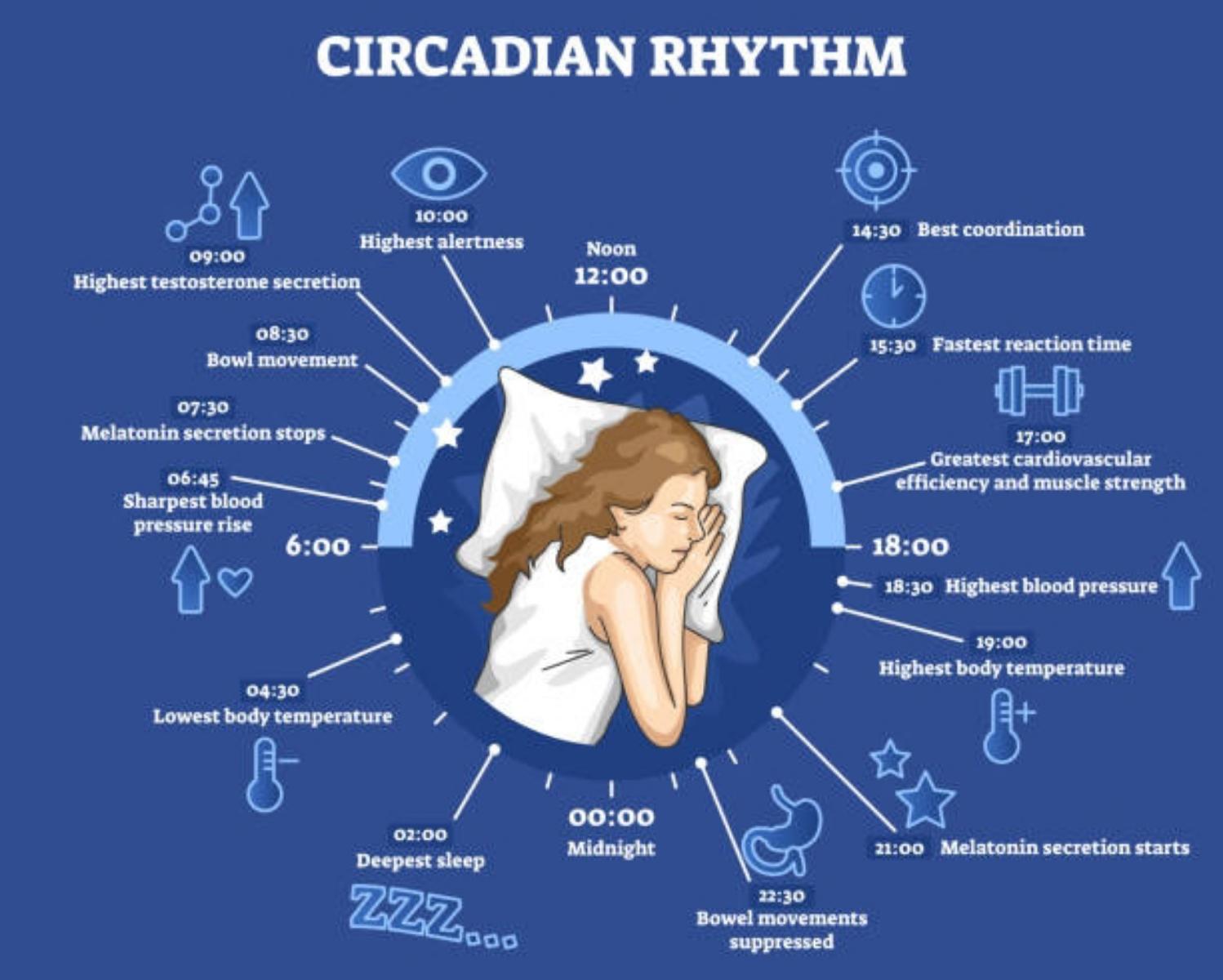
- Circadian Rhythms: biological cycles that occur about every twenty-four hours. Sleep follows a circadian rhythm. Hormone secretion, blood pressure, body temperature, and urine production also have circadian rhythms.
- Infradian Rhythms: biological cycles that take longer than twenty-four hours. For example, women’s menstrual cycles occur about every twenty-eight days.
- Ultradian Rhythms: biological cycles that occur more than once a day. Sleep follows an ultradian rhythm of about ninety minutes as well as a circadian rhythm. Alertness and hormone levels also follow ultradian rhythms.
130
554 reads
Endogenous
Biological rhythms usually synchronize with environmental events such as changes in daylight. However, experiments have shown that many biological rhythms continue to have the same cycle even without cues from the environment. Such biological rhythms are Endogenous, which means that they originate from inside the body rather than depend on outside cues.
114
474 reads
Biological Clocks
Endogenous rhythms exist because the body has biological clocks that keep time. Biological clocks can be adjusted by environmental cues, such as changes in temperature.
In humans, the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) is the main biological clock that regulates circadian rhythms of sleep. The SCN lies in the brain’s hypothalamus. When light stimulates receptors in the retina of the eye, the receptors send signals to the SCN. The SCN then sends signals to the nearby Pineal Gland, which secretes Melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep cycle.
116
323 reads
Jet Lag
Jet lag is the fatigue and disorientation air travelers feel after a long flight. Although traveling itself drains energy, the time change also contributes to fatigue. People experience jet lag when the events in their environment are out of sync with their biological clocks.
EXAMPLE: A traveler leaves NYC at eight in the morning and arrives in London about seven hours later. For her, it’s three in the afternoon, but because of the time change, in London it’s eight in the evening. Her body, thinking it’s mid-afternoon, will be confused by the lack of sunlight, and she’ll experience jet lag.
112
260 reads
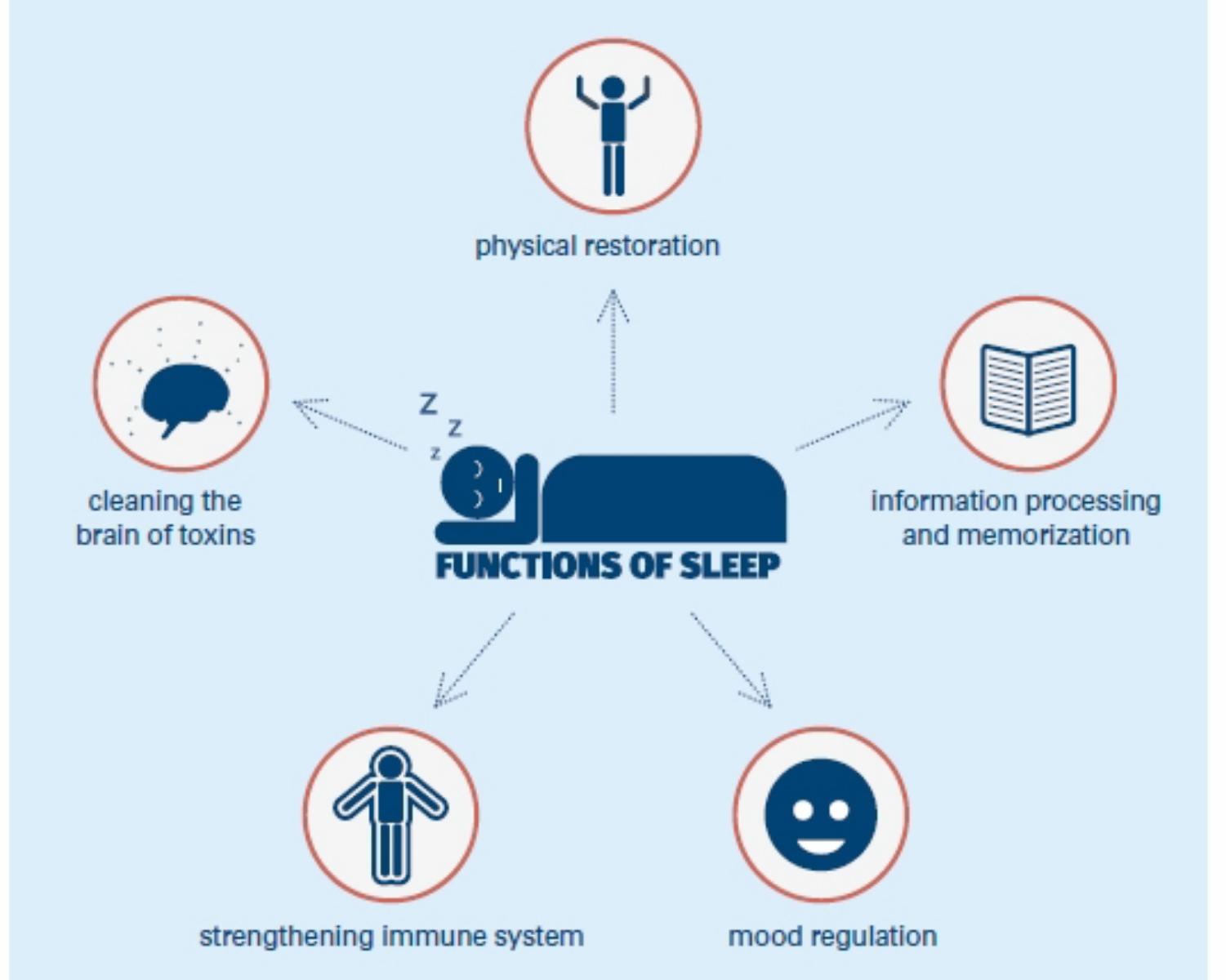
The Function Of Sleep
Although everyone sleeps, no one really knows why people sleep. Researchers have proposed several theories to explain how sleep evolved to be a necessary behavior:
- People conserve energy by sleeping periodically.
- Sleep has a protective function, as it keeps people tucked away at night, safe from predators.
- Sleep restores body tissues that are depleted during daily activities.
115
312 reads
Sleep Research
Sleep research has provided a lot of information about what happens to the brain and body during sleep. Researchers study sleep by monitoring subjects who spend the night in labs, and they use various instruments for different purposes:
- Electroencephalographs(EEGs): record brain waves
- Electromyographs(EMGs): record muscle activity
- Electrooculographs(EOGs): record eye movements
- Electrocardiographs(EKGs): record the activity of the heart
Other instruments monitor breathing, body temperature, and pulse.
114
207 reads
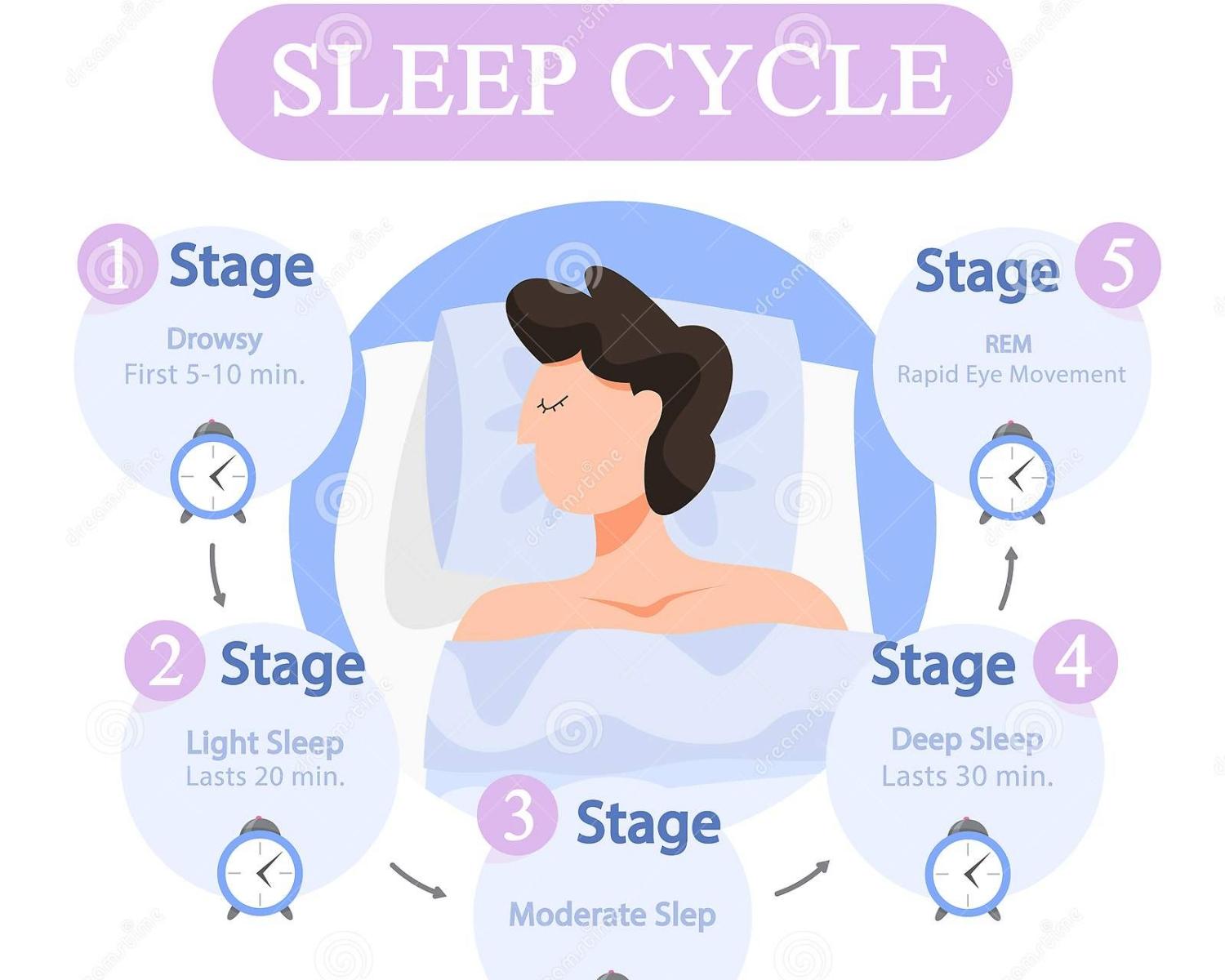
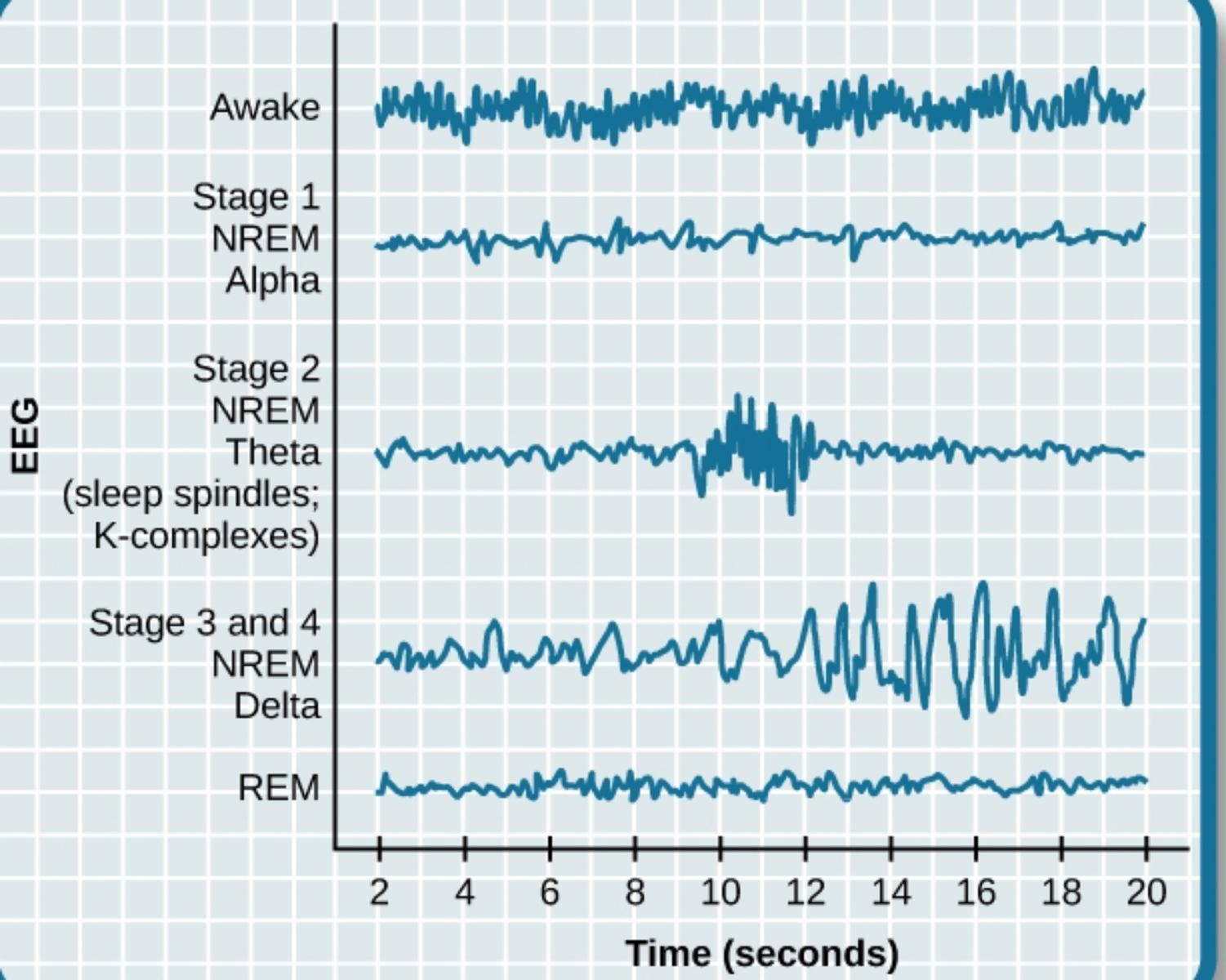
Sleep Stages
During one night’s sleep, people pass through several cycles of sleep, each lasting about ninety to one hundred minutes. There are five distinct stages of sleep in each cycle: 1, 2, 3, 4, and REM.
116
260 reads
Stages 1 To 4
- When people are relaxed and ready to fall asleep, their EEG will show mostly alpha waves. When people fall asleep, they enter into stage 1 sleep, which lasts just a few minutes. In stage 1, the EEG shows mostly theta waves. Heart rate, breathing rate, and body temperature drop, and muscles relax. Fantasies or bizarre images may float around in the mind.
- After a few minutes of stage 1 sleep, people move into stage 2 sleep. Stage 2 lasts about twenty minutes and is characterized by short bursts of brain waves called Sleep Spindles.
116
193 reads
Sleepwalking
Most people in stage 4 sleep are still, quiet, and difficult to rouse. Sleepwalkers, however, sometimes become physically active during stage 4. They may get up and walk around their room or even carry on a conversation, take a bath, cook, or go outside and get in their car. Because they are in a deep sleep, most sleepwalkers remember nothing of their actions when they wake up.
112
210 reads
REM Sleep
- At the end of stage 4, people go back through the stages in reverse, from stage 4 to 3 to 2 to 1. When they reach stage 1, instead of waking up, people go into REM, or rapid eye movement, sleep. A single cycle might look like this: ' 123432REM '
- REM sleep is a stage of deep sleep in which, paradoxically, brain wave activity resembles that of an alert person. REM sleep is also called paradoxical sleep.
114
221 reads
- During REM sleep, pulse rate and breathing become irregular, eyes move rapidly under closed lids, and muscles remain very relaxed. Genital arousal also happens during REM. In women, the clitoris becomes swollen with blood, and vaginal lubrication increases. In men, the penis becomes erect. EEGs show mostly beta waves during REM sleep. Although dreaming happens in other sleep stages as well, dreams are most vivid and frequent during REM sleep.
112
196 reads
- People typically go through about four sleep cycles during one night of sleep. The REM stage of sleep gets longer and longer as the night passes, while stage 3 and 4 sleep gets shorter and shorter. During the night’s first sleep cycle, the REM stage lasts about ten minutes. During the night’s last sleep cycle, people may spend about forty to sixty minutes in REM sleep. Non-REM sleep becomes more shallow as the night goes on, and eventually the sleeper awakens.
113
162 reads
Sleep Deprivation
Different people need different amounts of sleep. Some people can function with fewer than six hours of sleep a night, while others can’t manage without at least nine hours. Research shows that getting insufficient sleep can have negative effects on health, etc.
Experiment subjects who are intentionally deprived of REM sleep tend to enter the REM stage of sleep more and more frequently during the night. After an REM-deprivation experiment has ended, subjects usually experience a REM Rebound effect, spending more time in the REM stage on subsequent nights to make up for lost REM time.
113
206 reads
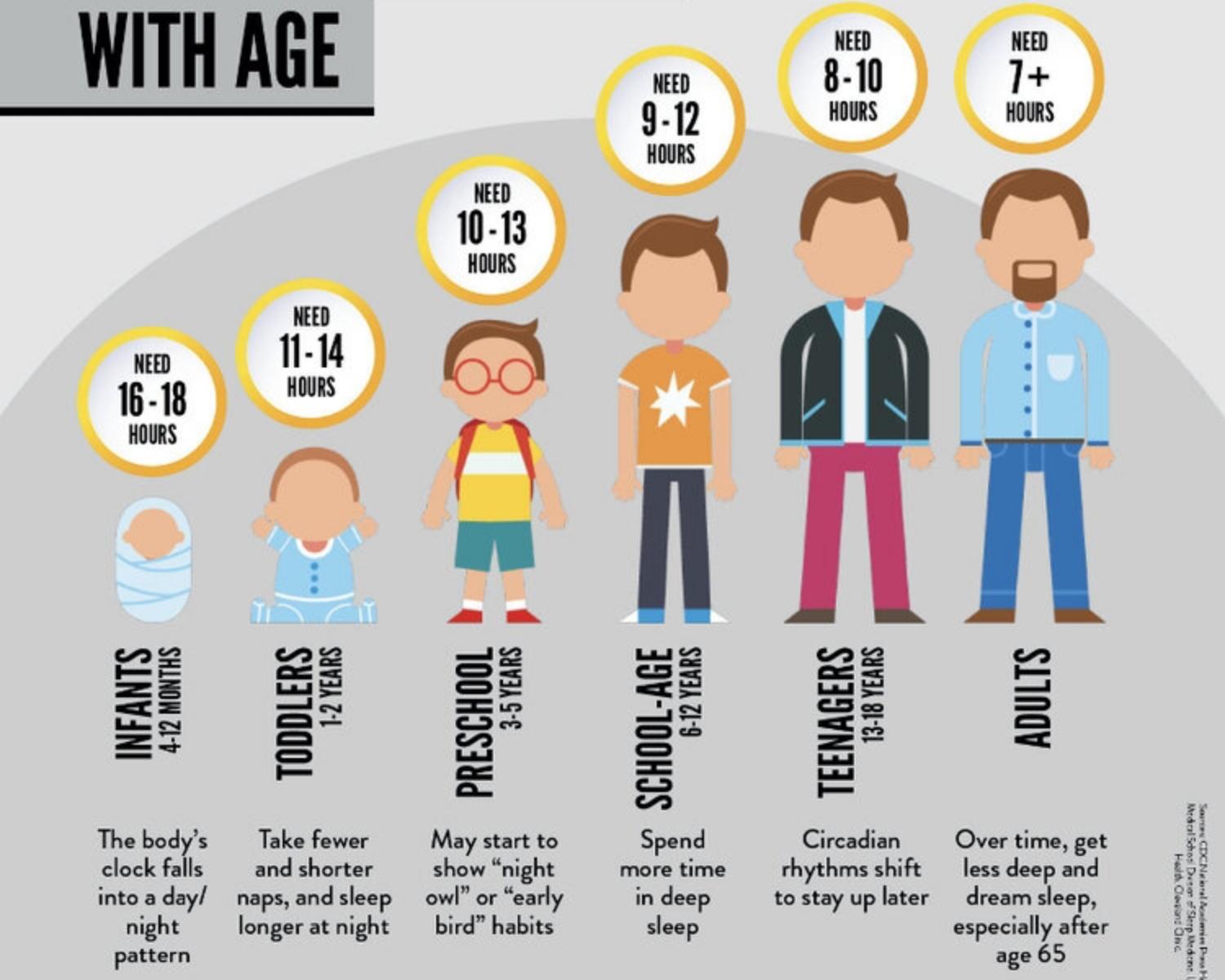
Aging and Sleep
Sleep patterns change as people get older. Newborn babies spend about two-thirds of their time in sleep. As people age, they tend to sleep less. The amount of time spent in REM sleep also changes over time. In very young babies, about half of all sleep is REM sleep. As babies get older, the proportion of REM sleep decreases.
111
207 reads
Sleep Disorders
- Everyone has occasional difficulty sleeping, but some people have Insomnia, a chronic problem with falling or staying asleep. Another kind of sleep disorder is Narcolepsy, which is a tendency to fall asleep periodically during the day. Narcolepsy can be dangerous, as people who experience it may fall asleep while driving or operating machinery.
113
209 reads
- Sleep apnea is another condition that can have negative effects on health and safety. People who have Sleep Apnea stop breathing many times during a night’s sleep, and each time they stop breathing, they wake up briefly and gasp for air. This prevents them from getting enough deep sleep, which leads to irritability and sleepiness during the day. Chronic sleep apnea can also result in high blood pressure.
112
221 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
R . SUGA's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about health with this collection
How to choose the right music for different tasks
The benefits of listening to music while working
How music affects productivity
Related collections
Similar ideas
3 ideas
4 ideas
Synchronizing Your Biological Clock With a Schedule
verywellmind.com
5 ideas
The Science of Deep Sleep - Mindful
mindful.org
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates