Develop a "Probabilistic" Approach to Managing Uncertainty
Curated from: hbr.org
Ideas, facts & insights covering these topics:
4 ideas
·2.25K reads
5
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
Data and how it frames your thinking
What’s more important than how much data you have is how it frames the way you think.
Some leader when they're under pressure to appear decisive, approach complex situations with simple rules or analogies, selectively using data to justify poor judgment calls.
155
757 reads
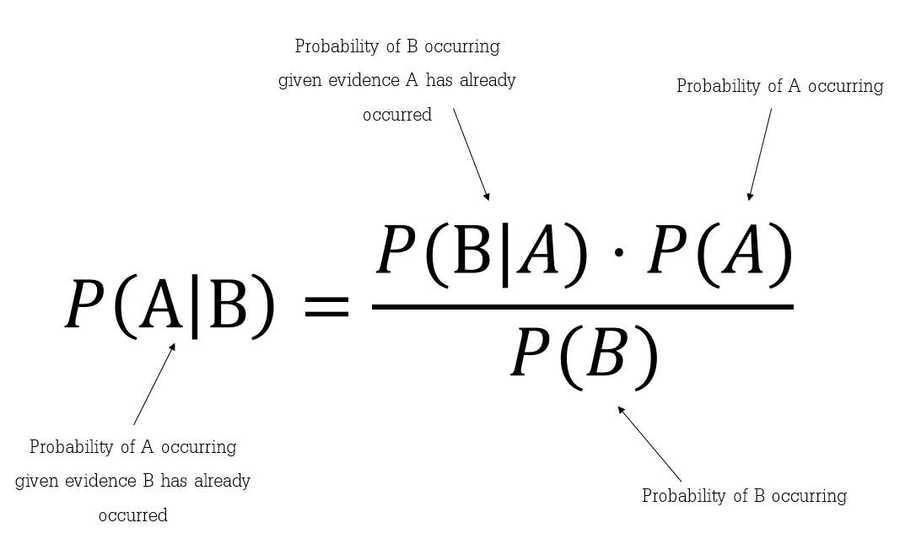
Thomas Bayes'd thought experiment
He wondered how he could predict the probability of a future event if he only knew how many times it had occurred, or not, in the past. Bayes figured out that even when it comes to uncertain outcomes, we can update our knowledge by incorporating new, relevant information as it becomes available.
His theorem describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event.
175
588 reads
Importance of using probabilistic thinking
Data can be imperfect, incomplete, or uncertain. Most of the time, there is more than one explanation for why things happened the way they did; by examining those alternative explanations using probability, you can gain a better understanding of causality and what is really going on.
157
443 reads
The human mind is naturally deterministic
So thinking probabilistically takes some getting used to. We generally believe that something is true or false.
Our instinct for determinism may well have been an evolutionary innovation. To survive, we had to make snap judgments about the world and our response to it. However, the deterministic approach won’t help us make good decisions in complex, unpredictable environments.
153
467 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Brian 's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about problemsolving with this collection
Strategies for promoting inclusivity
How to address unconscious bias
How to create a diverse and inclusive workplace
Related collections
Similar ideas
5 ideas
4 ideas
3 ideas
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates