The Hedonic Treadmill: Why People Are Never Truly Happy And How You Can Change That
Curated from: medium.com
2
Explore the World's Best Ideas
Join today and uncover 100+ curated journeys from 50+ topics. Unlock access to our mobile app with extensive features.
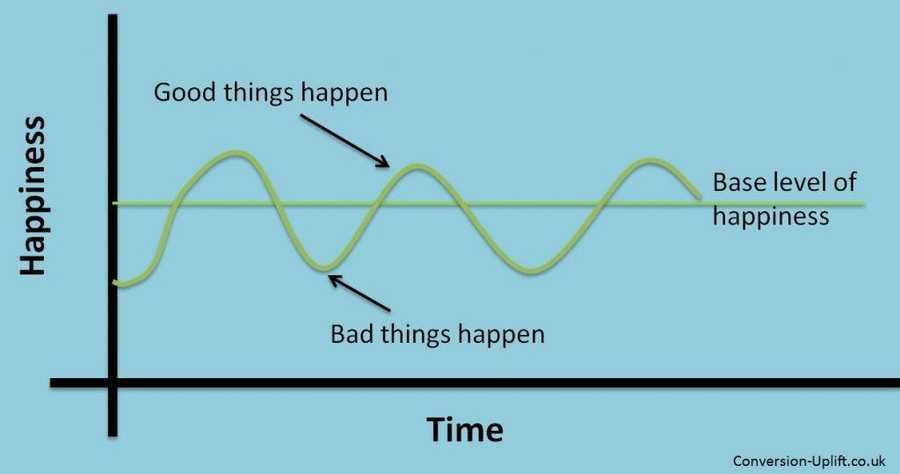
The hedonic treadmill
The hedonic treadmill is the tendency to quickly return to a relatively stable level of happiness after a major positive or negative event or life change.
You want something because you think it’ll make you happy. But when you get what you want, the new thing will only make you happy for a short while before you revert to your earlier, less happy state.
188
298 reads
Recognize the signs
Almost everyone experiences the hedonic treadmill. It's a trap and makes you think that a salary raise, a new car, or a new house or career will give you lasting happiness. Those events may make us happy, but only for a short time.
If we can learn to recognize the signs and build better habits, we can be happy and content for longer.
144
204 reads
Healthy habits
Instead of waiting for major life changes, invest in healthy habits that can guarantee satisfaction in life.
Choose activities like writing, playing music, creating art, or practicing a sport that allows you to savor the moment fully. Other people enjoy endeavors like volunteering and charity work.
171
337 reads
Happiness is a state of mind
Happiness is not out there for us to find; it's within us. It's in what we do, how we act, how we think.
We have the potential to be happy when we choose to focus on what matters.
177
240 reads
IDEAS CURATED BY
Claudia Stark's ideas are part of this journey:
Learn more about personaldevelopment with this collection
How to focus on the present moment
How to improve relationships through mindful communication
How to reduce stress and anxiety through mindfulness
Related collections
Similar ideas
5 ideas
8 ideas
How to Stop Sabotaging Yourself
greatergood.berkeley.edu
5 ideas
The Psychology Of Hedonic Adaptation
betterhelp.com
Read & Learn
20x Faster
without
deepstash
with
deepstash
with
deepstash
Personalized microlearning
—
100+ Learning Journeys
—
Access to 200,000+ ideas
—
Access to the mobile app
—
Unlimited idea saving
—
—
Unlimited history
—
—
Unlimited listening to ideas
—
—
Downloading & offline access
—
—
Supercharge your mind with one idea per day
Enter your email and spend 1 minute every day to learn something new.
I agree to receive email updates