Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
What is a thought
The first problem with describing what happens in your body when you are thinking is that not everyone agrees on what constitutes a thought.
For example, this morning while lying in bed you might have had the thought, "I don't want to get up."
Is the thought "I don't want to get out of bed" something that spontaneously appeared in your mind? Or was it triggered by something? Is it just a physical process of your brain or the manifestation of something deeper like a soul, spirit, or other entity?
65
685 reads
Anatomy of a thought
Scientist would argue first that the thought you had was not spontaneous and random. instead, your thought was likely a reaction to something around you.
In this case, it might have been an alarm clock, checking your phone to see what time it is, or hearing something like the garbage truck go by that reminds you of time passing. In other cases, thoughts might be triggered by memories.
now, once you have that thought, what happens?
63
419 reads
Some neuroscience terms defined
The brain operates in a complex way with many parts intersecting and interacting with each other simultaneously. So, when you have that thought in the morning, it's likely that all these different component of your brain (prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, neurons, neurotransmitters, etc.) are all involved at the same time.
- Action potential: sudden burst of voltage caused by chemical changes ( how neurons signal one another)
- Neuron: a nerve cell through which signals are sent
- Neurotransmitter: Chemical messengers released by neurons that help them communicate with other cells (e.g., dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine)
- Prefrontal cortex: Part of the brain involved in planning, personality, decision making, and social behavior.
- Hippocampus: part of the brain crucial in variety of memory functions
- Synapse: A structure that allows a neuron (nerve cell) to pass a chemical or electrical signal to a target cell.
88
187 reads
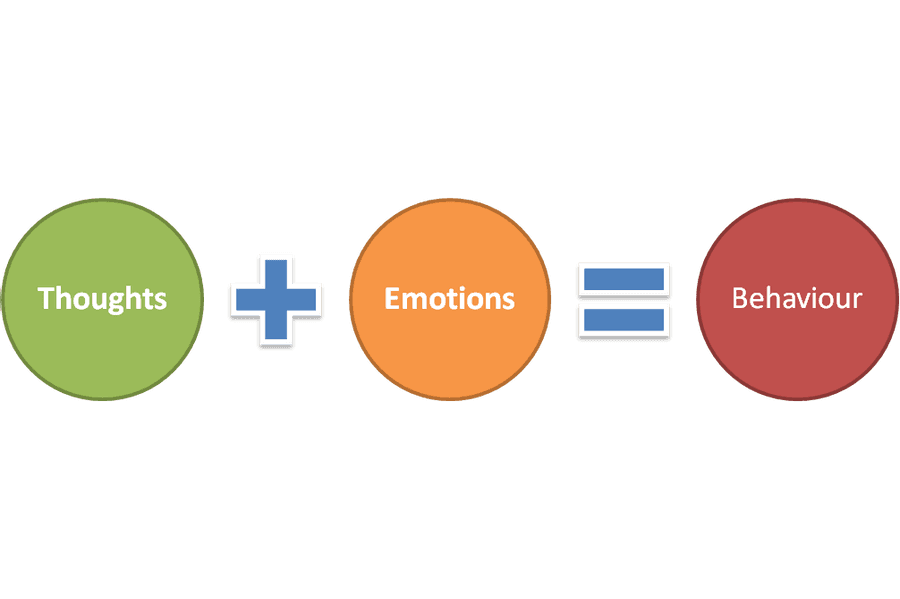
Thoughts and emotions
we know that your thoughts can influence the neurotransmitters in your brain.
So, if you throw the covers over your head, and that triggers other thoughts such as "I'm tired," "I can't get up," or "Life is hard," complex interactions in your brain may send signals to other parts of your body.
if you reverse that and think something elke, then the signals will be different.
Your brain is constantly receiving signals, whether from the outside environment in terms of perceptions or memories from your past. It then activates different patterns through waves in the brain through billions of synapses. In this way, your thoughts grow more complex as they interact with other content produced by your brain functions.
76
219 reads
Regulating your thoughts
Whenever you have thought, there is a corresponding chemical reaction in your mind and body as a result.
this is important to realize because it means that what you think can affect how you feel.
If you accept the scientific view that your thoughts are physical parts of your brain and that changing your thoughts can have an effect on your body, then you've just developed a powerful weapon.
Of course, your thoughts don't arise out of a vacuum. For example, you are reading this article and gaining new ideas from it that you can potentially put to use in changing your thoughts.
- You're starting to think a different way.
- You've started to feed your brain different information.
- You've surrounded yourself with information that programs your brain to start thinking the way that you want it to.
What this means is that if you want to start changing your thoughts, you need to be aware of the triggers of your thoughts and also the patterns of thoughts that you have in response to those triggers.
74
137 reads
How to change your thought and change your body
Get very clear about the triggers of your thoughts and you will have the power to change your emotions and you health.
example: you've got a mental association between the alarm clock and the thought "i don't want to get out of bed"
you've worn a mental groove in your brain, so to speak, that instantly connects that trigger with that thought. so if you want to change that reaction, you either need to change the trigger of break the association with that thought.
Stuck in a traffic jam and feeling irritated and frustrated? The thought, "I can't stand traffic" will send signals from your brain to your body to speed up your breathing and tense your muscles. Whereas the thought, "I can't control this, might as well relax," will send the signal to your body to calm down.
73
216 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
I'm passionate about helping people live their best lives. I'm a lifestyle coach & burnout coach.
Rogier. H's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about productivity with this collection
How to choose the right music for different tasks
The benefits of listening to music while working
How music affects productivity
Related collections
Similar ideas
15 ideas
11 Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Your Body
healthline.com
4 ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates